Report Overview
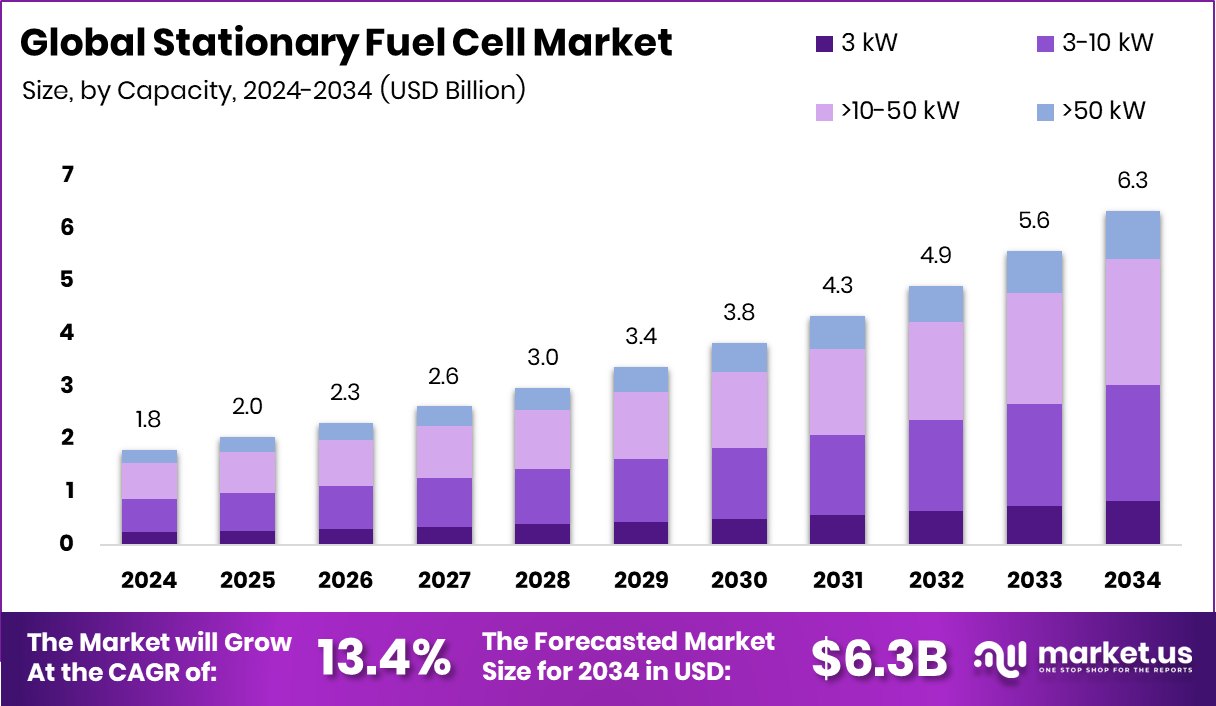
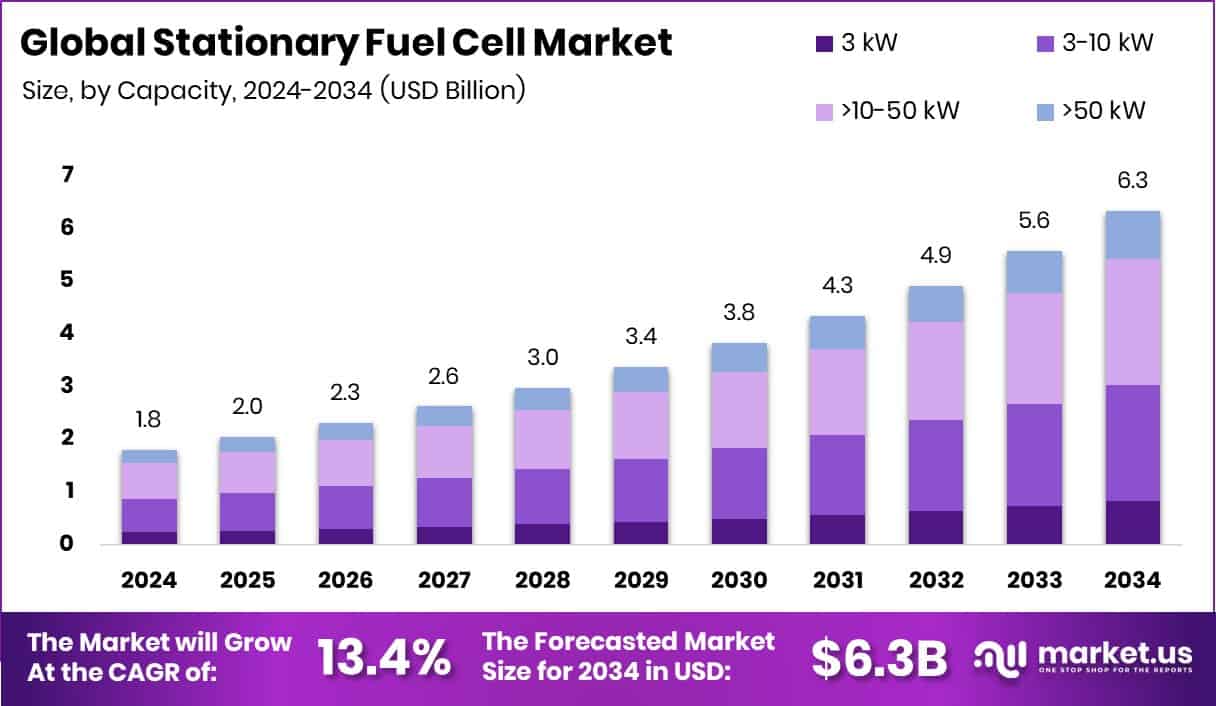
The Global Stationary Fuel Cell Market is expected to be worth around USD 6.3 billion by 2034, up from USD 1.8 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.4% from 2025 to 2034. Strong industrial growth and clean energy goals boosted Asia-Pacific’s 38.60% market share.
A stationary fuel cell is an electrochemical device that converts chemical energy—typically from hydrogen or other fuels—directly into electricity, heat, and water, and is deployed in fixed installations rather than in mobile systems. It’s commonly used as a backup power source, for combined heat and power (CHP) in buildings, or as a localized energy generator to supplement the grid supply. Unlike batteries, it continuously generates power as long as fuel and oxidant are supplied.
The stationary fuel cell market refers to the global industry ecosystem around the design, manufacture, deployment, and servicing of fixed (non-vehicle) fuel cell systems for residential, commercial, industrial, and utility use. It encompasses modules of varying sizes (from a few kilowatts to megawatt-scale), applications (prime power, CHP, backup power), and end users who seek decentralized, clean, and reliable energy solutions.
One key driver is the rising focus on decarbonization and clean energy transitions: as governments and utilities aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, interest in zero-emission power sources grows. Coupled with this, the push to build out hydrogen infrastructure supports fuel cell adoption more widely. Another driver is the