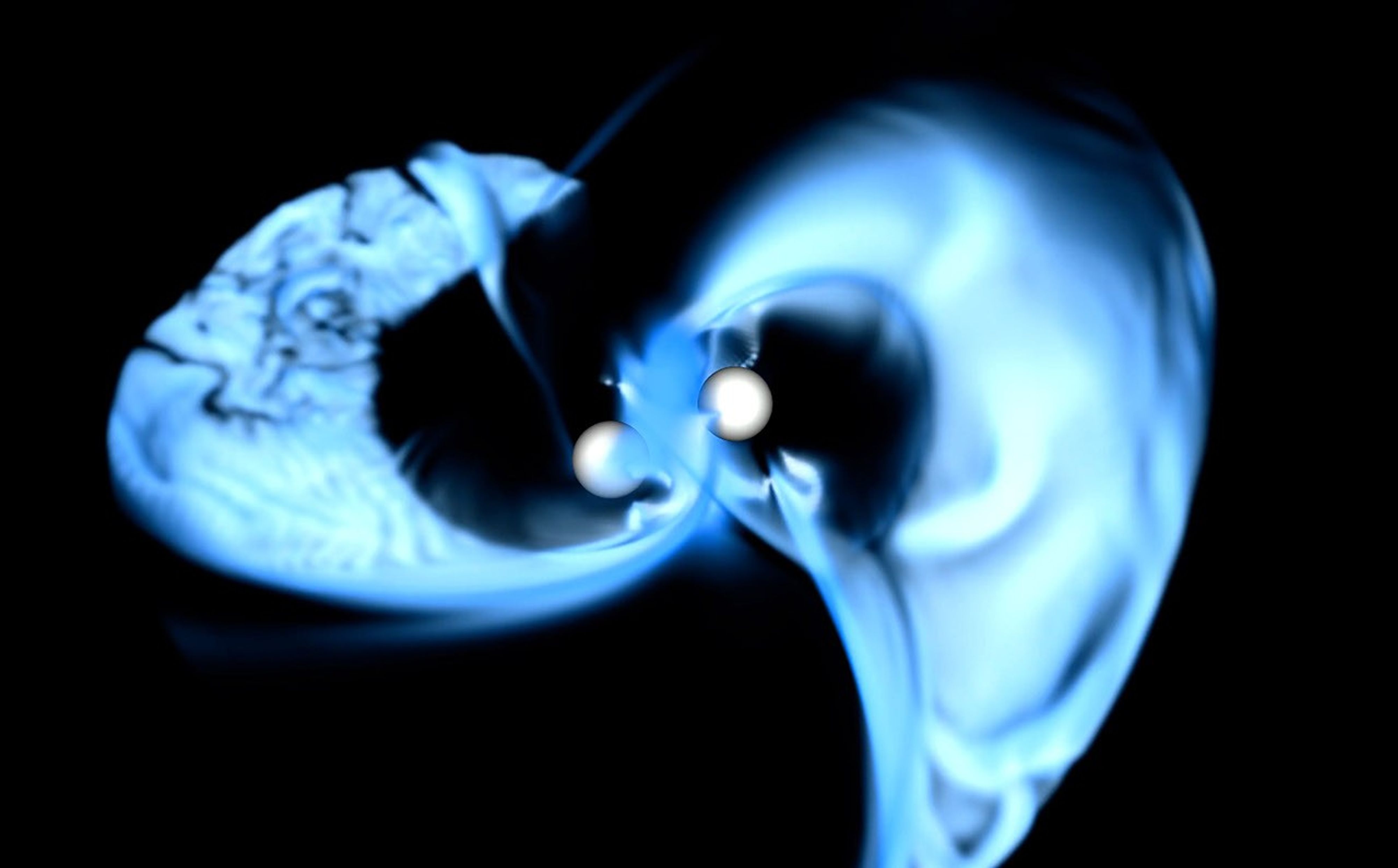
A new simulation created using a NASA supercomputer has shown how things get messy for merging neutron stars even before they slam together; their magnetospheres, the most powerful magnetic fields in the known universe, entwine and generate chaos.
You may like
A screenshot of a NASA supercomputer simulation showing neutron stars spiraling together, creating magnetic chaos (Image credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/D. Skiathas et al. 2025)
“Just before neutron stars crash, the highly magnetized, plasma-filled regions around them, called magnetospheres, start to interact strongly,” team leader Dimitrios Skiathas, a researcher at NASA’s Goddard Flight Center, said in a statement. “We studied the last several orbits before the merger, when the entwined magnetic fields undergo rapid and dramatic changes, and modeled potentially observable high-energy signals.”
