Report Overview
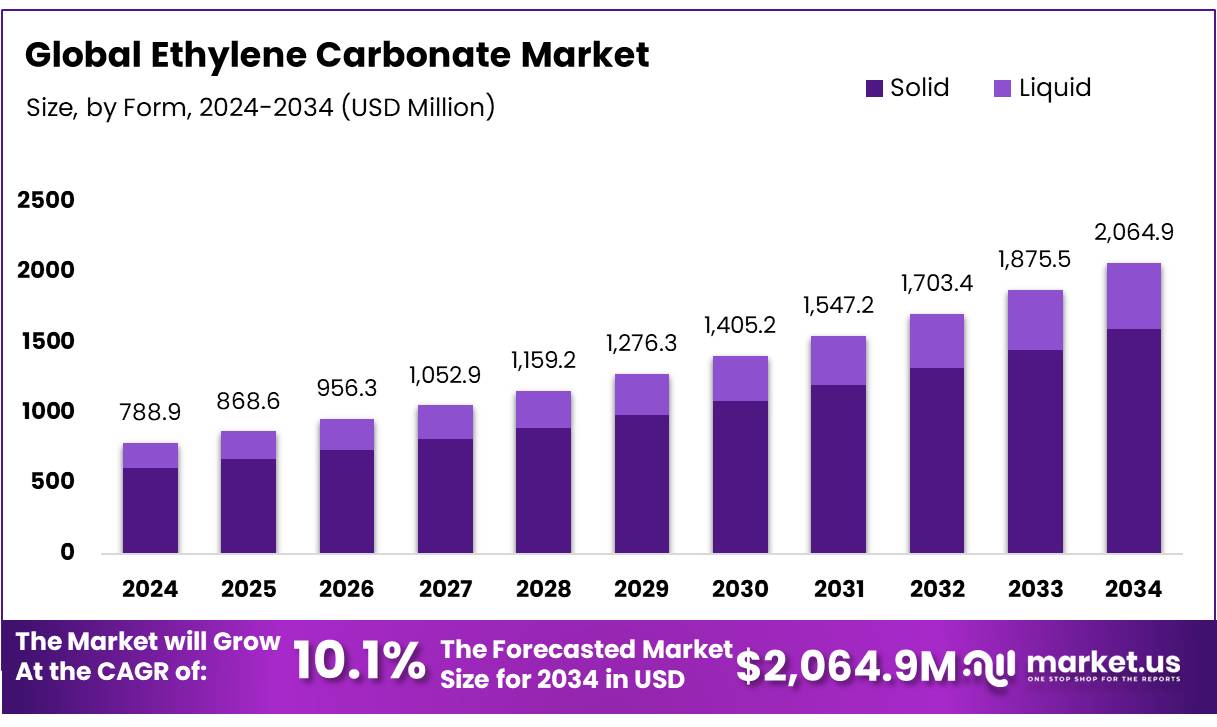
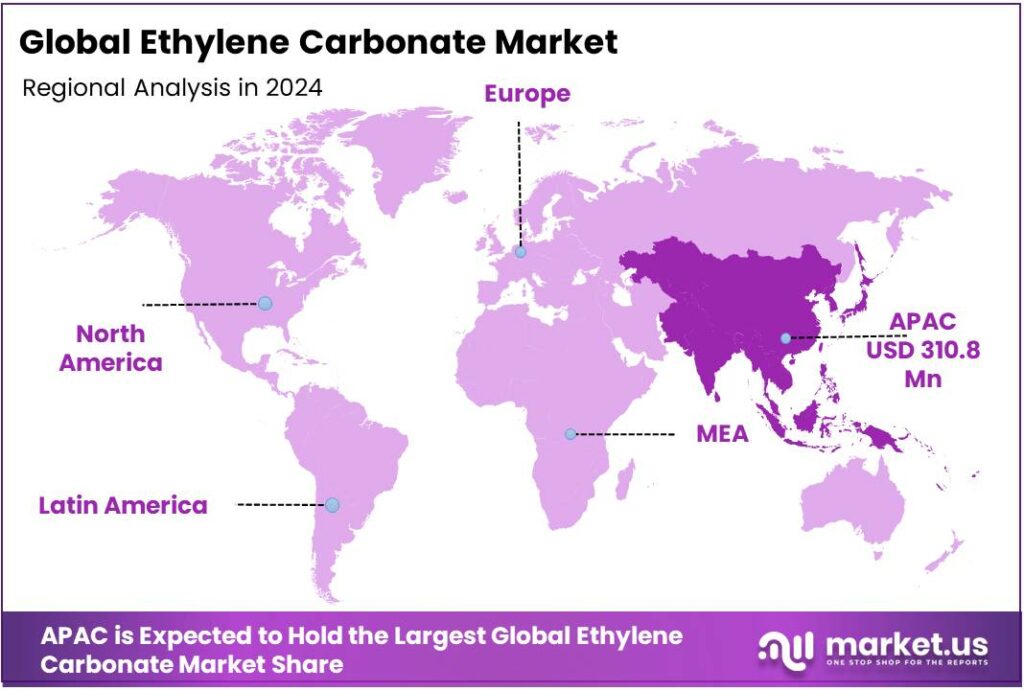
The Global Ethylene Carbonate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2064.9 Million by 2034, from USD 788.9 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Asia Pacific held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.4% share, holding USD 310.8 Million in revenue.
