September 13, 2025
By Karan Singh
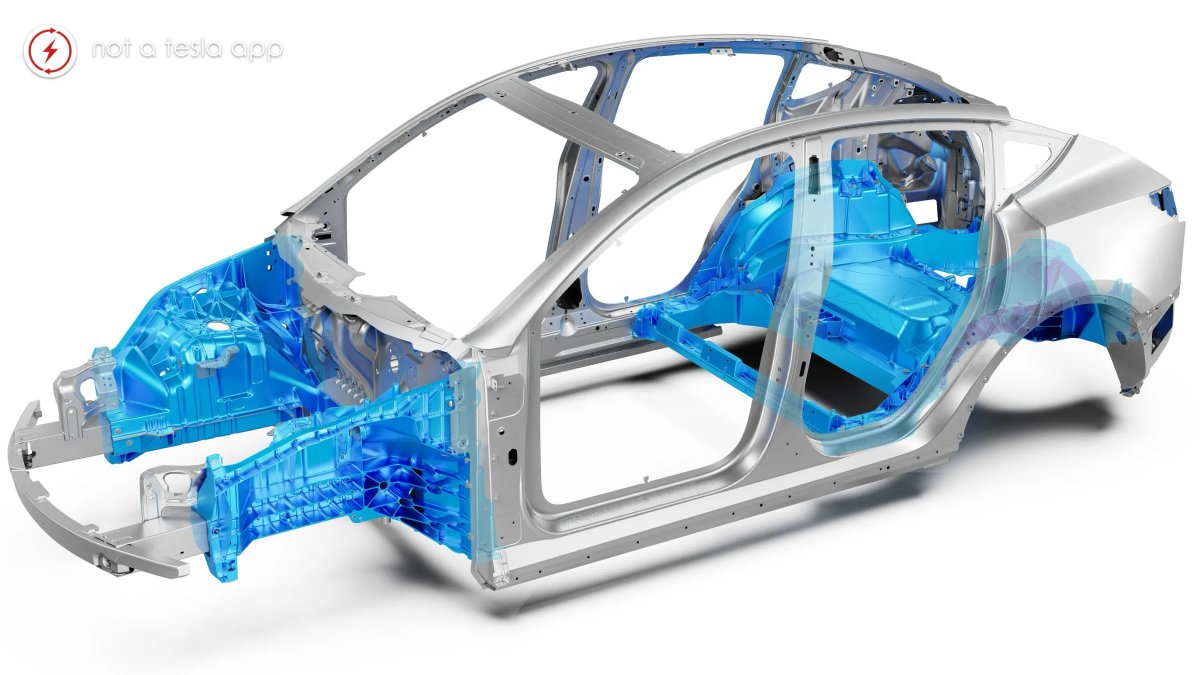

Despite widespread assumptions about Tesla’s gigacasting technologies, a new report reveals that large structural castings simplify both assembly and collision repair.
For years, a pervasive narrative has shadowed Tesla’s innovative gigacasting technology. While revolutionary for manufacturing efficiency, these massive single-piece castings were widely believed to be a repair nightmare, driving up costs and complexity in the event of a collision.
However, a new report from Thatcham Research directly challenges this assumption, concluding that gigacasting can actually save on vehicle repair expenses. This finding is supported by none other than Wes Morrill, Tesla’s Lead Engineer for the Cybertruck, who stated:
If you simplify the body design with large structural castings, it’s better both for initial assembly and for repair.
The Fears of Gigacastings
The traditional fears surrounding gigacastings centered on the idea that if a section of the casting was damaged, the entire piece would need to be replaced. That means exorbitant labor costs and extensive replacement of parts, small and large. The Thatcham Research study, however, presents a different reality, suggesting that the very design principles that help Tesla streamline production also inherently simplify repairs.