What makes neutron stars so extreme?
When stars with around the same mass as the sun run out of hydrogen, the fuel necessary for nuclear fusion in their cores, their cores collapse and their outer layers swell out and are eventually lost. This leads to the stars ending their lives as smoldering stellar embers called white dwarfs.
However, the situation is different for stars with around 10 times the mass of the sun and more. When their hydrogen-depleted cores collapse, the extra mass generates the pressure and temperatures needed to allow the helium, created in these cores over millions of years of hydrogen fusion, to fuse, forming even heavier elements.
This repeated process of fuel exhaustion, collapse and reignition continues until the massive star’s heart is filled with iron. When this final collapse happens, shockwaves ripple out to the star’s outer layers, which are blown away in a supernova explosion, taking with them the vast majority of the star’s mass.
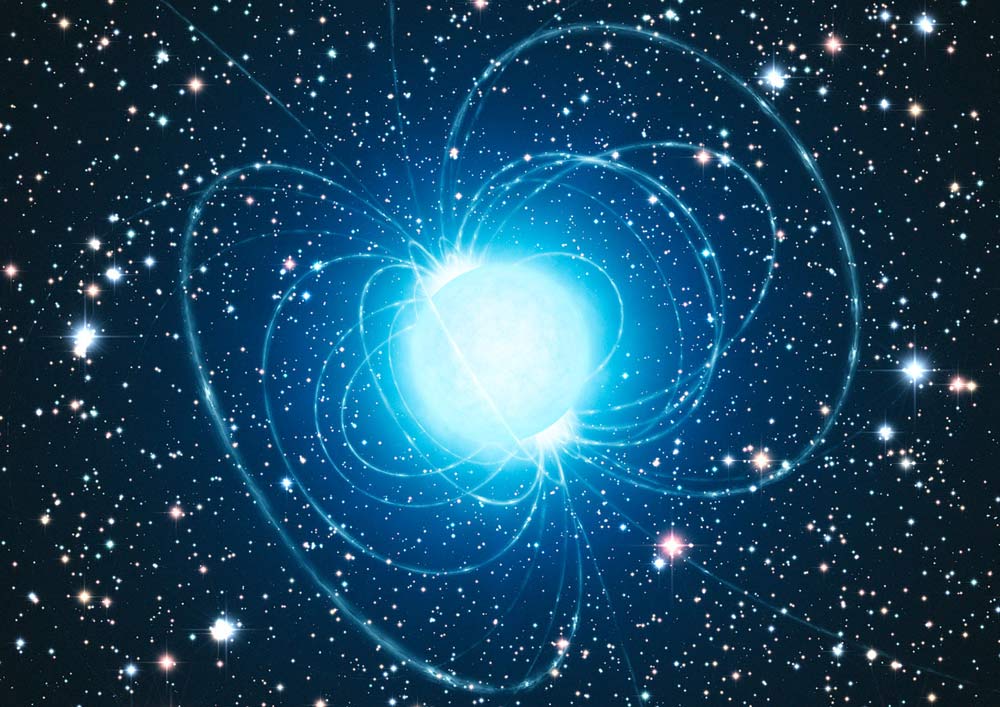
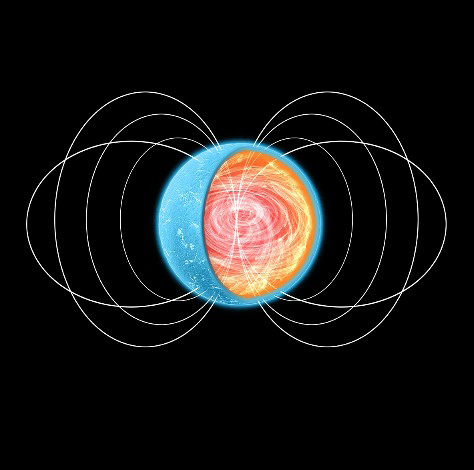
The result is a stellar remnant with a mass between one and two times the mass of the sun, filled with neutron-rich matter crammed into a width of around 12 miles (20 kilometers). The rapid crushing down of this stellar core doesn’t just create a body of incredible density, but also creates magnetic fields that can be 1 quadrillion times stronger than Earth’s magnetosphere.