Ethylene carbonate (EC) is a high-boiling, polar, cyclic carbonate widely used as a lithium-ion battery (LiB) electrolyte solvent/additive, as well as a reactive intermediate for lubricants, plasticizers, and specialty polymers. Industrially, EC is typically produced by cyclo-addition of ethylene oxide with CO₂ (1:1 stoichiometry), a route documented in process studies that integrate EC within carbon-to-chemicals schemes (Ethylene Oxide + CO₂ → Ethylene Carbonate). This direct reaction underpins EC’s relevance to carbon-utilization pathways and downstream carbonate chemistries.
Demand for EC closely tracks lithium-ion battery scale-up. Globally, electric-car sales exceeded 17 million units in 2024, lifting EVs to >20% share of all cars sold—an unmistakable pull signal for electrolyte solvents. Parallel to sales, battery manufacturing surged: in 2023 alone, the world added 780 GWh of cell manufacturing capacity, bringing installed capacity to 2.5 TWh. These system-level indicators translate into robust upstream requirements for carbonate solvents and lithium salts where EC is foundational for forming stable SEI layers on graphite.
Grid-scale storage is a second growth engine for EC through lithium-ion BESS. The IEA reports total installed grid-scale battery capacity near 28 GW at end-2022, and deployments accelerated: 42 GW of battery storage were added to global power systems in 2023 (a 130% jump versus 2022), with calls to expand storage to ~1,500 GW by 2030 to meet clean-energy goals. In the United States, the EIA records 10.4 GW of new utility-scale battery capacity added in 2024, taking cumulative capacity beyond 26 GW—evidence that multi-hour BESS is becoming mainstream on the grid. These numbers underscore a durable, multi-segment pull on electrolyte value chains where EC is a standard co-solvent.
Policy moves are reinforcing this build-out. In the United States, the Department of Energy announced ~$3 billion to support battery manufacturing and recycling projects; within that portfolio, Dow was slated to receive ~$100 million to produce battery-grade carbonate solvents used in LiB electrolytes—explicit recognition of EC-family solvents as strategic inputs. DOE also issued a notice of intent for up to $725 million to strengthen domestic processing of critical materials and battery components—funding lines that typically encompass electrolyte supply chains and precursors.
In Europe, the EU Battery Regulation (Reg. 2023/1542) entered into force on 18 February 2024, introducing lifecycle, due-diligence, and performance requirements that are cascading into electrolyte quality, traceability, and recycling targets—factors that favor compliant EC producers.
Key Takeaways
Ethylene Carbonate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2064.9 Million by 2034, from USD 788.9 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.1%.
Solid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 77.3% share in the ethylene carbonate market.
Lithium Battery Electrolyte held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 36.7% share.
