Study population and data source
The NHANES program, initiated by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) in the United States since 1960, aims to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the country. Since 1999, NHANES has operated on a two-year cycle, employing a complex, multistage probability sampling design to select a representative sample of participants nationwide. Health data are collected through in-home interviews and visits to Mobile Examination Centers (MECs). To date, over 240,000 individuals have participated in NHANES.
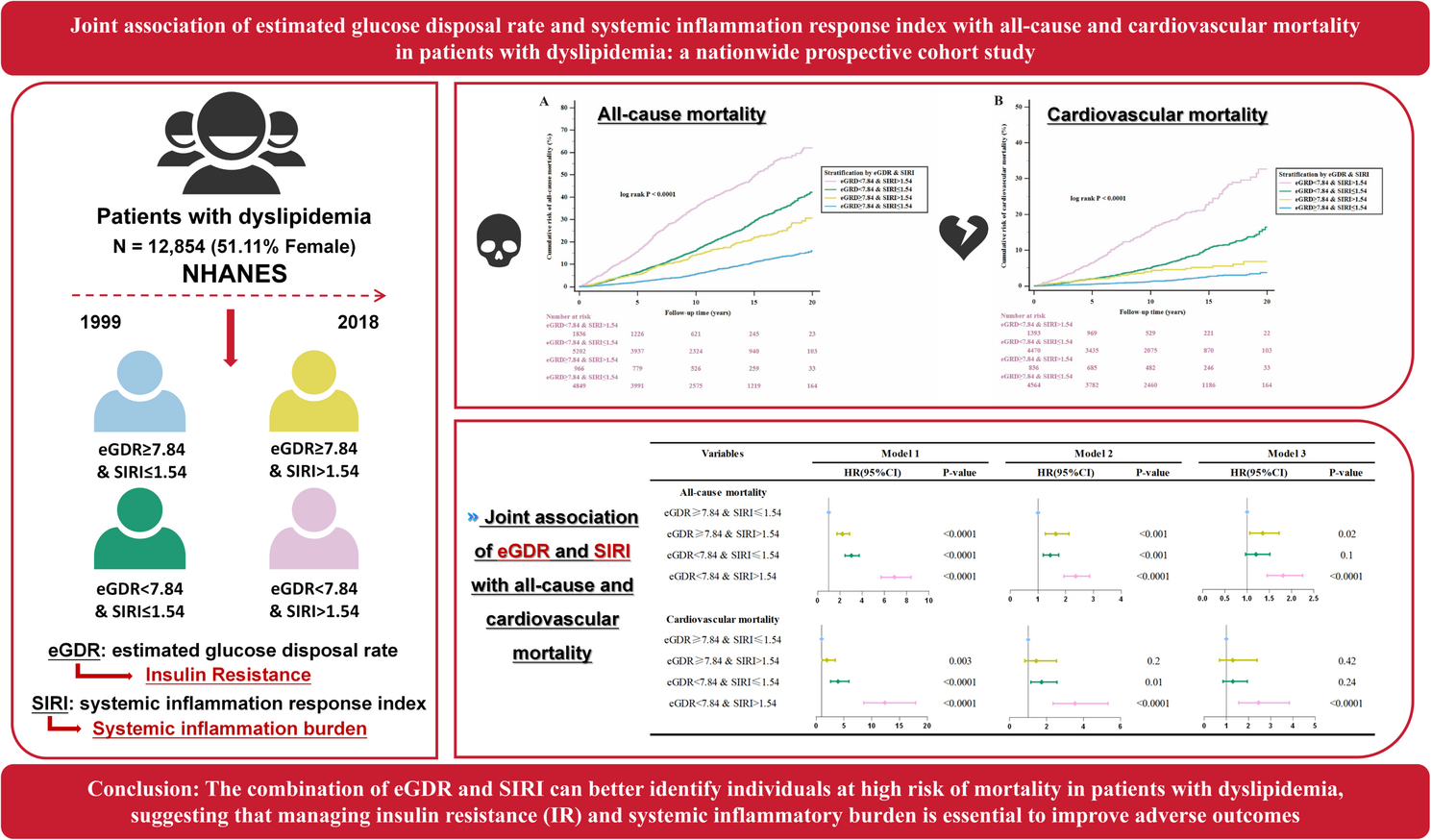
In this study, we linked the SENQ variable for each participant in the NHANES data with the National Death Index (NDI) data to obtain survival outcomes and causes of death. Ultimately, we included 12,854 adult participants diagnosed with dyslipidemia from 10 cycles of NHANES (1999–2018), as detailed in Fig. 1. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the NCHS, and all participants provided written informed consent before enrollment.
