Leewenhoeck, A. An abstract of a letter from Mr. Anthony Leevvenhoeck at Delft, dated Sep. 17. 1683. Containing some microscopical observations, about animals in the scurf of the teeth, the substance call’d worms in the nose, the cuticula consisting of scales. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 14, 568–574 (1997).
Ursell, L. K. et al. The interpersonal and intrapersonal diversity of human-associated microbiota in key body sites. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129, 1204–1208 (2012).
Derovs, A., Laivacuma, S. & Krumina, A. Targeting microbiota: what do we know about it at present? Medicina 55, 459 (2019).
Lederberg, J. & Mccray, A. T. ‘Ome Sweet ‘Omics—a genealogical treasury of words. Scientist 15, 8–8 (2001).
Berg, G. et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 8, 103 (2020).
Kim, M. & Kim, C. H. Regulation of humoral immunity by gut microbial products. Gut Microbes 8, 392–399 (2017).
Rinninella, E. et al. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 7, 14 (2019).
Rowland, I. et al. Gut microbiota functions: metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 57, 1–24 (2018).
Jeong, S. Factors influencing development of the infant microbiota: from prenatal period to early infancy. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 65, 438 (2021).
Sender, R., Fuchs, S. & Milo, R. Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol. 14, e1002533 (2016).
Lozupone, C. A., Stombaugh, J. I., Gordon, J. I., Jansson, J. K. & Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489, 220–230 (2012).
Kers, J. G. & Saccenti, E. The power of microbiome studies: Some considerations on which alpha and beta metrics to use and how to report results. Front. Microbiol. 12, 796025 (2022).
Belda, I. et al. Microbial contribution to wine aroma and its intended use for wine quality improvement. Molecules 22, 189 (2017).
Cryan, J. F. & Dinan, T. G. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 701–712 (2012).
Pechal, J. L., Schmidt, C. J., Jordan, H. R. & Benbow, M. E. A large-scale survey of the postmortem human microbiome, and its potential to provide insight into the living health condition. Sci. Rep. 8, 5724 (2018).
Wilson, D. R., Binford, L. & Hickson, S. The gut microbiome and mental health. J. Holist. Nurs. 42, 79–87 (2024).
Biagi, E. et al. Gut microbiota and extreme longevity. Curr. Biol. 26, 1480–1485 (2016).
Kumar, A. et al. Gut microbiota in anxiety and depression: unveiling the relationships and management options. Pharmaceuticals 16, 565 (2023).
Madhogaria, B., Bhowmik, P. & Kundu, A. Correlation between human gut microbiome and diseases. Infect. Med. 1, 180–191 (2022).
Cussotto, S., Sandhu, K. V., Dinan, T. G. & Cryan, J. F. The neuroendocrinology of the microbiota-gut-brain axis: a behavioural perspective. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 51, 80–101 (2018).
Malan-Muller, S. et al. The gut microbiome and mental health: implications for anxiety- and trauma-related disorders. Omics 22, 90–107 (2018).
Carlson, A. L. et al. Infant gut microbiome associated with cognitive development. Biol. Psychiatry 83, 148–159 (2018).
Erdman, S. E. & Poutahidis, T. In International Review of Neurobiology (eds Cryan, J. F. & Clarke, G.) Vol. 131, 91–126 (Academic Press, 2016).
Varian, B. J. et al. Microbial lysate upregulates host oxytocin. Brain, Behav., Immun. 61, 36–49 (2017).
Williams, B. L., Hornig, M., Parekh, T. & Lipkin, W. I. Application of novel PCR-based methods for detection, quantitation, and phylogenetic characterization of Sutterella species in intestinal biopsy samples from children with autism and gastrointestinal disturbances. mBio, https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00261-11 (2012).
Borkent, J., Ioannou, M., Laman, J. D., Haarman, B. C. M. & Sommer, I. E. C. Role of the gut microbiome in three major psychiatric disorders. Psychol. Med. 52, 1222–1242 (2022).
Knudsen, J. K. et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation from patients with depression or healthy individuals into rats modulates mood-related behaviour. Sci. Rep. 11, 21869 (2021).
Zheng, P. et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 786–796 (2016).
Pan, B. et al. Efficacy and safety of gut microbiome-targeted treatment in patients with depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 25, 64 (2025).
Reid, G. Disentangling what we know about microbes and mental health. Front. Endocrinol. 10, 81 (2019).
Robinson, J. M. et al. Twenty important research questions in microbial exposure and social equity. MSystems 7, e0124021 (2022).
Alexandrova, A. Well-being as an object of science. Philos. Sci. 79, 678–689 (2012).