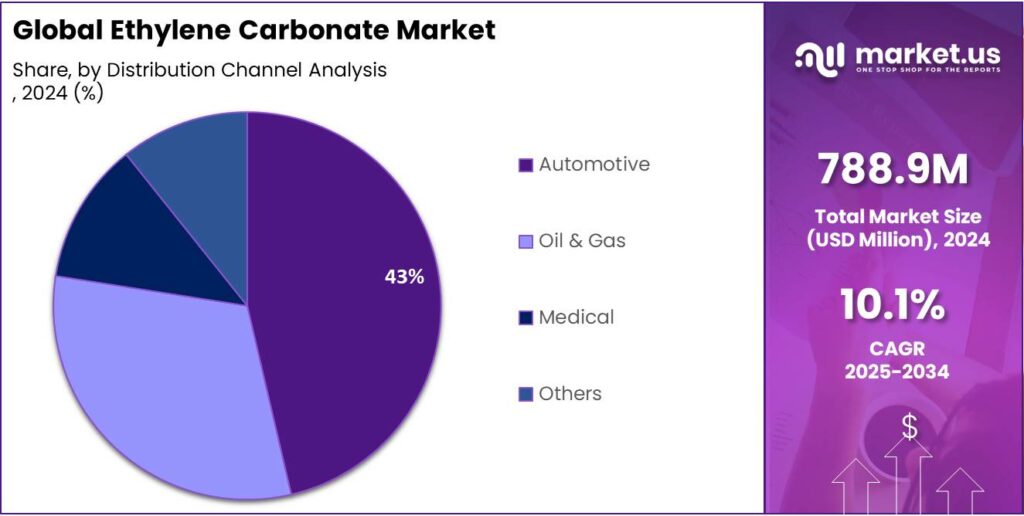
Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.2% share in the ethylene carbonate market.
Asia Pacific region dominated the global ethylene carbonate market, capturing a significant 39.4% share, equating to approximately USD 310.8 million.
By Type Analysis
Solid Form dominates with 77.3% share in 2024
In 2024, Solid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 77.3% share in the ethylene carbonate market by form. This strong preference for the solid form can be attributed to its ease of handling, storage stability, and wide applicability across key industrial sectors, particularly in lithium-ion battery electrolytes and plasticizer formulations. The solid form ensures consistent quality and reduced risk of contamination compared to its liquid counterpart, making it the preferred choice for large-scale manufacturing and industrial processes.
In 2025, the solid segment continued to maintain its stronghold, driven by ongoing demand from electric vehicle battery production and high-performance chemical applications. The segment’s resilience is supported by its adaptability to various production and transport conditions, ensuring reliable supply chains and operational efficiency across multiple industries. As industries increasingly focus on safety, stability, and cost-effective solutions, the solid form of ethylene carbonate is expected to sustain its dominant market position in the near term.
By Nature Analysis
Lithium Battery Electrolyte leads with 36.7% share in 2024
In 2024, Lithium Battery Electrolyte held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 36.7% share in the ethylene carbonate market by application. This prominence is driven by the growing demand for high-performance lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. Ethylene carbonate plays a crucial role in enhancing the electrolyte’s conductivity and stability, ensuring longer battery life and efficient energy storage.
By 2025, the application continued to expand as global adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy storage solutions increased, further solidifying its position in the market. The segment benefits from ongoing technological improvements in battery design and safety, as well as the increasing shift towards sustainable and low-emission transportation, making lithium battery electrolyte the most significant application for ethylene carbonate in industrial use.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Automotive leads with 43.2% share in 2024
In 2024, Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.2% share in the ethylene carbonate market by end use. This strong presence is largely driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, where ethylene carbonate is a key component in lithium-ion battery electrolytes that power these vehicles. The automotive sector’s focus on energy efficiency, longer battery life, and reduced emissions has significantly boosted demand for high-quality ethylene carbonate.
By 2025, this trend continued as global automotive manufacturers expanded their electric vehicle production, further reinforcing the material’s importance in the sector. The segment benefits from ongoing advancements in battery technologies and government initiatives promoting sustainable transportation, ensuring that the automotive end use remains the largest consumer of ethylene carbonate in industrial applications.
Key Market Segments
By Form
By Application
Lithium Battery Electrolyte
Lubricants
Surface Coatings
Plasticizers
Others
By End Use
Automotive
Oil & Gas
Medical
Others
Emerging Trends
Battery-enabled cold chains and circular battery rules
Food-system decarbonization pressures add momentum. FAO estimates agrifood systems emitted 16.2 Gt CO₂e in 2022 (just under a third of global emissions by many accounting frames), keeping retailers, processors, and 3PLs under scrutiny to lower energy use and waste. Battery-ready designs—solar on the roof, storage in the plant, efficient chillers on the floor—are becoming the reference build in new warehouses and retrofits. Each incremental battery pack adds electrolyte demand, sustaining EC’s role in graphite SEI formation and blend stability.
Upstream energy and mobility data reinforce the trend. The International Energy Agency notes electric-car sales exceeded 17 million in 2024, reaching >20% of all new cars—momentum that spills into commercial fleets and refrigerated delivery vehicles, where battery packs power both traction and cooling. On the grid side, the U.S. Energy Information Administration records 10.4 GW of utility-scale battery additions in 2024, taking cumulative capacity past 26 GW; more storage on the system improves reliability for cold warehouses and processing plants, supporting battery-backed designs at sites that handle temperature-sensitive inventory. Both vectors sustain electrolyte demand where EC is standard in many formulations.