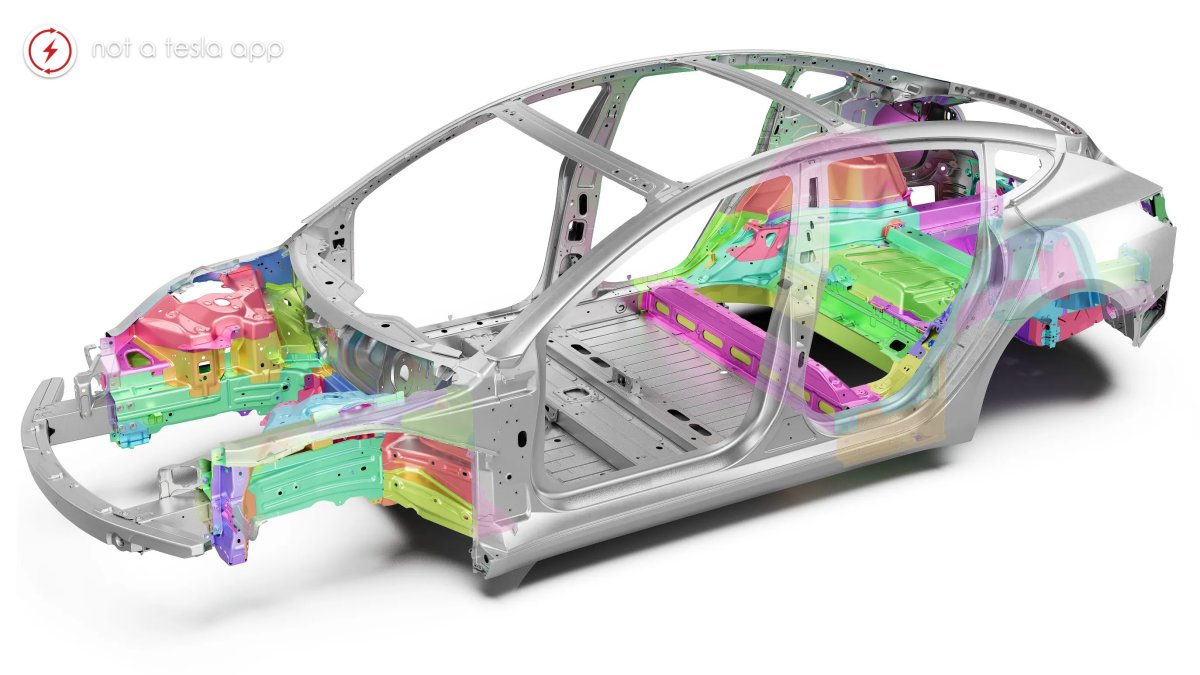 Fewer Parts, Easier Fixes
Fewer Parts, Easier Fixes
The core of that myth was based on a misunderstanding of how structural castings are designed and repaired. Conventional vehicle bodies are assemblies of hundreds of stamped metal parts, welded, riveted, and bonded together.
This creates numerous potential failure points and connections between parts, which can cause forces to propagate during a collision, resulting in damage to unrelated areas. Repairing such a structure often involves sectioning, cutting, and rejoining smaller components.
Gigacastings, by contrast, drastically reduce the number of individual parts. Tesla’s approach simplifies the vehicle’s body into a few large, structurally robust segments. This means fewer parts, so less labor, fewer welds, and faster production lines during initial assembly.
In collision repair, with fewer individual components and a more integrated structure, damage can often be more localized, or when a replacement is necessary, it involves fewer parts than repairing a traditional multi-segment body. Tesla uses advanced repair methods, including Gigacast Sectioning to replace only damaged portions of the casting, rather than the entire piece.
To put that into numbers, the study found that partial repairs on a Model Y’s rear gigacast resulted in savings of over £2,000 ($2,700 USD) compared to similar repairs on a Model 3 with a conventional multi-part steel body.
Recasting the Repair Paradigm
The implications of this study are larger than you might think, especially for both the automotive insurance and collision repair industries. Insurers, wary of potential total loss scenarios due to gigacasting damage, will likely look to re-evaluate their models with this new information.
Repair shops, which might have anticipated requiring specialized equipment and training for gigacastings, will likely find the streamlined design, when approached with new techniques, easier and faster to repair than before.
Tesla’s first-principles approach to engineering, often focused on its manufacturing innovations, also extends its benefits throughout the vehicle’s lifespan. While multi-section bodies have been the norm, Tesla is always challenging, breaking, and redefining those rules. Gigacastings are here to stay and becoming more common throughout the automotive industry.
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay up to date on the latest Tesla news, upcoming features and software updates.