increasing need for energy resilience: aging grids, more frequent blackouts, and distributed generation trends push institutions to seek on-site generation. Also, ongoing improvements in materials, manufacturing, and system scaling are helping reduce costs and improve durability, making the technology more viable in more markets.
Demand stems from sectors that need uninterrupted, high-quality power—data centers, telecom hubs, hospitals, and industrial facilities. In places where grid reliability is weak or where peak demand surcharges are high, onsite fuel cells can offer both resilience and cost savings. Also, integration with renewable systems (solar, wind) creates hybrid setups where fuel cells fill gaps when renewables are intermittent.
Opportunity lies where hybrid systems combine fuel cells with solar, wind, or battery storage to create stable, clean microgrids. Also, funding and policy support can unlock scale: for example, “Prime Intellect Secures $15 M to Build a Peer-to-Peer AI Future” and a government pushing forward “£300 million for Great British Energy to invest in offshore wind supply chains ahead of the Future of Energy Security summit” signal that sectors adjacent to energy are receiving serious backing, potentially opening more capital flows toward clean energy infrastructure like stationary fuel cells.
Key Takeaways
The Global Stationary Fuel Cell Market is expected to be worth around USD 6.3 billion by 2034, up from USD 1.8 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.4% from 2025 to 2034.
In 2024, the >10–50 kW capacity segment held a 37.8% share in the Stationary Fuel Cell Market.
