Quantum computing concept
getty
In today’s world, quantum technology is no longer a far-off concept that is just a theoretical physics concept. In the not-too-distant future, it is becoming a disruptive force that has the capacity to rethink computers, cybersecurity, and data analytics as conventionally understood. Quantum innovation will stimulate revolution across sectors, from healthcare and finance to logistics and national security. It will bring new capabilities while posing hazards that have never been seen before.
Leaders in both the public and business sectors need to start preparing for this technological inflection point as quantum technologies go from being prototypes in the laboratory to being used in the real world. Those that act early will not only be able to neutralize newly emerging dangers, but they will also be able to exploit first-mover advantages in an environment that is quickly shifting.
The Quantum Leap: Altering the Way We Think About Computing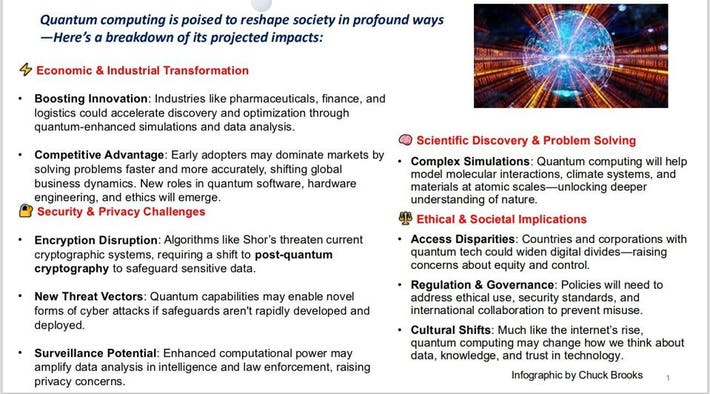
Infographic by Chuck Brooks
Chuck Brooks
Computing in the quantum realm functions in a fundamentally different manner than traditional computing has. Quantum computers make use of qubits, which are able to exist in several states simultaneously owing to superposition and entanglement. Traditional machines process data using binary bits, which are represented by the numbers 0 and 1. Quantum systems are able to do complicated calculations at rates that may take classical systems years to match.
Many high-priority fields, including the following will be influenced by quantum capabilities: fusion with machine learning and artificial intelligence, information security, biotech and genomics, drug discovery, materials science, real-time analytics, energy modeling, modeling of financial transactions and optimization of portfolios, logistics, space systems, and the evolving Metaverse and immersive tech.
The importance of this surge in computing capacity is especially noteworthy for industries that are reliant on high-throughput data processing and real-time analytics. Physicists refer to this period of time as the Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) era. However, we are still working in the preliminary phases. Quantum machines of today are prone to errors, have a restricted size range, and are sensitive to perturbations in their surrounding environment.
Please also see: Quantum Computing Has Arrived; We Need To Prepare For Its Impact

Quantum Technology Background
getty
Expansion of Threat Surface: The Peril of Q-Day
But there is significant risk to information security and privacy from quantum computing. It poses a significant risk to both private businesses and public institutions. The coming cybersecurity event known as “Q-Day” is one of the most pressing concerns associated with quantum computing. This event is the hypothetical time when quantum computers become strong enough to defeat commonly used public-key encryption schemes such as RSA, ECC, and Diffie-Hellman.
Data that has long-term value is currently in danger, despite the fact that Q-Day may be several years away. This is because attackers may capture encrypted data now and decode it in the future when quantum systems develop. This threat is sometimes referred to as “store now, decrypt later.”
Progress Being Made
The pace of quantum progress is quickening; key players keep an eye on the target. As the number of businesses that are attempting to push the limits of what is feasible with quantum computing continues to rise. Different approaches are being taken by each of them with regard to the hardware architecture, software integration, and commercial readiness:
In 2019, Google made a well-known demonstration of quantum supremacy, and the company is still working toward the development of error-corrected qubit systems at scale.
The IBM Quantum Network is being used to commercialize quantum hardware, and the company has released roadmaps that lead to the creation of more than one thousand qubit computers.
Azure Quantum is a platform developed by Microsoft that combines quantum cloud services and investigates topological qubits.
The company Quantum Computing Inc. (QCI) is a pioneer in the development of photonic quantum systems that are user-friendly and ready to deploy.
IonQ, Rigetti, D-Wave, and Quantinuum, which is a spinoff of Honeywell, are at the forefront of innovation in the areas of trapped ion, superconducting, and annealing techniques.
Through their collaborative efforts, these businesses are establishing a competitive innovation ecosystem that is reducing the gap between theoretical promise and practical application in the current world. Quantum technologies are seeing a dramatic increase in both investment and patent activity, which is an indication that commercialization may come sooner than many people anticipate.
Please also see: The Growing Impact Of AI And Quantum On Cybersecurity

Encryption your data. Binary code and digital Lock. Hacker attack and data breach. Big data with encrypted computer code. Safe your data. Cyber internet security and privacy concept. Database storage 3d illustration
getty
Post-Quantum Readiness is the Strategic Need that Must be Met
Getting ready for a world dominated by quantum computing requires more than just keeping up with the latest technological news. Investing consciously, coordinating policies, and developing a business strategy are all necessary components.
1. Implement Post-Quantum Cryptography, also known as PQC:
Organizations need to initiate the transition toward algorithms that are resistant to quantum computing. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has already chosen many finalists for its process of professional quality control (PQC) standardization, and it is anticipated that implementation timetables will be completed by the year 2030. The early implementation of this technology will be necessary in order to limit exposure, particularly in industries that manage sensitive or long-lived data.
2. Utilize Quantum to Strengthen, Rather Than Simply Disrupt:
Quantum computing presents issues for cybersecurity, but it also has the potential to improve resilience. It is possible to establish secure communication networks using quantum key distribution (QKD) and quantum sensing, which may also significantly increase detection capabilities for a wide range of issues, including structural faults and cyber abnormalities.
3. Encourage Employee Development and Collaboration Between the Public and Private Sectors: A multidisciplinary workforce that includes professionals from physics, engineering, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and software is required for quantum advancement. The development of talent pipelines requires collaboration between academic institutions and the executives of corporations. In order to speed up the innovation process, governments are required to not only support national projects but also act as early adopters.
A Defining Moment for Digital Transformation
Future of Quantum
The Economist
In the next five years, the transition from potential to impact will be crucial. When we look to the future, we may anticipate that quantum computing will merge with artificial intelligence, cloud infrastructure, 5G, and edge computing, which will dramatically transform the way that we model the world and make choices. Through the process of convergence, it is possible that computer power will reach quadrillions of operations per second in the near future.
Additionally, due to the fact that quantum technology may be used for both empowering and destructive purposes, it is imperative that it be treated with ethical forethought and coordinated control.
Quantum technology represents one of the most consequential advances of the 21st century. Business leaders, policymakers, and technologists must act now to shape its trajectory—preparing for both its opportunities and its risks. By investing in quantum readiness today, organizations can build a resilient, competitive edge for tomorrow.