September 12, 2025
By Karan Singh
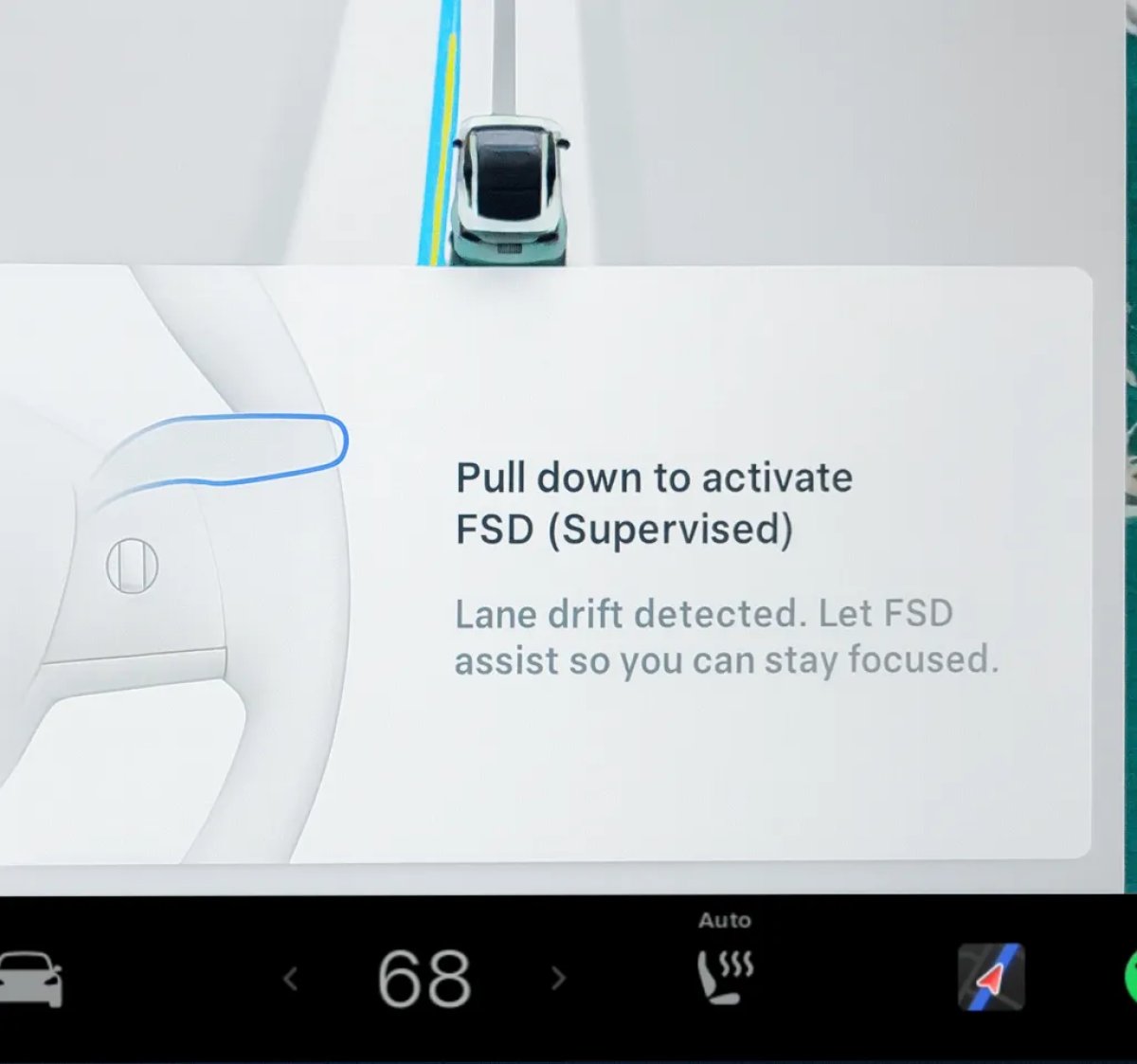
Tesla update 2025.32.3 includes an undocumented change to Tesla’s drowsiness detection feature. The change was discovered by Tesla hacker Green, who detected the change in decompiled Tesla code.
When your vehicle detects that the driver is drowsy or notices multiple lane departure assistance warnings, your vehicle will display a pop-up on the screen, prompting you to proactively engage FSD to help you keep an eye on the road.
The on-screen alert uses the same design as a previous prompt that reminds owners and subscribers of FSD to activate and use the feature.
From Passive Warning to Active Intervention
For years, advanced safety systems in vehicles have operated on a simple principle. Detect a problem, such as drifting from a lane, and alert the driver with a chime or vibration. The responsibility for correcting the issue remained entirely with the human driver.