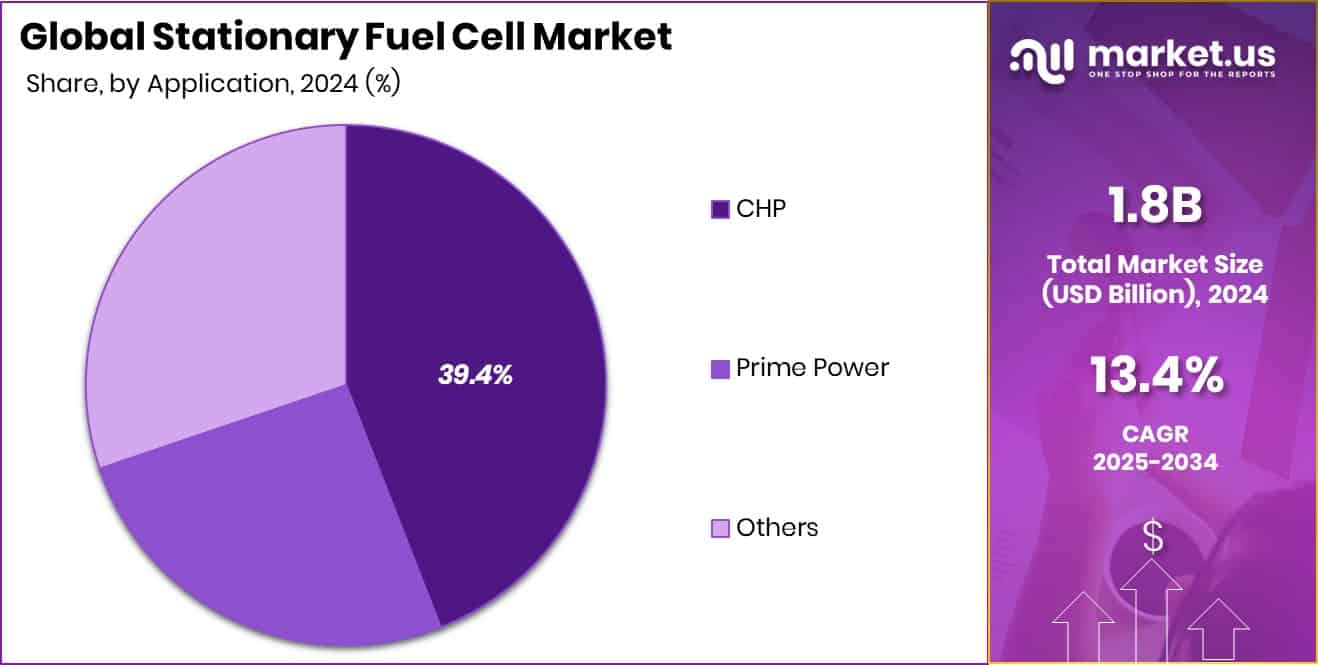
The CHP application segment captured a 39.4% share, highlighting efficiency in combined heat and power generation systems.
The Industry/Utility end-use segment dominated the Stationary Fuel Cell Market with a significant 56.3% share.
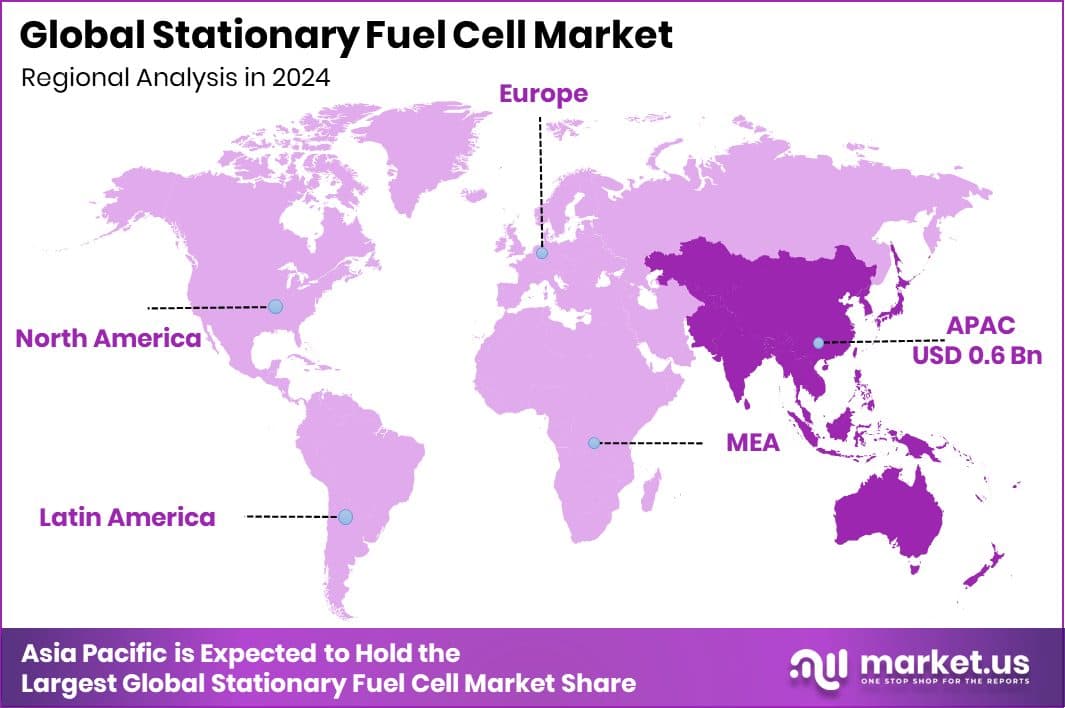
The Asia-Pacific market reached a significant valuation of around USD 0.6 billion.