Screening flowchart of participants with dyslipidemia from NHANES 1999–2018
Definition of dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia was defined as meeting one or more of the following criteria: LDL-C ≥ 130 mg/dL (3.37 mmol/L), total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL (5.18 mmol/L), triglycerides (TG) ≥ 150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L), or HDL-C < 40 mg/dL (1.04 mmol/L) for male and < 50 mg/dL (1.30 mmol/L) for female. Additionally, individuals using lipid-lowering medications were also classified as having dyslipidemia.
Calculation of eGDR and SIRI and determination of the optimal cutoff values
Previous studies have demonstrated that eGDR can be used to assess IR and is calculated using the following formula: eGDR = 21.158 – (0.09 × WC [cm]) – (3.407 × Hypertension status [1 = yes, 0 = no]) – (0.551 × HbA1c [%])15. SIRI is calculated based on a complete blood count using the formula: neutrophil count × monocyte count/lymphocyte count [18].
The MSRSM was used to determine the optimal cut-off values of eGDR (low: < 7.84; high ≥ 7.84) and SIRI (low ≤ 1.54; higher > 1.54)28, which were most significantly associated with mortality (Figure S1). Based on these thresholds, participants were categorized into four groups: those with eGDR ≥ 7.84 and SIRI ≤ 1.54, eGDR ≥ 7.84 and SIRI > 1.54, eGDR < 7.84 and SIRI ≤ 1.54, and eGDR < 7.84 and SIRI > 1.54. This classification allowed for the stratification of participants based on the combined impact of eGDR and SIRI on mortality risk.
Study variables
Standardized questionnaires were used to collect demographic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle data from participants, including age, sex (male, female), race (Non-Hispanic Black, Mexican American, Non-Hispanic White, and Other), educational attainment (less than high school, high school or equivalent, and more than high school), family income-to-poverty ratio (PIR) (< 1, 1–3, > 3), smoking status (never, former, current), and alcohol consumption (never, former, mild, moderate, heavy). The examination and laboratory data primarily included height, weight, waist circumference, HbA1c, FBG, TG, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, white blood cell count, neutrophil count, monocyte count, and lymphocyte count. All routine biochemical tests were conducted in strict accordance with the guidelines specified in the NHANES Laboratory/Medical Technologist Manual of Procedures. Hypertension was defined based on a self-reported diagnosis, current use of antihypertensive medications, or an average systolic blood pressure (SBP) of ≥ 140 mmHg and/or an average diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of ≥ 90 mmHg. DM was diagnosed using multiple criteria, including fasting plasma glucose (≥ 7.0 mmol/L), 2-hour OGTT (≥ 11.1 mmol/L), random blood glucose (≥ 11.1 mmol/L), HbA1c (≥ 6.5%), current use of diabetes medication or insulin, or a self-reported diagnosis [29]. Data on the presence of cardiovascular diseases (including coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, stroke, or angina), cancer status, and the use of lipid-lowering drugs were all obtained through questionnaire surveys.
Statistical analysis
Following the recommendations of the NHANES Official Guide, we accounted for survey weights in our statistical analysis. Basic characteristics were presented as counts and percentages (%) for categorical variables and medians (interquartile range, IQR) for continuous variables. Group differences were assessed using the Chi-squared test for categorical variables and the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables. The MSRSM was applied to determine the optimal cut-off values of eGDR and SIRI that were most significantly associated with mortality. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate the cumulative mortality risk (1 – survival probability) across groups, and differences were assessed using the log-rank test. Weighted multivariable Cox regression analysis was used to assess the independent and joint associations of eGDR and SIRI with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, with Model 1 without adjustments, Model 2 adjusted for sex and age, and Model 3 adjusted for sex, age, BMI, education level, race, PIR, smoking status, alcohol consumption, CVD, cancer, DM, and lipid-lowering drugs. RCS was used to visualize the linear or non-linear associations between eGDR, SIRI, and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. In addition, subgroup analysis and interaction tests were performed to assess whether the association between the combination of eGDR and SIRI and the risk of mortality was influenced by the state of the covariates (age, sex, race, smoking status, alcohol consumption, PIR, cancer, and DM). Time-dependent ROC curves were used to assess the predictive accuracy of eGDR, SIRI, and the combination of eGDR and SIRI for survival outcomes at various time points. All statistical analyses were performed using R (version 4.2.2) and MedCalc software (version 20.022). A P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.