November 14, 2025: With the waning crescent moon before sunrise, look for the Andromeda Galaxy, the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The Great Square of Pegasus guides the way to this deep sky object visible from rural settings without optical assistance.
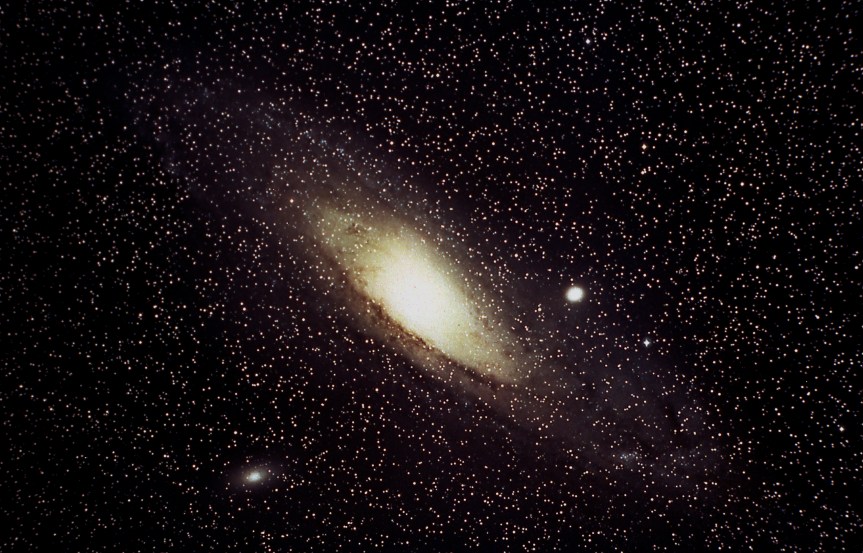 Image Caption – The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31 since it is the 31st object on Messier’s list of diffuse sky objects, is the nearest large galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. Our galaxy is thought to look much like Andromeda. (NASA photo)
Image Caption – The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31 since it is the 31st object on Messier’s list of diffuse sky objects, is the nearest large galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. Our galaxy is thought to look much like Andromeda. (NASA photo)
by Jeffrey L. Hunt
Chicago, Illinois: Sunrise, 6:39 a.m. CST; Sunset, 4:31 p.m. CST. Times are calculated by the US Naval Observatory’s MICA computer program. Check local sources for sunrise and sunset times.
Related Articles
Venus Summary Article
The Starry Night
With the moon at the waning crescent phase and visible before sunrise, look for dimmer celestial bodies beyond the solar system, known as deep sky objects in astronomy. This is the season to look for the galaxy closest to our Milky Way galaxy.
About two hours after sunset, after evening twilight ends, step outside and look around the sky. At this hour, Saturn, in the south-southeast, is the closest celestial body. Uranus is low in the eastern sky, and Neptune, invisible without optical assistance, is in the same binocular field with the Ringed Wonder.
Every other point of light is a star with characteristics broadly similar to the sun. Deneb, the bright star nearly overhead in the west, is the most distant star visible without optical assistance. Its distance is estimated at 1,400 light years, and it shines with the intensity of about 50,000 suns.