By Capacity Analysis
In 2024, >10–50 kW capacity held 37.8% share in the Stationary Fuel Cell Market.
In 2024, >10–50 kW held a dominant market position in the By Capacity segment of the Stationary Fuel Cell Market, with a 37.8% share. This capacity range is widely adopted for medium-scale applications such as commercial buildings, small industrial sites, and community energy systems requiring reliable and efficient power output. Its balance between compact size and high energy efficiency makes it suitable for distributed generation and combined heat and power installations.
The segment’s growth is supported by the rising demand for decentralized power systems and reduced carbon emissions. Moreover, >10–50 kW systems offer operational flexibility, enabling integration with renewable sources while maintaining grid stability, which continues to strengthen their adoption across various stationary installations.
By Application Analysis
CHP applications dominated the Stationary Fuel Cell Market with 39.4% overall share.
In 2024, CHP held a dominant market position in the By Application segment of the Stationary Fuel Cell Market, with a 39.4% share. Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems are favored for their ability to generate both electricity and useful heat from a single fuel source, achieving higher overall efficiency. This segment’s strong presence is driven by growing adoption in commercial and industrial facilities aiming to lower energy costs and carbon emissions.
CHP fuel cell systems provide stable, on-site power with minimal transmission losses, making them ideal for regions with high energy demand and strict emission standards. Their efficiency, reliability, and contribution to energy independence continue to strengthen their dominance within the stationary fuel cell market.
By End Use Analysis
The industry/utility end-use segment led the Stationary Fuel Cell Market with 56.3% share.
In 2024, Industry/Utility held a dominant market position in the By End Use segment of the Stationary Fuel Cell Market, with a 56.3% share. This segment leads due to the growing need for continuous, high-capacity power in industrial operations and utility-scale applications. Stationary fuel cells in this category are valued for their ability to deliver efficient, low-emission, and reliable energy suitable for heavy-duty processes and grid support.
Industries and utilities prefer these systems for their long operational lifespan, minimal maintenance, and compatibility with renewable hydrogen. Additionally, the ability of fuel cells to provide both primary and backup power supports energy resilience, helping utilities maintain stability and meet stringent environmental standards, thereby driving their widespread adoption.
Key Market Segments
By Capacity
3 kW
3-10 kW
>10-50 kW
>50 kW
By Application
By End Use
Residential
Commercial
Industry/utility
Driving Factors
Rising Demand for Clean and Reliable Power Solutions
One major driving factor for the stationary fuel cell market is the increasing global shift toward clean, efficient, and reliable power generation. Governments and industries are actively reducing dependence on fossil fuels to cut carbon emissions. Stationary fuel cells offer a strong alternative by providing electricity with low environmental impact and high energy efficiency. Their ability to operate continuously, even during grid outages, makes them ideal for critical facilities like hospitals, data centers, and industrial plants.
Additionally, advancements in hydrogen infrastructure and supportive energy policies are accelerating adoption. As more countries invest in sustainable energy systems and promote carbon-neutral technologies, the demand for stationary fuel cells continues to rise across both developed and emerging economies.
Restraining Factors
High Installation and Maintenance Costs Limit Growth
A key restraining factor for the stationary fuel cell market is the high initial cost of installation and ongoing maintenance. Producing and assembling fuel cell systems involves expensive materials such as platinum catalysts and specialized membranes, which raise overall system costs. Additionally, the setup requires advanced infrastructure for hydrogen storage, distribution, and safety compliance, making it challenging for small- or medium-scale users to adopt.
Maintenance and skilled technical support further add to operational expenses. These high upfront and servicing costs often discourage investment, especially in regions with limited financial incentives or subsidies. As a result, despite their environmental benefits, the economic barrier continues to slow the wider adoption of stationary fuel cell systems globally.
Growth Opportunity
Integration with Renewable Energy and Microgrid Systems
A major growth opportunity for the stationary fuel cell market lies in integrating fuel cells with renewable energy and microgrid systems. As solar and wind power expand, their intermittent nature creates a need for stable, continuous energy sources. Stationary fuel cells can complement these renewables by providing consistent base-load power and balancing grid fluctuations. They also enable energy storage and distributed generation, supporting off-grid and remote operations.
