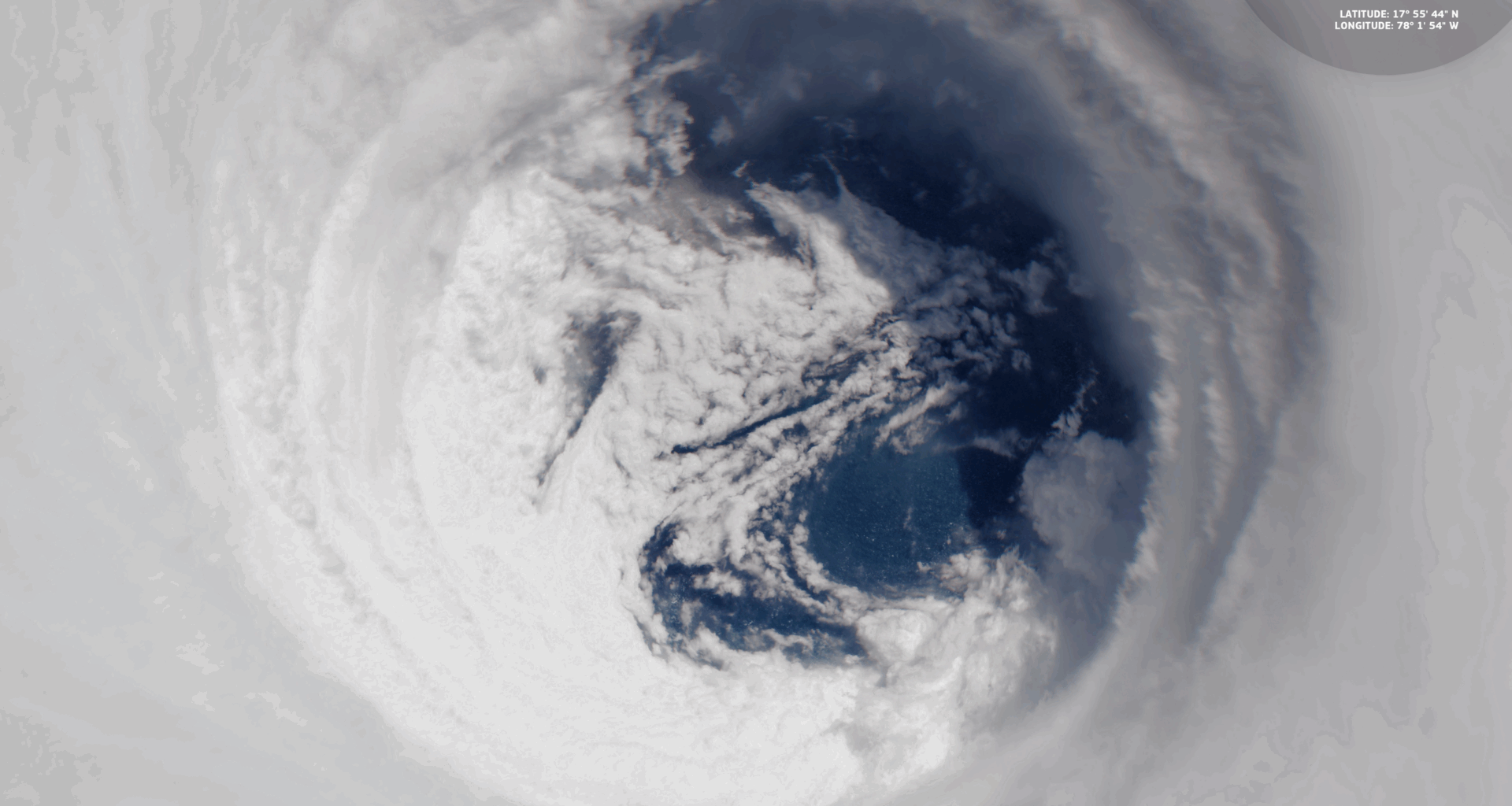
High above Earth, satellites like the European Union’s Copernicus Sentinel-2 watch and track storms such as Hurricane Melissa, a category 5 maelstrom. These satellites help keep continuous eyes on the tempest and provide valuable data about how these natural disasters form and how they can impact communities in a changing world.
Because the data is freely available to researchers under the Copernicus program, scientists can support disaster management, build better early warning systems, and have better insights into how global warming and climate change are affecting hurricanes.
You may like
Where is it?
Hurricane Melissa made landfall in Jamaica on Oct. 28, 2025.
Hurricane Melissa was a record-breaking storm for Jamaica. (Image credit: ESA)Why is it amazing?
Hurricane Melissa underwent a period of rapid intensification, becoming one of the most powerful storms in the Atlantic in 2025. When it made landfall in Jamaica on Oct. 28, 2025, it was the most powerful storm in the country’s history. Monitoring how storms change is crucial because intensification rates are hard to predict, and stronger storms mean higher risk of catastrophic damage.
Understanding and analyzing the processes behind hurricane intensification, via the use of satellites like Sentinel-2, can help to improve hurricane forecasting and, in the process, save lives.
Want to learn more?
You can learn more about Earth-monitoring satellites and the European Space Agency.