HER2 remains one of the most therapeutically actionable oncogenic drivers in solid tumors, most prominently in breast and gastric cancers, and increasingly across a broader spectrum of HER2-expressing or HER2-mutant malignancies, including lung cancer. While multiple HER2-targeted agents are already integrated into clinical practice, resistance, cumulative toxicity, and heterogeneous HER2 expression continue to limit durable benefit.
GSK5764227, also known as HS-20093, is an investigational HER2-directed antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) being developed through a collaboration between GSK and Hansoh Pharma. The program reflects a broader strategic shift toward next-generation ADCs engineered to improve tumor selectivity, payload delivery, and therapeutic index compared with earlier HER2-targeted platforms.
Although still in early clinical development, GSK5764227 is positioned as a potentially differentiated HER2 ADC designed to address limitations observed with first-generation conjugates.

Molecular Design and Mechanism of Action
GSK5764227 is composed of three core elements typical of modern ADC architecture: a HER2-specific monoclonal antibody, a cleavable linker, and a highly potent cytotoxic payload. The antibody component binds HER2 expressed on tumor cells, enabling selective internalization of the conjugate via receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Once internalized, lysosomal processing releases the cytotoxic payload into the tumor cell, inducing cell death through direct DNA damage or disruption of critical cellular processes, depending on the payload class. While detailed public disclosure of the exact payload chemistry remains limited, the design philosophy aligns with contemporary ADC strategies favoring high-potency payloads with controlled bystander effect, allowing activity even in tumors with heterogeneous HER2 expression.
This mechanism positions GSK5764227 within the evolving paradigm of HER2 ADCs that aim not only to target HER2-overexpressing tumors but also to extend activity into HER2-low or HER2-heterogeneous disease contexts.
Rationale for Clinical Development
Despite the success of HER2-targeted therapies, several unmet needs persist. Many patients develop resistance after exposure to trastuzumab-based regimens, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, or earlier ADCs. In addition, cumulative toxicities, particularly hematologic and pulmonary events observed with some payload classes, can limit long-term use.
GSK5764227 was engineered with the intent to optimize drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR), linker stability, and tumor-selective payload release, thereby improving efficacy while minimizing off-target toxicity. This approach reflects lessons learned from prior ADC programs, where premature payload release or excessive bystander effect contributed to safety concerns.
Early Clinical Development Program
GSK5764227 is currently being evaluated in early-phase clinical studies enrolling patients with advanced or metastatic HER2-expressing solid tumors. These trials are designed to assess safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary antitumor activity across a range of HER2-driven malignancies.
Dose-escalation cohorts follow standard phase I objectives, including identification of the recommended dose for expansion and characterization of dose-limiting toxicities. Expansion cohorts are expected to explore specific tumor types of interest, such as HER2-positive breast cancer, gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer, and potentially HER2-altered lung cancer.
At present, publicly available information emphasizes safety profiling and biological feasibility, rather than definitive efficacy outcomes, consistent with the early stage of development.
ARTEMIS Trial: First-in-Human Clinical Evaluation
The clinical development of GSK5764227 is anchored by the ARTEMIS study, a first-in-human, multicenter phase I trial designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary antitumor activity of HS-20093 in patients with advanced or metastatic HER2-expressing solid tumors.
Study Design and Objectives
ARTEMIS follows a traditional dose-escalation and dose-expansion framework. The primary objectives include identification of dose-limiting toxicities, establishment of the recommended dose for expansion, and characterization of the safety profile. Secondary and exploratory objectives include pharmacokinetic assessment, evaluation of HER2 expression as a predictive biomarker, and early signals of clinical activity across tumor types.
The study enrolls heavily pretreated patients with limited remaining therapeutic options, reflecting the early development stage of the agent.
Early Clinical Signals from ARTEMIS
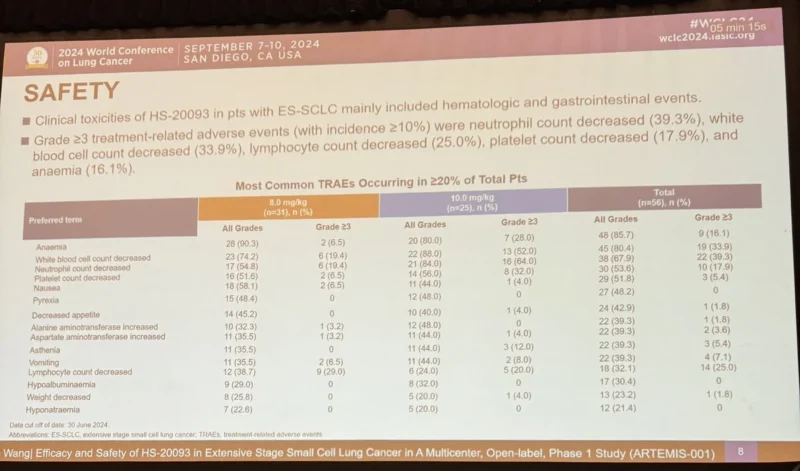
Initial data from ARTEMIS indicate that GSK5764227 demonstrates manageable safety consistent with the known class effects of HER2-directed ADCs. Reported treatment-emergent adverse events have been predominantly low grade, with careful monitoring for hematologic toxicity, gastrointestinal symptoms, and pulmonary events.
Importantly, early observations suggest biological activity across multiple HER2-expressing tumor types, including patients previously treated with other HER2-targeted therapies. While formal response rates and durability metrics remain immature and have not been fully disclosed, these early signals support continued dose exploration and cohort expansion.
From a translational perspective, pharmacokinetic analyses indicate predictable exposure and support the intended dosing schedule. Ongoing correlative studies within ARTEMIS are expected to further clarify relationships between HER2 expression level, ADC exposure, and clinical activity.
Safety Considerations and Class Effects
As with other HER2-directed ADCs, anticipated safety considerations for GSK5764227 include hematologic toxicity, gastrointestinal adverse events, fatigue, and potential pulmonary effects. ADC-specific risks such as interstitial lung disease, hepatotoxicity, and cumulative myelosuppression remain key areas of monitoring.
Preclinical optimization of linker stability and payload release kinetics is intended to mitigate these risks. However, careful dose optimization and long-term follow-up will be critical to defining the therapeutic window of GSK5764227 as development progresses.
Positioning Within the HER2 Therapeutic Landscape
The HER2 space has become increasingly crowded, particularly with the emergence of highly effective ADCs. Differentiation for GSK5764227 will depend on its ability to demonstrate one or more of the following: improved tolerability, activity in HER2-low or heterogeneous tumors, efficacy after progression on prior HER2 ADCs, or a favorable combination profile with immunotherapy or targeted agents.
From a strategic standpoint, the involvement of GSK underscores interest in building a diversified ADC portfolio, while Hansoh’s contribution reflects its growing footprint in innovative biologics and global oncology development.
Future Directions
Ongoing and planned clinical studies will clarify the role of GSK5764227 in HER2-driven cancers. Key questions include whether the agent can overcome resistance to existing HER2 therapies, how it performs across varying levels of HER2 expression, and whether its safety profile supports use earlier in the treatment sequence or in combination regimens.
As additional data emerge, GSK5764227 may contribute to the next wave of HER2-targeted strategies aimed at extending the benefits of precision oncology to broader patient populations.

