Between 2021 and 2023, 80% of enterprises in the EU experienced that their global value chains were affected by at least 1 constraint or underwent reorganisation. These results come from the first global value chains survey carried out under the European business statistics regulation, building on earlier voluntary surveys conducted in previous years.
This information comes from the Statistics Explained article on international sourcing, business functions and global value chains.
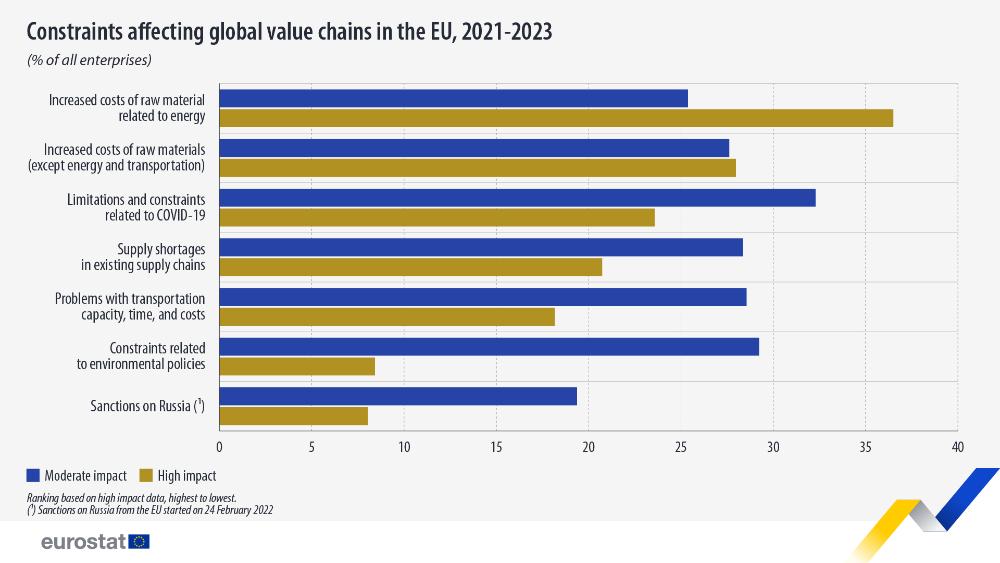
The most frequently reported issues included increased energy-related input costs (62%), limitations related to COVID-19, and rising costs for non-energy raw materials and goods (each 56%).
Policy-related factors also affected enterprises’ global value chains. Around 27% of enterprises reported that EU sanctions on Russia had a moderate or high impact on their global value chains, while 38% reported that constraints related to environmental policies had a moderate or high impact. These constraints refer to challenges arising from complying with national or EU environmental policy requirements, which in turn affect enterprises’ global value chains.
Source dataset: Eurostat (gvc_effgvc)
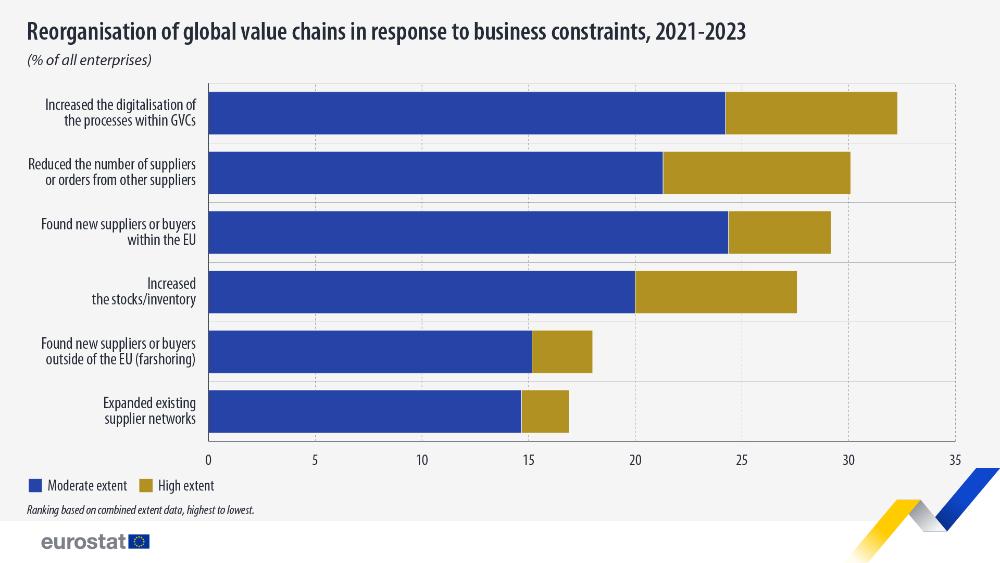
In response to these constraints, many enterprises implemented strategies to reorganise their global value chains. The most frequently reported measures were increased digitalisation of processes within global value chain (32%), prioritising the most reliable suppliers (30%) and finding new suppliers or buyers within the EU (29%). Another common enterprise strategy was expanding existing supplier networks (17%).
Source dataset: Eurostat (gvc_effgvc)