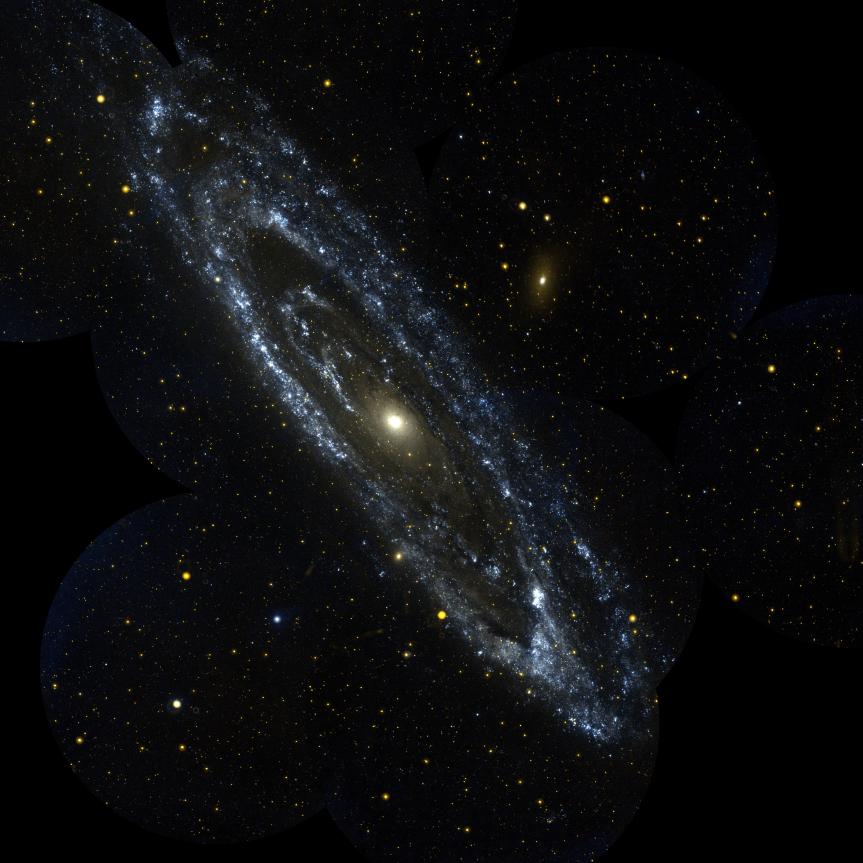 Photo Caption – The Great Galaxy in Andromeda (Messier 31) from the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (Photo Credit: NASA/JPL/California Institute of Technology)
Photo Caption – The Great Galaxy in Andromeda (Messier 31) from the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (Photo Credit: NASA/JPL/California Institute of Technology)
Beyond these stars is another stellar island in the universe — the Great Andromeda Galaxy. It has been in the morning sky since earlier this year and began appearing in the eastern evening sky near summer’s midpoint. Now, after autumn’s midpoint, it is higher in the sky at a more convenient time, especially with earlier sunsets and a morning moon.
Pegasus and Andromeda
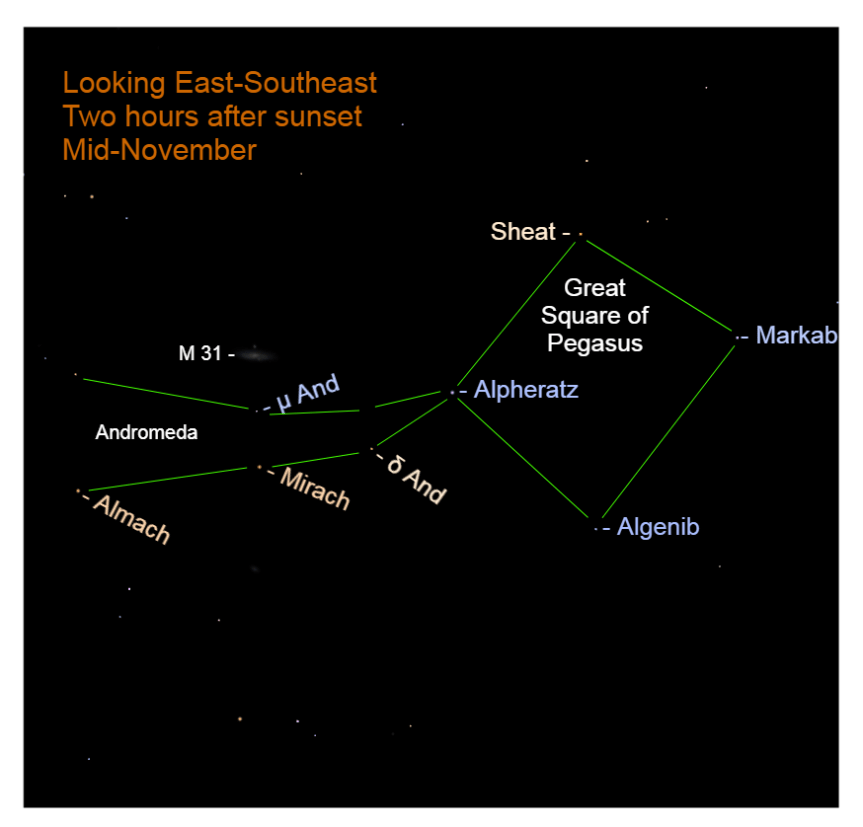 Chart Caption – 2025, Mid-November: The Andromeda galaxy, M 31, is visible in the southeastern sky after evening twilight ends.