Policy is aligning with this build-out and shaping solvent choices through circularity. The European Union’s new battery framework—Regulation (EU) 2023/1542—is in force and sets staged requirements across the battery life cycle. Critically, new rules for calculating and verifying recycling-efficiency and material-recovery rates apply from 24 July 2025, raising traceability expectations on electrolyte constituents alongside metals. This puts a premium on compliant, well-documented solvent supply and on producers that can support end-of-life recovery. For EC suppliers, meeting documentation, purity, and stewardship criteria becomes a route to preferred-vendor status in projects financed under green public-procurement and donor programs geared to food resilience.
Drivers
Battery growth to electrify cold chains and logistics
Ethylene carbonate demand is rising because lithium-ion batteries are scaling across electric vehicles and stationary storage that keep food cold and moving efficiently. The International Energy Agency reports electric-car sales exceeded 17 million in 2024, lifting EVs to over 20% of global car sales—an unmistakable pull for electrolyte solvents where ethylene carbonate is a core co-solvent.
In the United States, utility-scale battery storage also surged, with 10.4 GW added in 2024, taking cumulative capacity past 26 GW—evidence that multi-hour systems are moving from pilot to grid asset. These trends matter to food systems. The UN Food and Agriculture Organization highlights that 526 million tons—about 12% of global food production—are lost due to inadequate refrigeration, underscoring the need for reliable, distributed cold chains powered by storage and electrified transport.
As retailers, processors, and 3PLs expand cold warehouses, reefer fleets, and last-mile delivery, batteries are being embedded from forklifts to yard tractors to delivery vans, all relying on carbonate-based electrolytes. The FAO knowledge base estimates the food cold chain accounts for ~4% of global greenhouse-gas emissions, including emissions from lost food due to insufficient cooling—so electrification with storage is both an efficiency and decarbonization lever.
Food security and energy security are converging around storage. FAO and UNEP quantify the refrigeration gap; grid and mobility data from the IEA and EIA quantify how quickly batteries are filling it. Each grid-connected warehouse, battery-backed micro-cold-chain site, and electrified delivery route adds to electrolyte demand where ethylene carbonate remains a standard choice. With EVs already >20% of global car sales in 2024 and U.S. grid batteries >26 GW by 2024, policy-backed scale-up across regions is set to keep ethylene carbonate on a firm growth path aligned to resilient, lower-waste food supply chains. Sources as linked above.
Restraints
Infrastructure, safety and compliance pressures in food-cold-chain electrification
A major brake on ethylene carbonate (EC) demand is the uneven pace of battery adoption across food cold chains—which need reliable power, safe facilities, and clear recycling routes. The UN Food and Agriculture Organization estimates that weak or absent refrigeration still causes 526 million tons of food losses—about 12% of global production—showing how much infrastructure is still missing before battery-backed systems can scale widely in agrifood logistics. FAO/UNEP. Agrifood systems already account for about one-third of global anthropogenic greenhouse-gas emissions, so new warehouses and vehicle fleets face added pressure to prove lower-emission designs—slowing procurement cycles and electrolyte purchases that would otherwise pull EC volumes faster.
Basic electricity access is another hard limit for battery uptake in rural processing, fisheries landings, and last-mile hubs. The International Energy Agency reports ~750 million people still lacked electricity in 2023, with ~80% of the unelectrified in sub-Saharan Africa—regions where cold chains and e-logistics most need growth. Where power exists, affordability can be fragile; energy-intensive cold stores delay or resize battery storage to manage bills, which flattens near-term electrolyte demand.
Safety and occupational-health considerations add friction. Ethylene carbonate is labeled “Warning” with hazards H302 (harmful if swallowed), H319 (serious eye irritation), and H373 (organ damage from prolonged exposure if swallowed) in safety data sheets used by warehouse operators and chemical handlers—tightening training, PPE, and insurance requirements before facilities green-light larger electrolyte inventories.
In parallel, the European Chemicals Agency lists EC with GHS07/GHS08 pictograms in public substance information, which can trigger stricter handling protocols in EU food warehouses and battery-assembly lines.
