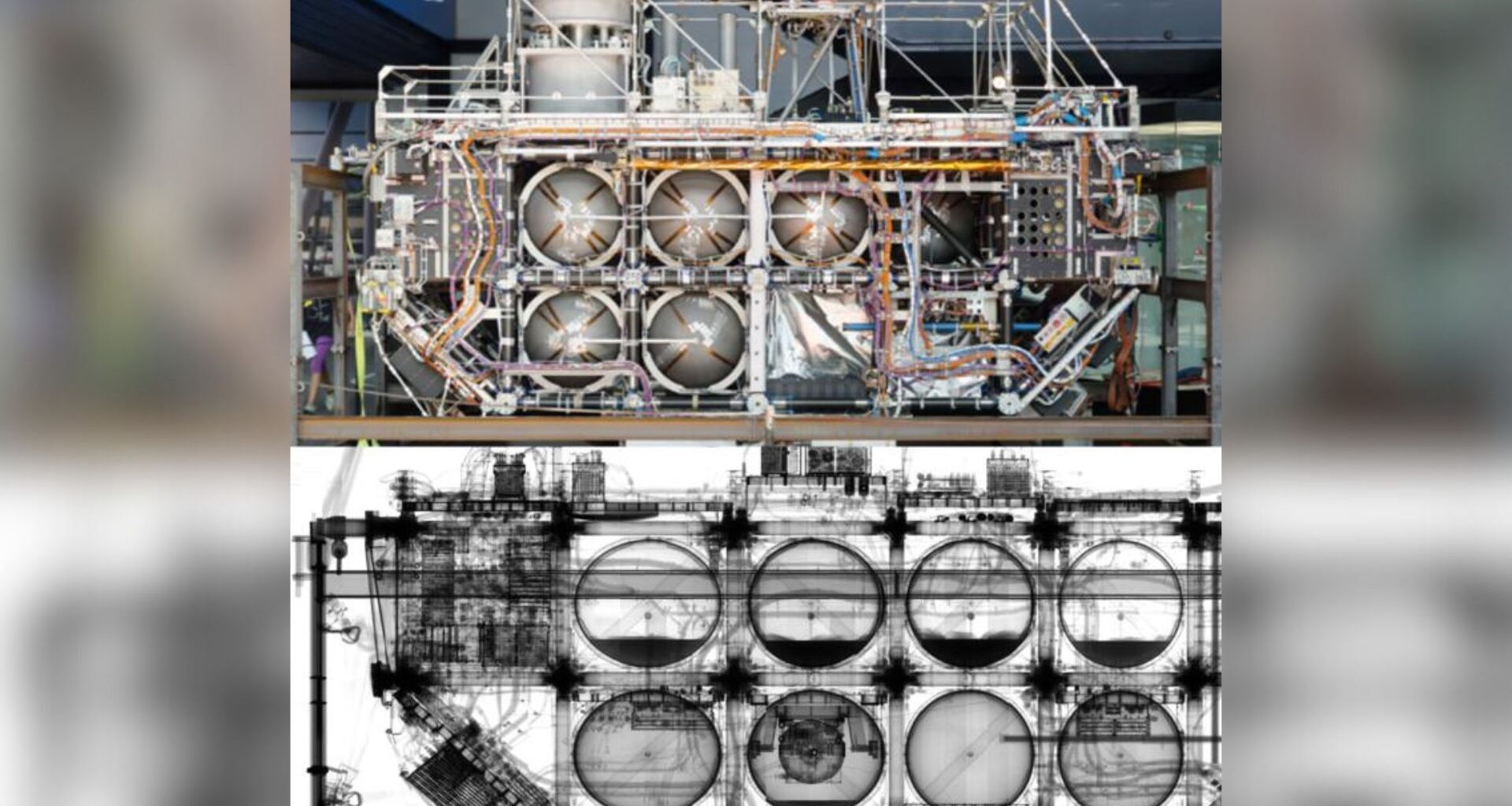
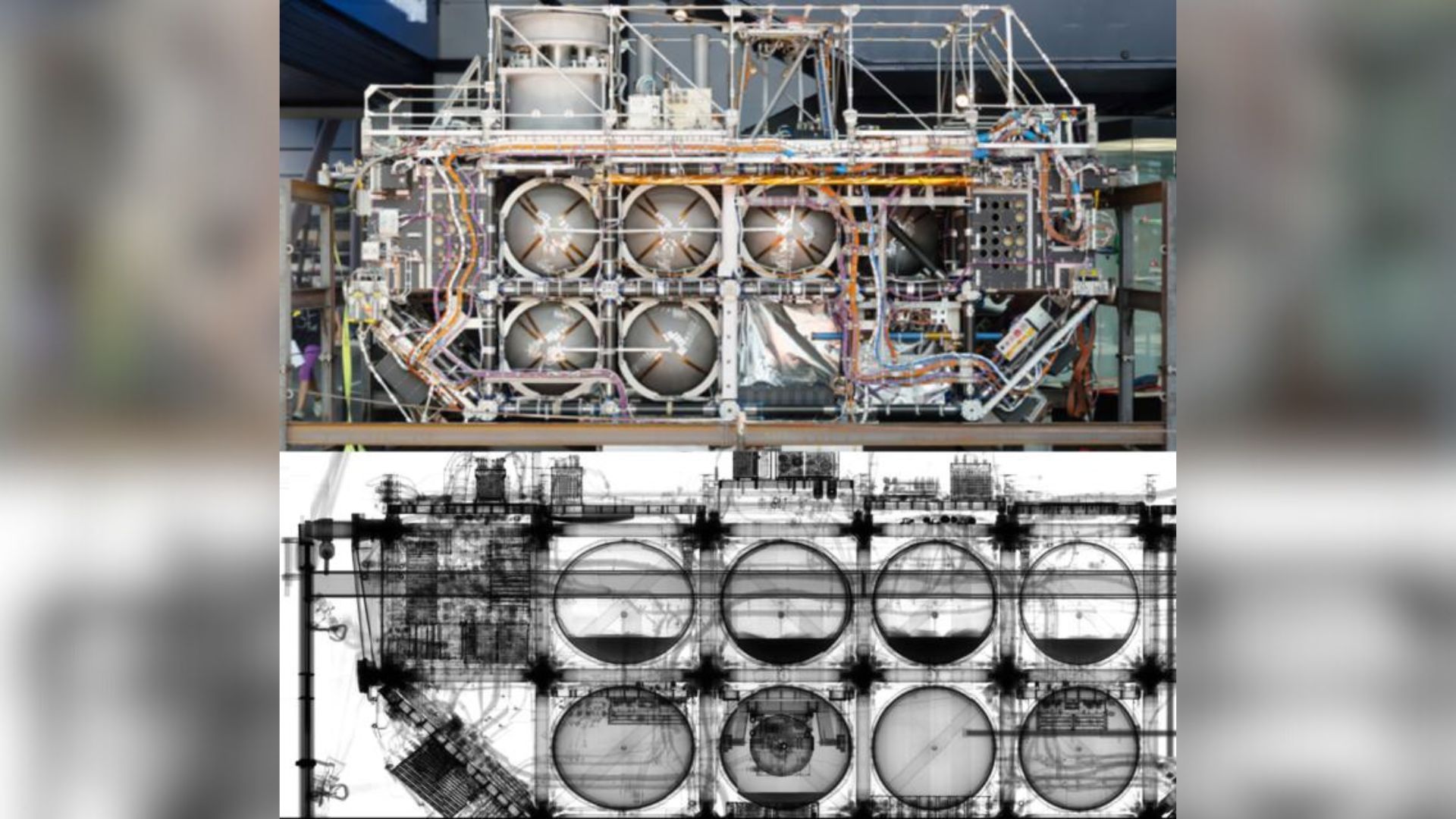
In a hangar outside Zurich, a veteran of low Earth orbit lay under a kind of medical scanner no spacecraft was ever designed for. The patient was the European Retrievable Carrier mission, or EURECA, a 16.-4-foot-long (5 meters) European satellite that flew on the space shuttle Atlantis in early 1992 and, unusually for a satellite, actually came home. Instead of engineers with wrenches, its exam team of researchers aimed something far more penetrating than a flashlight at its aluminum skin.
Using a high-energy X-ray system, they turned the satellite effectively transparent, revealing fuel and gas tanks, hidden residues of cleaning solutions, and the modular skeleton that once held 15 scientific instruments steady in orbit. It’s the kind of “full-body scan” that, until now, has mostly been reserved for people, not hardware that’s been to space and back.
X-rays are already the quiet workhorses of modern life, from hospital radiology to airport security scanners and industrial non-destructive testing. They are invaluable when you need to see inside something without destroying it. In engineering, this often means looking for cracks or voids in aircraft components, checking welds, or inspecting complex assemblies. The recent test with EURECA, published in the October issue of the journal Acta Astronautica takes that same principle and scales it up to an entire flown satellite. It shows not only that such a scan is possible, but that it can reveal details that matter for the future of reusable space hardware.
You may like
