On September 26th, Jensen Huang of NVIDIA discussed topics such as AI industry trends, the future of computing, and NVIDIA’s moat in a recent interview. He also revealed for the first time the reasons behind NVIDIA’s $100 billion investment in OpenAI.
He believes that the failure of Moore’s Law means that the cost and energy consumption of transistors are no longer significantly improving, and traditional computing can no longer provide the necessary performance enhancements. Against this backdrop, the demand for AI is experiencing double exponential compound growth. Firstly, the usage of AI by users is exploding exponentially. Secondly, there has been a qualitative change in the way of AI inference. It has evolved from a simple one – shot answer to a complex “thinking” process. This upgrade of the inference paradigm has led to an exponential increase in the amount of computation required for each use of AI, and it is expected to bring a 10 – billion – fold increase in inference demand.
The AI infrastructure is triggering an industrial revolution. General purpose computing has come to an end, and the existing global computing infrastructure worth trillions of dollars (including search, recommendation engines, data processing, etc.) is migrating from using CPUs to AI – accelerated computing. NVIDIA’s AI infrastructure will generate tokens to enhance human intelligence, ultimately bringing huge economic benefits. The current annual market size of $400 billion is expected to grow at least 10 times in the future.
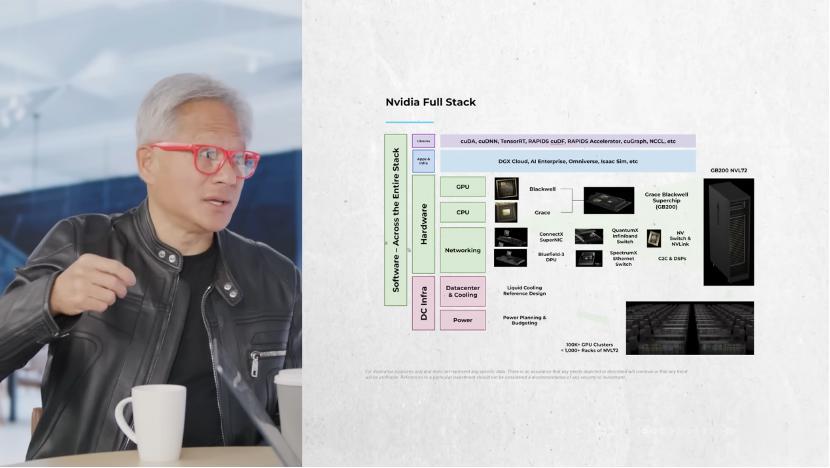
NVIDIA’s strategic focus is not just being a chip company but an AI infrastructure partner, building a strong competitive barrier through “Extreme Co – Design”. Since the performance improvement of a single chip is limited, NVIDIA must innovate and optimize simultaneously across the entire stack, including algorithms, models, systems, software, networks, and chips. It is this full – stack design that enables NVIDIA to achieve a performance leap, such as from Hopper to Blackwell, in a short period.
Jensen Huang emphasized that the core value of the strategy is to provide the highest performance per unit of energy consumption. For hyperscale customers with limited power, even if the competitor’s chips are free, the huge opportunity cost loss caused by giving up the NVIDIA system is unacceptable.
In terms of business cooperation, NVIDIA regards OpenAI as the next trillion – dollar hyperscale company and is collaborating with it to build the AI infrastructure, including assisting OpenAI in building its first AI factory.
Key points from Jensen Huang’s interview:
1. The demand for AI computing is growing exponentially, and inference is the key driving force
Currently, there are three rules for AI training: pre – training, post – training, and inference. Traditional inference is “one shot”, but the new – generation inference has evolved into “thinking”, which means conducting research, checking real – world situations, and learning before giving an answer. “Thinking” leads to an exponential increase in the amount of computation required for each use of AI. Therefore, the inference demand is expected to grow 10 billion times. This astonishing growth comes from two exponential compound effects: one is the exponential growth in the number of AI customers and usage rates, and the other is the exponential growth in the amount of computation required for each use.
2. OpenAI is expected to become the next trillion – dollar hyperscale company
Jensen Huang believes that OpenAI is very likely to become the next trillion – dollar hyperscale company, providing both consumer – grade and enterprise – grade services. NVIDIA’s investment in OpenAI is considered “one of the wisest investments imaginable”. NVIDIA is helping OpenAI build its own AI infrastructure for the first time, covering all aspects of chips, software, systems, and AI factories.
