Demographics of the patients
We reviewed the medical records of 34 ROP eyes (34 patients) treated with laser PC, 5 spontaneously regressed ROP eyes (5 patients), and 15 age-matched full-term controls (15 control eyes; Table 1). No significant differences were observed between the groups in terms of age or sex. The mean BCVA in the PC-treated, regressed ROP, and control groups was 0.07 ± 0.16 logMAR units, 0 ± 0.12 logMAR, and − 0.08 ± 0.04 logMAR units. The mean spherical equivalent in the PC-treated, regressed ROP, and control groups was − 1.2 ± 3.0 D, −0.25 ± 0.98 D, and − 0.7 ± 4.3 D. The mean axial length in the PC-treated, regressed ROP, and control groups was 22.8 ± 2.0 mm, 22.4 ± 0.2 mm, and 22.8 ± 0.2 mm, respectively. No significant differences were found in the spherical equivalent and axial length.
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of the patients and control.SSOCT and widefield OCTA parameters
The mean foveal thickness in the PC-treated, regressed ROP, and control groups was 242.2 ± 38.6 μm, 207.8 ± 34.5 μm and 203.2 ± 22.6 μm, respectively (Table 2). The mean foveal thickness in the PC-treated patients was significantly thicker compared to that in the control children. The FAZ in the PC-treated, regressed ROP and control groups was 0.16 ± 0.06 mm2, 0.19 ± 0.11 mm2, and 0.39 ± 0.14 mm2, respectively. The FAZ in the PC-treated patients was significantly smaller compared to that in the control children (Table 2). SSOCT images indicated that 7 of 34 eyes in the treated ROP group had a dome-shaped macula, while 16 had an elongated barrel shape. The OSI was significantly lower in the PC-treated patients than in the control children (Table 2). A smaller OSI shows a more dome-shaped macula in PC-treated ROP eyes.
We analyzed the relationship between the FAZ, OSI, and OCT parameters. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) adjusted for gestational age and birth weight revealed that the FAZ in the PC-treated group was smaller than that in the control group (Table 3). In the Pearson analysis, the FAZ correlated with gestational age and foveal thickness (Table 4). In the Pearson analysis, the better visual acuity was correlated with later gestational age, larger birth weight and larger FAZ (Table 5). In the multiple regression analysis, the smaller OSI was related to the smaller gestational age (Table 6).
Table 3 Effect of laser treatment on the retinal structure.Table 4 Pearson correlation of patients and controls.Table 5 Pearson correlation of patients and controls.Table 6 Multiple linear regression analysis between OSI and independent variables.Representative ROP patient
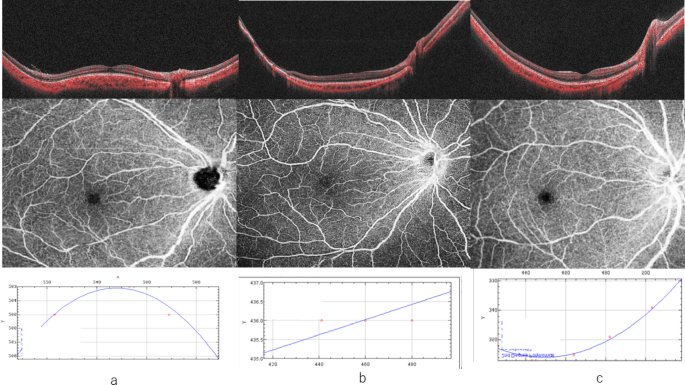
Case 1: Dome-shaped macula (Fig. 1A).
Upper image: SSOCT image. Middle image: OCT-A image. Lower image: The ocular shape index was defined as the coefficient of determination of the quadratic curve equation. (a) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the treated dome-shaped macular retinopathy of prematurity (ROP). Case 1 was a 9-year-old girl born at 24 weeks of gestation (weighing 784 g). FAZ was 0.20 mm2. The ocular shape showed a dome-shaped macula, with an OSI of −2.0 × 10−4. (b) OCT image of a representative eye of a treated elongated barrel-shaped ROP. Case 2 was a 9-year-old boy born at 26 weeks of gestation (weighing 900 g). FAZ was 0.11 mm2. The ocular shape showed an elongated barrel-shaped macula, with an OSI of −6.8 × 10−5. (c) OCT image of the control eye. Case 3 was an 8-year-old girl. FAZ was 0.67 mm2. The OSI was 3.6 × 10−4.
Case 1 was a 9-year-old girl whose gestational age was 24 weeks (weighing 784 g). She had Zone II Stage III ROP without plus disease; she had no additional complications, such as severe retinal vascular dilation or tortuosity. PC therapy was performed to treat the ROP. Her BCVA was 0 logMAR in both eyes. Her axial length was 23.39 mm, SE was − 6 D, and FAZ was 0.20 mm2. In terms of ocular shape, she had a dome-shaped macula with an OSI of −2.0 × 10−4.
Case 2: Barrel shaped elongated macula(Fig. 1B).
Case 2 was 9-year-old boy whose gestational age was 26 weeks (weighing 900 g). He had Zone II Stage III ROP without plus disease. PC therapy was performed to treat the ROP. His BCVA was 0 logMAR in both eyes. His axial length was 24.06 mm, SE was − 5.25 D, and FAZ was 0.11 mm2. In terms of ocular shape, he had an elongated barrel-shaped macula with an OSI of −6.8 × 10−5.
Case 3: Control eye (Fig. 1C).
Case 3 was an 8-year-old girl. Her BCVA was 0 logMAR in both eyes. Her axial length was 22.70 mm, SE was − 5 D, and FAZ was 0.67 mm2. Her OSI was 3.6 × 10−4.