Where is it?
This image was taken in the laboratory of the Empa Center for X-ray Analytics in Dübendorf, Germany.
The recent study turned the EURECA satellite almost transparent. (Image credit: Empa, CC BY 4.0)Why is it amazing?
This X-ray study exposed what time and stress have done to the spacecraft. The researchers found cracks in some of EURECA’s composite struts, as well as fractures and deformations in several scientific instruments that remained on board. Some of that damage could have occurred during the violent minutes of launch, as the satellite endured vibrations and acceleration. Other defects may have built up slowly during months in orbit, where EURECA was exposed to strong radiation, large temperature swings between sunlight and shadow, and tiny impacts from micrometeoroids and debris. Reentry and landing add yet another phase of stress. X-rays alone cannot say exactly when each crack formed, but they show clearly where the structure is most vulnerable.
The timing of this research is key, as the number of active satellites in Earth orbit has now exceeded 10,000, with thousands more being launched each year. On top of that, there are decades’ worth of spent rocket stages, dead satellites, and fragments from collisions and explosions. This cloud of space debris poses risks to functioning satellites and to crewed missions. One proposed part of the solution is greater reusability, spacecraft and upper stages that can survive, return, and fly again, rather than becoming junk after a single use.
Want to learn more?
You can learn more about space junk and satellites orbiting Earth.