Published on Jul. 26, 2025, 4:05 PM
The Moon and Earth periodically ‘photobomb’ this crucial space weather mission.
NASA’s eye on the Sun took a little break on Friday, to watch two different solar eclipses throughout the day.
The Solar Dynamics Observatory is parked out in geosynchronous orbit above North America, keeping its cameras trained on the Earth-facing side of the Sun. It’s mission: to keep us in the loop on solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections.
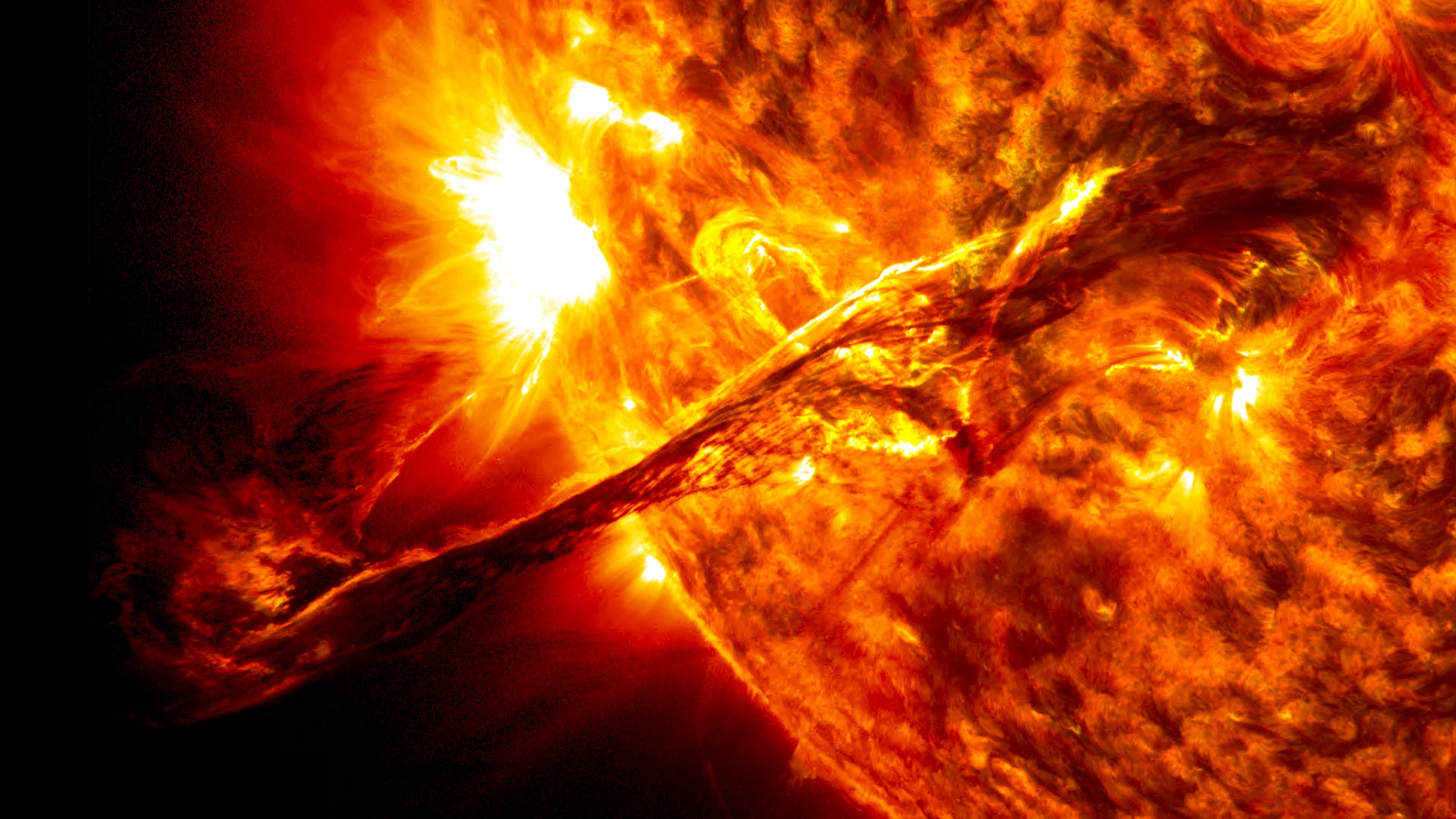

This immense solar filament tore itself away from the Sun’s surface in August 2012, becoming a coronal mass ejection as it expanded out into space. (NASA SDO)
On July 25, 2025, that mission was briefly interrupted — twice, in fact — as two other objects blocked the satellite’s view of the Sun.