The interior of a neutron star (Image credit: University of Alicante)
Massive stars are often found in binary pairs with a stellar companion, and in these cases, when both stars die, a neutron star binary is the result. As the two dead stars swirl around each other, they generate ripples in spacetime called gravitational waves, which carry away angular momentum. This results in the neutron star binary tightening. In other words, the stellar remnants move closer, causing them to emit gravitational waves of higher frequencies, losing angular momentum more rapidly and drawing together even faster.
This ends when the neutron stars are close enough to each other for their gravity to take over, leading to an inevitable collision and merger. This causes a blast of high-energy radiation called a gamma-ray burst (GRB), a final screech of gravitational waves, and sends out a spray of neutron-rich matter, which allows a process to occur that generates very heavy but unstable elements. These eventually decay to create gold, silver, and other metals heavier than iron. The decay also creates a glow that astronomers call a kilonova.
You may like
The fact that these events are responsible for the creation of some of our most precious and important elements, as well as bright cosmic phenomena like GRBs and kilonovas, means there has been a heavy bias toward studying the aftereffects of neutron star mergers.
Skiathas and colleagues took a different approach, looking in more depth at what happens prior to the neutron stars meeting.
Messy magnetism
To consider the 7.7 milliseconds prior to neutron stars merging, the team turned to NASA’s Pleiades supercomputer at NASA’s Ames Research Center, creating over 100 simulations of a system of two neutron stars, each with around 1.4 times the mass of the sun.
“In our simulations, the magnetosphere behaves like a magnetic circuit that continually rewires itself as the stars orbit. Field lines connect, break, and reconnect while currents surge through plasma moving at nearly the speed of light, and the rapidly varying fields can accelerate particles,” team member Constantinos Kalapotharakos of NASA Goddard said in the statement. “Following that nonlinear evolution at high resolution is exactly why we need a supercomputer!”
The team’s main aim was to investigate how the magnetic fields of these stellar remnants impacted light, or electromagnetic radiation in technical terms, during the final orbits of the neutron stars around each other.
“Our work shows that the light emitted by these systems varies greatly in brightness and is not distributed evenly, so a far-away observer’s perspective on the merger matters a great deal,” team member Zorawar Wadiasingh of the University of Maryland, College Park, and NASA Goddard, added in the statement. “The signals also get much stronger as the stars get closer and closer in a way that depends on the relative magnetic orientations of the neutron stars.”
The simulations revealed that respective magnetic fields of the neutron stars swept out behind them as they orbited each other, connecting the stellar remnants, then breaking, then reconnecting once again.
An illustration of a neutron star with an incredibly powerful magnetic field, also known as a magnetar (Image credit: ESO/L. Calçada)
The researchers were also able to use Pleiades to simulate how electromagnetic forces impacted the surfaces of the neutron stars. The aim of this was to determine how magnetic stress accumulates in such systems, but future modeling will be needed to determine how magnetic interplay plays a role in the final moments of a neutron star merger.
“Such behavior could be imprinted on gravitational wave signals that would be detectable in next-generation facilities,” team member and NASA Goddard researcher Demosthenes Kazanas said in the statement. “One value of studies like this is to help us figure out what future observatories might be able to see and should be looking for in both gravitational waves and light.”
The researchers were able to use the simulated magnetic fields to identify the points where the highest-energy emissions were created and how these emissions would propagate through the environment of the neutron star merger.
An illustration shows a gamma-ray burst erupting from the site of a neutron star merger. (Image credit: Robert Lea (created with Canva))
The researchers found that regions around neutron star mergers produce gamma-rays with high energy, but this radiation was unable to escape. That was because gamma-ray photons, individual particles of light, were rapidly transformed into pairs of electrons and positrons. However, lower-energy gamma-rays were able to escape the neutron star merger along with even lower-energy radiation like X-rays.
This means future gamma-ray space telescopes, particularly those with wide fields of view, could be used to detect signals from neutron stars on the brink of merging. One other way these systems could be studied before a merger in the future is via the detection of gravitational waves.
The NASA/European Space Agency project Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) could be particularly useful in this regard. Set to launch in the mid-2030s, LISA will be the first space-based gravitational wave detector, benefiting from a much greater sensitivity than the current generation of Earth-based detectors, including the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO).The team’s results were published on Nov. 20, 2025 in The Astrophysical Journal.