While some manufacturers did offer driver assistance pull-over systems, they are far and few between, and mostly only operate on the highway, enabling the vehicle to pull over if the driver is unconscious.
Tesla is taking a different approach, and the new alerts in 2025.32.3 demonstrate just how they plan to do that. Drivers will see prompts such as:
“Lane drift detected. Let FSD assist so you can stay focused.”,
“Drowsiness detected. Stay focused with FSD.”
Addressing the Elephant in the Room
This relatively small change is interesting because of how Tesla is now recommending FSD. When you engage FSD, Tesla still tells you to keep your hands on the wheel and actively supervise. Now, when you’re unable to drive at your best, Tesla suggests you use FSD and supervise rather than drive.
At this point, FSD is getting close to what we always wanted it to be, software that can get you to your destination with minimal driver input. However, it’s not at the point of human-level safety yet, and the driver still needs to be attentive and take over at a second’s notice.
This new tip offers to take on the complex task of driving, the car can de-escalate a potentially dangerous situation far more effectively than a simple chime or vibration can. It’s a tangible first step towards a future where your Tesla will pre-emptively assist a driver who is impaired or distracted.
While it’s a step forward, the wording of the new prompts is interesting. Asking an already inattentive or incapable driver to supervise a system that requires attention is an interesting suggestion, and one that will have to be refined over time, especially as Tesla continues to push towards Unsupervised FSD.
However, this wrinkle in the design doesn’t detract from the importance of the underlying statement. The primary goal here is to make the driver and vehicle safer, and offering the use of FSD in combination with the driver’s attention should result in a safer ride for everyone involved.
The Future of Safety
Ultimately, this update is more than just a new alert; it’s a sign that Tesla is immensely confident in FSD’s ability to be a safer alternative when compared to a compromised human driver. While there are still some kinks to work out regarding supervision, FSD can be a real-time safety net for tired drivers.
Driving while tired can happen for any number of reasons, but if it prevents an accident, that’s a huge win. We’re sure Tesla’s ultimate goal is to have FSD take over if a driver is completely incapable, and given that some other manufacturers already offer this as an emergency intervention feature, we’re sure Tesla will do so sometime in the near future as well.
September 12, 2025
By Karan Singh

Tesla’s ambitious plan for a nationwide robotaxi network is inching closer, as Nevada’s Department of Motor Vehicles has provided official approval for Tesla to begin testing autonomous vehicles in the state.
The approval is another milestone for Tesla, establishing Nevada as the next proving ground for Robotaxi as it looks to expand its operational footprint beyond its current service areas in Austin and the Bay Area.
Nevada Green Light
In an email exchange with Sawyer Merritt, the Nevada DMV confirmed that Tesla’s application for Testing Registry certification was submitted on September 3rd, then processed and approved by the Office of Business Licensing on September 10th.
According to the DMV, the physical autonomous vehicle license plates and the registry certificates were sent to Tesla the same day, allowing Tesla to begin accumulating real-world miles in the Silver State.
The Path to Public Rides
This isn’t a green light for Tesla to start offering public rides yet. This initial approval is for testing purposes and offers a path for Tesla to obtain the final certifications for operations. The next and final step is a Self-Certification for Operations with the Nevada DMV.
This self-certification process, once reviewed and approved, would grant Tesla a Certificate of Compliance for operations. This is the final item that would unlock a driverless service for the public in Nevada, similar to the one currently operating in Austin, where vehicles have no one in the driver’s seat.
It will be up to Tesla to include a safety monitor or driver for their own testing requirements, which they may be slowly moving away from as more confidence is gained with more miles on the latest builds of Robotaxi FSD.
Building on the Austin Blueprint
Securing approval in another state is a big development for Robotaxi. It demonstrates that Tesla’s model for deploying its autonomous fleet is scalable and can navigate the regulatory frameworks of different states. Nevada is a logical next step, too, being home to Tesla’s Giga Nevada and having a long history of being at the forefront of autonomous vehicle legislation.
Tesla’s rollout to Nevada will be part of its slow, deliberate, and strategic rollout of the Robotaxi network. With each new state that comes online, Tesla gathers invaluable data and experience, building on everything they’ve learned in Austin and the Bay Area.
The Nevada approval is more than just a simple permit. It’s a sign that Tesla is actively working with states to expand the Robotaxi network. We may see the next states, Arizona and Florida, coming online very soon.