World Health Organization. Strengthening Mental Health Promotion (Fact Sheet No. 220) (2001).
Huppert, F. A Positive mental health in individuals and populations. In The Science of Well-being (eds Huppert, F.A., Baylis, N. & Keverne, B.) 307–340 (Oxford University Press, 2005).
Diener, E. & Chan, M. Y. Happy people live longer: subjective well-being contributes to health and longevity. Appl. Psychol.: Health Well-Being 3, 1–43 (2011).
Steptoe, A., Deaton, A. & Stone, A. A. Subjective wellbeing, health, and ageing. Lancet 385, 640–648 (2015).
Gere, J. & Schimmack, U. When romantic partners’ goals conflict: effects on relationship quality and subjective well-being. J. Happiness Stud. 14, 37–49 (2013).
Busseri, M. A. & Quoidbach, J. The structure of everyday happiness is best captured by a latent subjective well-being factor. J. Res. Personal. 96, 104177 (2022).
Blum, H. E. The human microbiome. Adv. Med. Sci. 62, 414–420 (2017).
Iasiello, M. et al. What’s the difference between measures of wellbeing, quality of life, resilience, and coping? An umbrella review and concept map of 155 measures of positive mental health. Int. J. Wellbeing 14, 1–25 (2024).
Diener, E., Oishi, S. & Tay, L. Advances in subjective well-being research. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2, 253–260 (2018).
Dominianni, C. et al. Sex, body mass index, and dietary fiber intake influence the human gut microbiome. PLoS ONE 10, e0124599 (2015).
Hu, X. et al. Changes in the skin microbiome during male maturation from 0 to 25 years of age. Ski. Res. Technol. 29, e13432 (2023).
Mueller, S. et al. Differences in fecal microbiota in different European study populations in relation to age, gender, and country: a cross-sectional study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 1027–1033 (2006).
Shin, J.-H. et al. Serum level of sex steroid hormone is associated with diversity and profiles of human gut microbiome. Res. Microbiol. 170, 192–201 (2019).
Valeri, F. & Endres, K. How biological sex of the host shapes its gut microbiota. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 61, N.PAG–N.PAG (2021).
Aleman, F. D. D. & Valenzano, D. R. Microbiome evolution during host aging. PLoS Pathog. 15, e1007727 (2019).
Morar, N. & Bohannan, B. J. M. The conceptual ecology of the human microbiome. Q. Rev. Biol. 94, 149–175 (2019).
Goh, B. Y.-L., Yeo, J. Y. & Gan, S. K.-E. Psycho-otorhinomicrobiology: the link between the aerotolerant flora of the nose and ears, and that of the psyche. APDTrove. https://doi.org/10.30943/2019/25032019 (2019).
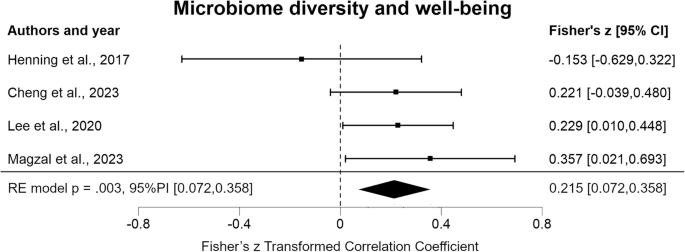
Cheng, Q. et al. Relationship functioning and gut microbiota composition among older adult couples. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20, 5435 (2023).
Henning, S. M. et al. Health benefit of vegetable/fruit juice-based diet: role of microbiome. Sci. Rep. 7, 2167 (2017).
Lee, S.-H. et al. Emotional well-being and gut microbiome profiles by enterotype. Sci. Rep. 10, 20736 (2020).
Magzal, F. et al. A personalized diet intervention improves depression symptoms and changes microbiota and metabolite profiles among community-dwelling older adults. Front. Nutr. 10, 1234549 (2023).
Li, L. et al. Gut microbes in correlation with mood: case study in a closed experimental human life support system. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 28, 1233–1240 (2016).
Michels, N. et al. Gut microbiome patterns depending on children’s psychosocial stress: reports versus biomarkers. Brain, Behav., Immun. 80, 751–762 (2019).
Valles-Colomer, M. et al. The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 623–632 (2019).
Adak, A. & Khan, M. R. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76, 473–493 (2019).
Lloyd-Price, J., Abu-Ali, G. & Huttenhower, C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 8, 51 (2016).
Heidary, M. et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori–induced gastric cancer on gastrointestinal microbiota: a narrative review. Front. Oncol. 14 (2025).