Chart Caption – 2025, Mid-November: The Andromeda galaxy, M 31, is visible in the southeastern sky after evening twilight ends.
Look in the southeast for a large box of stars about the same brightness as those in the Big Dipper. The shape is the Great Square of Pegasus. At this orientation, it appears like a diamond. The eastern star, Alpheratz, is part of Andromeda but completes the Square.
In addition to Alpheratz (“the horse’s navel”), the square’s other stars are:
• Sheat – “the leg;”
• Markab – “riding” or “that which is carried;”
• Algenib – “the side.”
Andromeda appears as two strands of stars beginning at Alpheratz and extending northward, nearly parallel to the horizon. Its named stars are:
• Mirach – “the loins;”
• Almach – “the earth-kid.”
The galaxy is visible beyond these stars and its distance is calculated at 2.2 million light years. It is visible from rural settings without optical assistance.
Finding the Galaxy
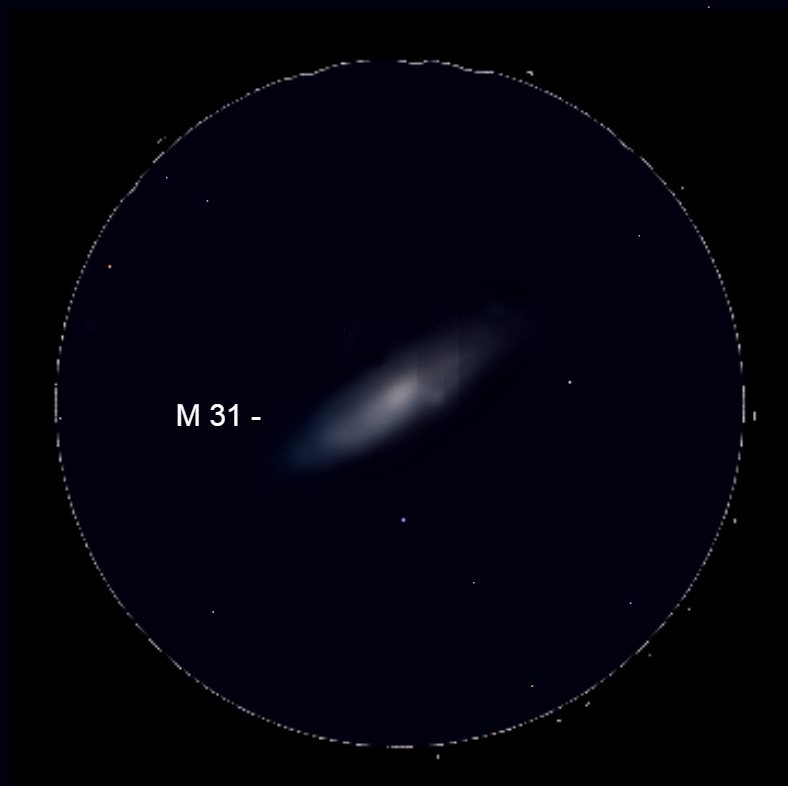 Chart Caption – The Andromeda galaxy is spectacular through a binocular.
Chart Caption – The Andromeda galaxy is spectacular through a binocular.