Starting around 2:40 UTC on Friday (10:40 p.m. EDT Thursday), the orbits of SDO and the Moon synced up, producing a partial solar eclipse as the Moon crossed SDO’s field of view.
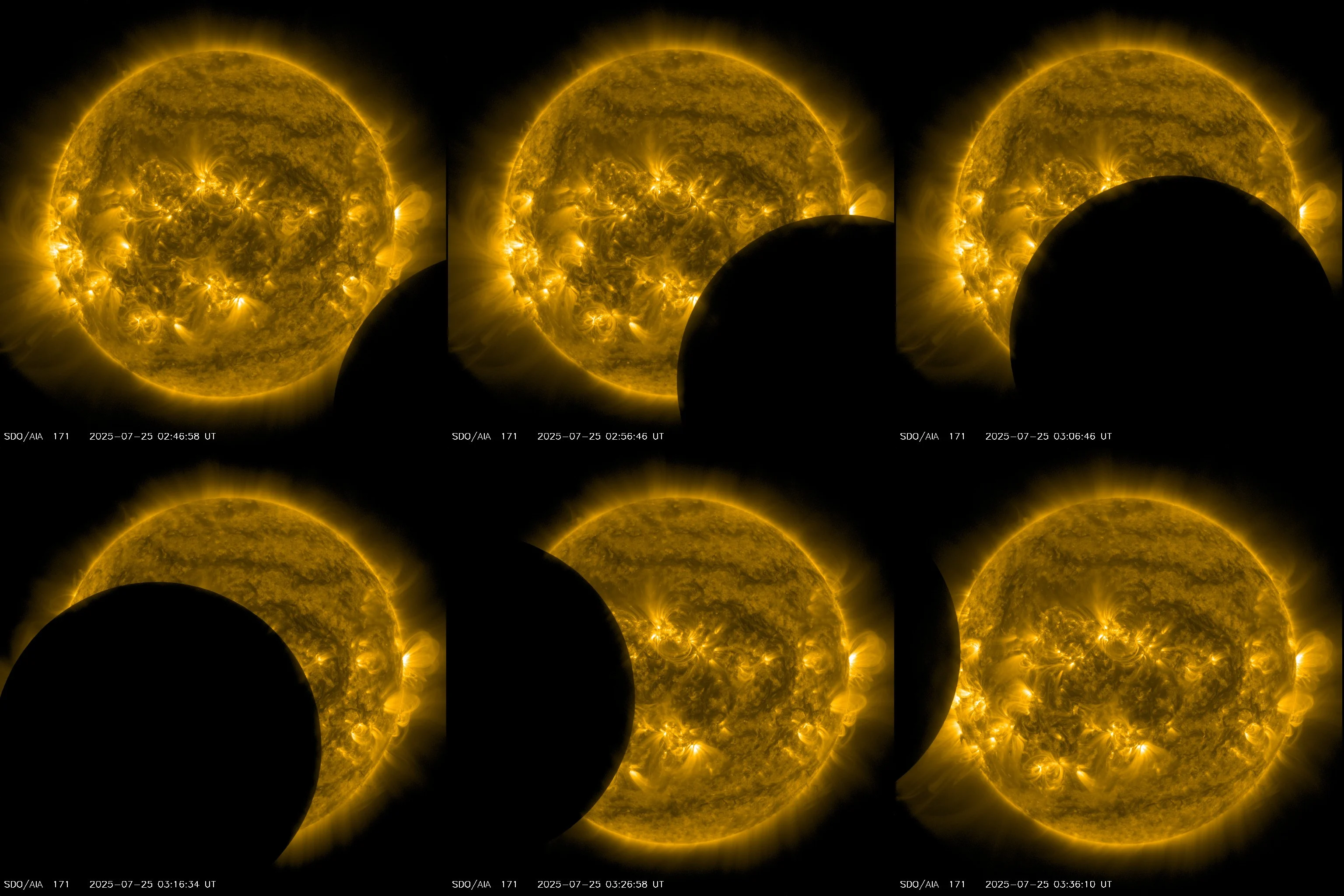
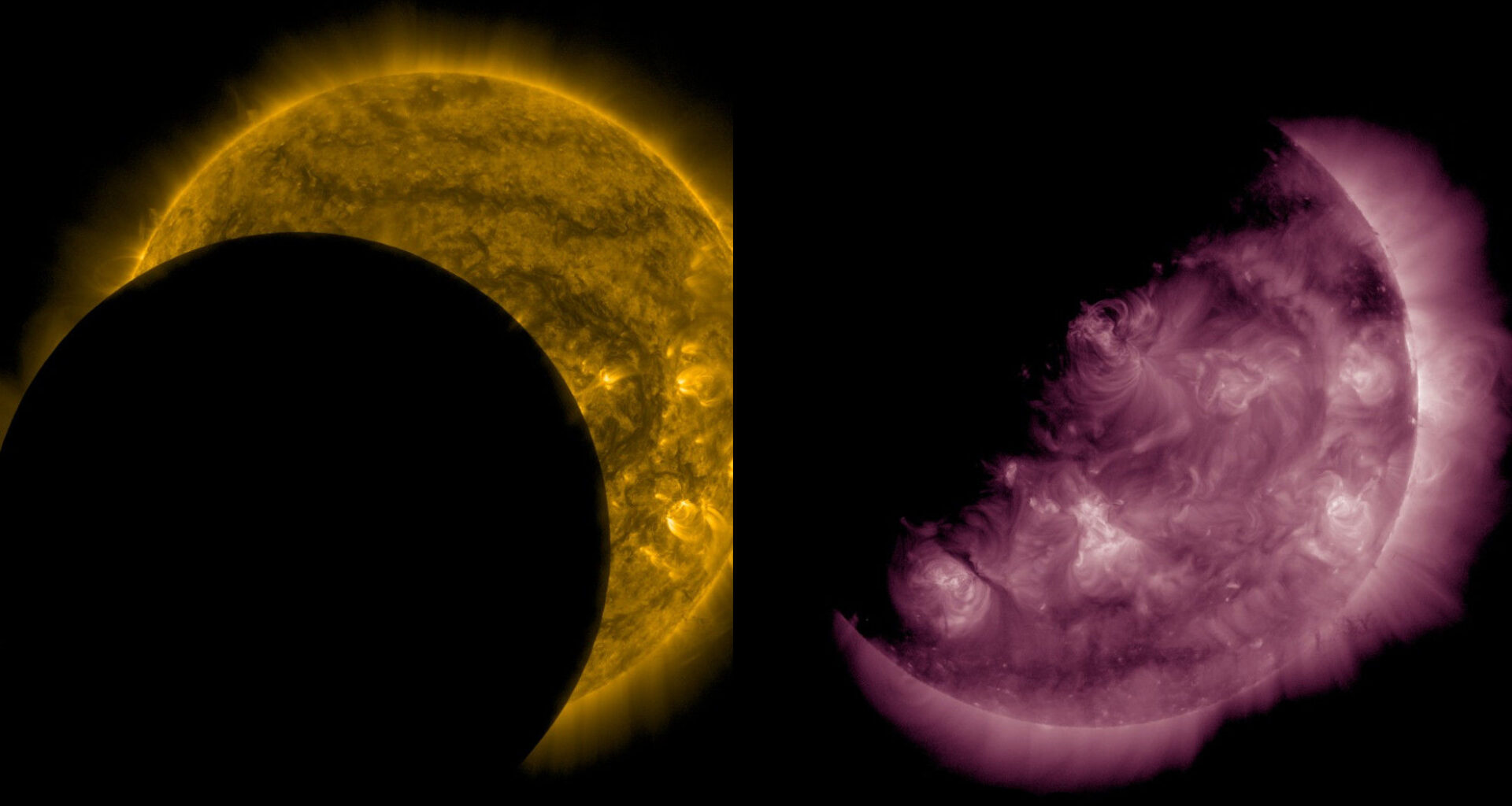
A partial solar eclipse viewed only from space, courtesy SDO’s 171 Angstrom filtered view, which captures extreme ultraviolet light to visualize the activity going on in the Sun’s lower atmosphere, including the immense coronal loops that extend away from the surface. The Moon’s disk took roughly an hour, from around 2:40-3:40 UTC, to pass across the Sun. (NASA SDO/Scott Sutherland)
These transits typically occur around the date of the New Moon, when the Moon is nearly or exactly in between the Sun and Earth. However, they rely heavily on the exact orientation of SDO’s orbit in relation to the Moon’s tilted orbit around Earth.
According to NASA, during this ‘lunar transit’, the Moon covered 62 per cent of the solar disk at maximum. This was the fourth time since April that the Moon passed in front of the Sun from SDO’s point of view. It was also the deepest transit so far in 2025 — 23 per cent of the Sun was covered during the April 27 pass, while on April 28, the Moon covered only 2 per cent, and on May 25, it covered only 4 per cent of the Sun’s disk.