The rising focus on decentralized power generation encourages hybrid systems that combine fuel cells with batteries or renewables. This integration not only enhances grid reliability but also reduces emissions, positioning fuel cells as a key technology in future clean energy networks and resilient power infrastructures worldwide.
Latest Trends
Growing Adoption of Hydrogen-Based Fuel Cell Systems
One of the latest trends in the stationary fuel cell market is the rising adoption of hydrogen-based fuel cell systems. As countries invest in hydrogen infrastructure, industries are shifting from natural gas to cleaner hydrogen fuels for power generation. Hydrogen fuel cells produce electricity with only water and heat as by-products, making them ideal for zero-emission energy solutions. Governments are supporting this transition through hydrogen roadmaps, subsidies, and public-private projects to accelerate deployment.
Moreover, technological improvements in hydrogen production, such as green hydrogen from renewable sources, are enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. This trend is reshaping the energy landscape, promoting hydrogen as a key driver in the global transition toward sustainable stationary power systems.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific dominated the Stationary Fuel Cell Market with a 38.60% share.
In 2024, Asia-Pacific dominated the global Stationary Fuel Cell Market, capturing a 38.60% share, valued at USD 0.6 billion. Rapid urbanization, industrial expansion, and government efforts toward clean power generation supported this regional dominance. Strong adoption in Japan, South Korea, and China boosted the Asia-Pacific’s market leadership in stationary fuel cell systems.
North America continued to expand steadily with strong infrastructure and clean energy transition initiatives. Supportive government policies and technological development increased North America’s adoption of stationary fuel cells. Rising demand for reliable backup power enhanced the region’s contribution to the global market.
Europe showed consistent growth driven by its low-carbon energy policies and hydrogen roadmap. The region’s efforts to reduce emissions strengthened its investment in stationary fuel cell projects. Growing renewable integration further supported Europe’s market performance in this sector.
The Middle East & Africa region witnessed gradual progress with interest in decentralized clean power systems. Supportive renewable energy projects encouraged the adoption of efficient fuel cell technologies for a stable energy supply.
Latin America demonstrated emerging potential with industrial applications and investments in sustainable distributed energy systems. Together, these regions represent a global shift toward reliable, efficient, and low-emission stationary fuel cell solutions.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
Europe
Germany
France
The UK
Spain
Italy
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
South Korea
India
Australia
Rest of APAC
Latin America
Brazil
Mexico
Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
GCC
South Africa
Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
In 2024, Altergy continued to strengthen its position in the global stationary fuel cell market through its focus on clean, reliable, and cost-effective hydrogen fuel cell power systems. The company’s technology is widely used in telecom, emergency backup, and remote site applications. Altergy’s proprietary design offers high durability and quick start-up capability, supporting uninterrupted power delivery. Its commitment to eliminating diesel generators from backup power networks aligns with growing environmental goals, helping the company expand in both developed and emerging economies.
AFC Energy remained active in advancing alkaline fuel cell systems aimed at stationary and distributed energy generation. The company focuses on flexible hydrogen-based solutions that enable zero-emission power for off-grid and industrial users. AFC’s innovations in hydrogen fuel cells and ammonia-fueled systems highlight its commitment to sustainability and efficiency. Through modular designs, the company is targeting scalability for diverse end-use applications, including utilities and heavy industries.
Bloom Energy maintained a strong foothold in solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) technology, delivering high-efficiency stationary power systems. Its fuel cell platforms are known for generating clean, on-site electricity with lower emissions compared to traditional sources. Bloom’s systems are widely adopted across commercial and utility sectors due to their reliability and grid independence. In 2024, the company focused on expanding the deployment of hydrogen-ready fuel cell solutions, supporting energy resilience and transition toward net-zero operations.
Top Key Players in the Market
Altergy
AFC Energy
Bloom Energy
Ballard Power Systems
Cummins
Doosan Fuel Cell
Fuji Electric
GenCell
Plug Power
Nuvera Fuel Cells
Siemens Energy
Toshiba Corporation
Recent Developments
In July 2025, AFC Energy revealed that it had reduced hydrogen generator manufacturing costs by about 85% compared to earlier models, and it introduced the Hy-5 under a “Fuel as a Service” (FaaS) model.
In November 2024, Bloom Energy announced a gigawatt-scale fuel cell procurement agreement with American Electric Power (AEP) to deploy its solid oxide fuel cell systems co-located at customer sites to power AI data centers.
Report Scope