To locate it, start at Alpheratz and then move to Delta Andromedae (δ And) and Mirach. Then move upward from Mirach. The galaxy is visible just above that star. It is often first seen from peripheral vision as a large cloud, larger than the moon. Across its diameter, it spans six times the moon’s apparent size.
It is best viewed through a binocular because it extends beyond a telescope’s eyepiece. Even then, it appears thin because we see the galaxy highly tilted.
The Galaxy
Before telescopes revealed its true nature, the galaxy was listed as the “Little Cloud” in early celestial catalogs. It is the 31st entry in Charles Messier’s 18th-century catalog of over 100 objects that could be mistaken for comets. Other items in the Messier list show similar characteristics.
 Image Caption – The largest NASA Hubble Space Telescope image ever assembled, this sweeping bird’s-eye view of a portion of the Andromeda galaxy (M31) is the sharpest large composite image ever taken of our galactic next-door neighbor. Though the galaxy is over 2 million light-years away, The Hubble Space Telescope is powerful enough to resolve individual stars in a 61,000-light-year-long stretch of the galaxy’s pancake-shaped disk. (NASA Photo)
Image Caption – The largest NASA Hubble Space Telescope image ever assembled, this sweeping bird’s-eye view of a portion of the Andromeda galaxy (M31) is the sharpest large composite image ever taken of our galactic next-door neighbor. Though the galaxy is over 2 million light-years away, The Hubble Space Telescope is powerful enough to resolve individual stars in a 61,000-light-year-long stretch of the galaxy’s pancake-shaped disk. (NASA Photo)
Today, backyard observers participate in Messier marathons, attempting to view all the objects on his list. Some complete it near a New Moon around the time of the vernal equinox when all can be seen in a single night. Others complete their observations at each season.
About 100 years ago, astronomers debated the nature of the spiral nebulae. Were they gas clouds or collections of stars inside the Milky Way? When large telescopes resolved individual stars and their distances were calculated, astronomers realized these were separate galaxies beyond our own — immense and innumerable.
With the moon in a favorable phase and location for the next several evenings, look for the Andromeda Galaxy. It is visible on moonless nights through early spring until it disappears into western evening twilight.
LATEST ARTICLES
 2025, November 14: Look for the Andromeda Galaxy on November Evenings
2025, November 14: Look for the Andromeda Galaxy on November Evenings
November 14, 2025: With the waning crescent moon before sunrise, look for the Andromeda Galaxy, the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The Great Square of Pegasus guides the way to this deep sky object visible from rural settings without optical assistance.
 2025, November 13: Waning Crescent Moon: Find Uranus and Neptune in the Night Sky
2025, November 13: Waning Crescent Moon: Find Uranus and Neptune in the Night Sky
November 13, 2025: With the moon returning to its waning crescent phase, look for Uranus and Neptune. Neptune appears in the same binocular field with Saturn, while Uranus is in front of Taurus near the Pleiades.
 2025, November 12-14: Morning Moon with Leo
2025, November 12-14: Morning Moon with Leo
November 12-14, 2025: After passing Jupiter, the morning moon crosses in front of Leo, the westward-facing Lion. Watch the lunar orb step eastward past Regulus, Rho Leonis, and Denebola. Each morning the moon wanes and appears farther eastward in the southern sky before sunrise.
November 11, 2025: Jupiter’s retrograde begins tonight, marking the start of its westward motion against Gemini’s stars. Watch the Jovian Giant rise earlier each night as Earth overtakes it, leading to opposition and a transition from the morning sky to evening visibility.
 2025, November 9-10: Moon Passes Between Jupiter and Pollux
2025, November 9-10: Moon Passes Between Jupiter and Pollux
November 9-10, 2025: During the night of November 9–10, 2025, the gibbous moon steps eastward between Jupiter and Pollux, one of the Gemini Twins. Watch the lunar orb rise in the east-northeast, glide between the bright planet and star, and shine high in the southwest by morning twilight.
Like this:
Like Loading…
Related