Blackmer-Raynolds, L. & Sampson, T. R. Overview of the gut microbiome. Semin. Neurol. 43, 518–529 (2023).
Rhee, S. H., Pothoulakis, C. & Mayer, E. A. Principles and clinical implications of the brain–gut–enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 306–314 (2009).
Sarkar, A. et al. Psychobiotics and the manipulation of bacteria–gut–brain signals. Trends Neurosci. 39, 763–781 (2016).
Kosyra, K., Drabczyk, M., Marczyńska, Z., Zyśk, A. & Magda, I. Microbiota and depressive disorders—a review. J. Educ., Health Sport 60, 188–203 (2024).
Yano, J. M. et al. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 161, 264–276 (2015).
Fakhoury, M. Revisiting the serotonin hypothesis: implications for major depressive disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 53, 2778–2786 (2016).
Hooper, L. V., Littman, D. R. & Macpherson, A. J. Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 336, 1268–1273 (2012).
Kau, A. L., Ahern, P. P., Griffin, N. W., Goodman, A. L. & Gordon, J. I. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system. Nature 474, 327–336 (2011).
Baechle, J. J. et al. Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging. Mol. Metab. 74, 101755 (2023).
Shamriz, O. et al. Microbiota at the crossroads of autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 15, 859–869 (2016).
Stokholm, J. et al. Maturation of the gut microbiome and risk of asthma in childhood. Nat. Commun. 9, 141 (2018).
Yang, X. et al. Investigation of Clostridium Butyricum on atopic dermatitis based on gut microbiota and TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Technol. Health Care. https://doi.org/10.1177/09287329241301680 (2025).
Barak, Y. The immune system and happiness. Autoimmun. Rev. 5, 523–527 (2006).
Beane, K. E. et al. Effects of dietary fibers, micronutrients, and phytonutrients on gut microbiome: a review. Appl. Biol. Chem. 64, 36 (2021).
Gupta, A., Singh, V. & Mani, I. Dysbiosis of human microbiome and infectious diseases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 192, 33–51 (2022).
Christian, L. M. et al. Gut microbiome composition is associated with temperament during early childhood. Brain, Behav., Immun. 45, 118–127 (2015).
Johnson, K. V.-A. Gut microbiome composition and diversity are related to human personality traits. Hum. Microbiome J. 15, 100069 (2020).
Flores, G. E. et al. Temporal variability is a personalized feature of the human microbiome. Genome Biol. 15, 531 (2014).
Falony, G., Vieira-Silva, S. & Raes, J. Richness and ecosystem development across faecal snapshots of the gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 526–528 (2018).
Boehm, J. K. & Kubzansky, L. D. The heart’s content: The association between positive psychological well-being and cardiovascular health. Psychol. Bull. 138, 655–691 (2012).
Lay, C. et al. Colonic microbiota signatures across five Northern European countries. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 4153–4155 (2005).
Baquero, F. & Nombela, C. The microbiome as a human organ. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18, 2–4 (2012).
Joos, R. et al. Examining the healthy human microbiome concept. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-024-01107-0 (2024).
Byrd, A. L., Belkaid, Y. & Segre, J. A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16, 143–155 (2018).
Kumpitsch, C. et al. Reduced olfactory performance is associated with changed microbial diversity, oralization, and accumulation of dead biomaterial in the nasal olfactory area. Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e0154923 (2024).
Turnbaugh, P. J. et al. The human microbiome project. Nature 449, 804–810 (2007).
Ivanov, I. I. et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented Filamentous Bacteria. Cell 139, 485–498 (2009).
Henao-Mejia, J. et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 482, 179–185 (2012).
Extremera, N. & Rey, L. The moderator role of emotion regulation ability in the link between stress and well-being.Front. Psychol. 6, 1632 (2015).
O’Neil, A. et al. Relationship between diet and mental health in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Am. J. Public Health 104, e31–e42 (2014).
Stewart, E. M., Landry, S., Edwards, B. A. & Drummond, S. P. A. In The Wiley Encyclopedia of Health Psychology 165–188 (John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2020).
Baker, S. H. A., El-Barrawy, M. A., Omran, E. A. & Raslan, H. S. Occurrence of some oral potentially pathogenic microorganisms and their associated risk factors. J. High. Inst. Public Health 47, 69–75 (2017).
Kraimi, N. et al. Microbiota and stress: a loop that impacts memory. Psychoneuroendocrinology 136, 105594 (2022).