Opportunity
Battery-backed cold chains and electrified food logistics
Ethylene carbonate (EC) has a clear growth lane in building resilient, low-waste food cold chains that use lithium-ion batteries for backup, load-shifting, and mobile refrigeration. The UN system quantifies the need. A joint FAO/UNEP assessment shows that lack of effective refrigeration causes 526 million tons of food production losses—about 12% of the global total—every year. Reducing that loss requires reliable cooling at farms, aggregation hubs, packhouses, ports, and retail, where batteries stabilize power and keep reefer systems running; EC is a core co-solvent in the electrolytes that enable those batteries to cycle safely and repeatedly.
System-level energy trends reinforce this pull. The International Energy Agency notes electric-car sales exceeded 17 million in 2024, more than 20% of global car sales. That momentum spills into commercial fleets—yard tractors, delivery vans, and refrigerated trucks—where battery packs power both traction and cooling, increasing electrolyte demand per vehicle. In the United States, the Energy Information Administration records 10.4 GW of utility-scale batteries added in 2024, taking cumulative capacity past 26 GW; more storage on the grid improves reliability for food-grade warehouses and processing plants, accelerating battery-ready retrofits and new builds that rely on EC-containing electrolytes.
Government policy is turning these needs into purchase orders. In September 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy announced over $3 billion for 25 battery manufacturing and materials projects across 14 states—funding that directly targets electrolytes and intermediate materials alongside cells and packs.
In the European Union, Regulation (EU) 2023/1542 makes battery recycling-efficiency and material-recovery rules mandatory from 2025 onward and sets a 24 July 2025 milestone for verifying recycling-efficiency rates. These measures localize supply, formalize recycling, and reward compliant solvent producers, positioning EC suppliers who can certify origin, purity, and circularity to win specifications in food-sector storage and logistics projects.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific leads with 39.4% share in 2024
In 2024, the Asia Pacific region dominated the global ethylene carbonate market, capturing a significant 39.4% share, equating to approximately USD 310.8 million in revenue. This robust market presence is primarily driven by the accelerating demand for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront of this expansion, propelled by substantial investments in clean energy technologies and supportive government policies promoting EV adoption.
China, in particular, plays a pivotal role in shaping the regional market dynamics. The nation’s rapid industrialization, coupled with a strong emphasis on electric mobility and renewable energy, has significantly boosted the consumption of ethylene carbonate. The government’s initiatives to reduce carbon emissions and enhance energy efficiency further contribute to the material’s increased demand in various applications, including battery electrolytes and lubricants.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
North America
Europe
Germany
France
The UK
Spain
Italy
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
South Korea
India
Australia
Rest of APAC
Latin America
Brazil
Mexico
Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
GCC
South Africa
Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Huntsman International LLC operates as a major supplier of ethylene carbonate, catering to diverse industrial sectors such as automotive, electronics, and chemical manufacturing. The company emphasizes quality and reliability, offering high-purity carbonate solutions suitable for lithium-ion batteries and other specialized applications. In 2024, Huntsman expanded its production capabilities to meet rising global demand, focusing on environmentally friendly processes. Its global distribution network allows it to serve key markets efficiently, solidifying its position as a trusted player in the ethylene carbonate sector.
TOAGOSEI CO., LTD. specializes in the production of ethylene carbonate for high-performance applications in batteries, lubricants, and chemical intermediates. The company prioritizes research and development, ensuring superior quality and stable supply. In 2024, TOAGOSEI strengthened its market presence in Asia and Europe, supporting the growing lithium-ion battery sector. Its focus on advanced manufacturing techniques and sustainability initiatives enhances operational efficiency and product reliability. The company remains a critical supplier for industries requiring consistent and high-grade ethylene carbonate.
Shinghwa Advanced Material Group Co., Ltd. is a prominent manufacturer of ethylene carbonate, focusing on battery electrolytes, coatings, and specialty chemical applications. The company invests heavily in technology and production optimization to ensure high-purity output. In 2024, Shinghwa expanded its capacity to support the increasing demand from electric vehicles and energy storage markets. Its commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability has enabled it to secure a significant share in the Asia Pacific and global ethylene carbonate markets, making it a key industry participant.
Top Key Players Outlook
Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
Huntsman International LLC
TOAGOSEI CO., LTD.
Shinghwa Advanced Material Group Co., Ltd.
Dubi Chem
ZIBO DONGHAI INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
Empower Materials
BASF
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Vizag Chemical
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024 Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation, was estimated to hold over 20% of the global market share for electronic-grade ethylene carbonate, producing several million tons annually alongside competitors like Toagosei and Solvay.
In 2024, Shinghwa Advanced Material Group Co., Ltd. produced approximately 500,000 tons of ethylene carbonate, contributing significantly to the global supply.
Report Scope