Cecchini, L. et al. The Bern Birth Cohort (BeBiCo) to study the development of the infant intestinal microbiota in a high-resource setting in Switzerland: rationale, design, and methods. BMC Pediatr. 23, 560 (2023).
Mariat, D. et al. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol. 9, 123 (2009).
Divella, R. et al. Diet, probiotics and physical activity: the right allies for a healthy microbiota. Anticancer Res. 41, 2759–2772 (2021).
Dimitri-Pinheiro, S., Soares, R. & Barata, P. The microbiome of the nose—friend or foe?. Allergy Rhinol.11, 2152656720911605 (2020).
Lorimer, J. Gut buddies: multispecies studies and the microbiome. Environ. Humanit. 8, 57–76 (2016).
Wilson, A. S. et al. Diet and the human gut microbiome: an international review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 65, 723–740 (2020).
Obregon-Tito, A. J. et al. Subsistence strategies in traditional societies distinguish gut microbiomes. Nat. Commun. 6, 6505 (2015).
Mutlu, E. A. et al. Colonic microbiome is altered in alcoholism. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 302, G966–G978 (2012).
Monda, V. et al. Exercise modifies the gut microbiota with positive health effects. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 3831972 (2017).
Melnik, A. V. et al. The molecular effect of wearing silver-threaded clothing on the human skin. MSystems 8, e0092222 (2023).
Moher, D. et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 4, 1 (2015).
de Vries, L. P., van de Weijer, M. P. & Bartels, M. The human physiology of well-being: a systematic review on the association between neurotransmitters, hormones, inflammatory markers, the microbiome and well-being. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 139, 104733 (2022).
Pigott, T. D. & Polanin, J. R. Methodological guidance paper: high-quality meta-analysis in a systematic review. Rev. Educ. Res. 90, 24–46 (2020).
Kraut, R. The Quality of Life Vol. 1 (Oxford University Press, 2018).
Babineau, J. Product review: covidence (systematic review software). J. Can. Health Libr Assoc. 35, 68 (2014).
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Study Quality Assessment Tools. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (2021).
Pallen, M. J. The dynamic history of prokaryotic phyla: discovery, diversity and division. Int. J. Syst. Evolut. Microbiol. 74, 006508 (2024).
McNair, D., Lorr, M. & Droppleman, L. EITS Manual for the Profile of Mood States (Editorial and Industrial Testing Service, 1971).
Hays, R. D. & Morales, L. S. The RAND-36 measure of health-related quality of life. Ann. Med. 33, 350–357 (2001).
Thompson, E. R. Development and validation of an internationally reliable short-form of the positive and negative affect schedule (PANAS). J. Cross-Cultural Psychol. 38, 227–242 (2007).
Grossi, E. et al. Development and validation of the short version of the Psychological General Well-Being Index (PGWB-S). Health Qual. Life Outcomes 4, 88 (2006).
McHorney, C. A., Ware, J. E. J., Rachel Lu, J. F. & Sherbourne, C. D. The MOS 36-ltem Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): III. Tests of data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability across diverse patient groups. Med. Care 32, 40 (1994).
Spanier, G. B. Measuring dyadic adjustment: new scales for assessing the quality of marriage and similar dyads. J. Marriage Fam. 38, 15–28 (1976).
The WHOQOL Group. Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment. Psychol. Med. 28, 551–558 (1998).
Hedges, L. V. & Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis (Academic Press, 2014).
Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Soft. 36, 1–48 (2010).
Viechtbauer, W. Bias and efficiency of meta-analytic variance estimators in the random-effects model. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 30, 261–293 (2005).
Cochran, W. G. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 10, 101–129 (1954).
Higgins, J. P. T. & Thompson, S. G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21, 1539–1558 (2002).
Begg, C. B. & Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50, 1088–1101 (1994).
Sterne, J. A. C. & Egger, M. In Publication Bias in Meta-analysis: Prevention, Assessment and Adjustments (eds Rothstein, H. R., Sutton, A. J. & Borenstein, M.) 99–110 (John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005).
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T. & Rothstein, H. R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis (John Wiley & Sons, 2021).
Orwin, R. G. A fail-safe N for effect size in meta-analysis. J. Educ. Stat. 8, 157–159 (1983).
Rosenberg, M. S. The file-drawer problem revisited: a general weighted method for calculating fail-safe numbers in meta-analysis. Evolution 59, 464–468 (2005).
Riley, R. D., Higgins, J. P. T. & Deeks, J. J. Interpretation of random effects meta-analyses. BMJ 342, d549 (2011).
Kuha, J. AIC and BIC: comparisons of assumptions and performance. Sociol. Methods Res. 33, 188–229 (2004).