3. The AI infrastructure is a new industrial revolution with huge market potential
The construction of the AI infrastructure is regarded as an industrial revolution. Most structured and unstructured data processing still runs on CPUs. Jensen Huang predicts that in the future, all this data processing will migrate to AI, which is a huge market. The existing global computing infrastructure worth trillions of dollars, including traditional hyperscale computing infrastructure such as search, recommendation engines, and shopping, needs to shift from using CPUs to using GPUs for AI – accelerated computing. The AI infrastructure will generate tokens to enhance human intelligence, ultimately generating huge economic benefits. For example, a $10,000 AI can increase the productivity of a $100,000 – salaried employee by 2 to 3 times. Currently, the annual market size of the AI infrastructure is about $400 billion, but the overall potential market size is expected to grow at least 10 times in the future.
4. Wall Street underestimates NVIDIA’s growth rate
Wall Street analysts predict that NVIDIA’s growth will stagnate in 2027. Jensen Huang refuted the analysts’ views, believing that the computing resources in the market are still in short supply. He emphasized that the possibility of oversupply is extremely low. Oversupply may only occur when all general purpose computing is converted to accelerated computing, all recommendation engines are based on AI, and all content generation is driven by AI. NVIDIA is responding to market demand, and the future market demand for AI infrastructure is very large.
5. NVIDIA builds its core competitive advantage through “Extreme Co – Design”
Due to the failure of Moore’s Law, the cost and power consumption of transistors remain basically unchanged, and it is currently impossible to improve performance through traditional methods. To address this challenge, NVIDIA has adopted Extreme Co – Design, optimizing and innovating simultaneously at the system, software, network, and chip levels.
Jensen Huang believes that NVIDIA’s powerful system platform advantage forms a competitive moat, even higher than the potential cost advantage of competitors’ ASIC chips. Since customers’ operations are limited by power, they hope to generate the highest revenue per watt of power. NVIDIA’s in – depth and extreme co – design achieves the best performance per watt. If customers give up the NVIDIA system and use lower – performance chips, even if the chips are free, due to the high opportunity cost (possibly losing 30 times the revenue), they will still choose NVIDIA. Therefore, NVIDIA believes that it is building a complex AI factory system, not just chips.
The following is the original interview text:
1. The paradigm revolution and exponential growth of AI computing
Host: Jensen, it’s great to have you back, and of course, my partner Clark Tang.
Jensen Huang: Welcome to NVIDIA.
Host: Your glasses are beautiful. They really look good on you. Now everyone will want you to keep wearing them. They’ll say, “Where are the red glasses?” So it’s been over a year since our last podcast. Now over 40% of your revenue comes from inference. But with the emergence of the chain of reasoning, inference is about to explode.
Jensen Huang: Yes, it’s about to grow 10 billion times. This is something that most people haven’t fully internalized yet. This is an industrial revolution.
Host: To be honest, I’ve been running this podcast every day since then. On the AI time scale, it’s been about 100 years. I was re – watching that podcast episode. Recently, we’ve discussed a lot of things, and for me, the most impressive moment might be when you banged the table. Do you still remember that? There was really a slump in pre – training at that time. People were saying, “Oh my god, pre – training has reached its end.” That was about a year and a half ago. You also said that inference wouldn’t grow 100 times or 1000 times; it would grow 10 billion times. And that brings us to this moment today.
Jensen Huang: Now we have three scaling laws, right? We have the Pre – training Scaling Law, the Post – Training Scaling Law. Post – training is like AI practicing, repeatedly practicing a skill until it gets it right. So it tries many different methods. And to do that, you have to perform inference. So now in reinforcement learning, training and inference have been integrated. That’s what we call post – training. The third one is inference. In the past, inference was done in one shot. But we’re really grateful for this new way of inference – thinking, which happens before the model gives an answer. So now you have three scaling laws. The longer you think, the better the quality of the answer you get. While you’re thinking, you’ll do research, check some factual evidence, learn something, think more, learn more, and then generate an answer. Don’t generate it right away at the beginning. So thinking, post – training, pre – training, we now have three scaling laws instead of one.
Host: You said these things last year, but how confident are you this year about the 10 – billion – fold growth of inference and how far it can elevate the intelligence level? Is it higher? Are you more confident than a year ago?
Jensen Huang: I’m more confident this year. The reason is to look at the current agentic systems. And AI is no longer just a language model. AI is a system composed of language models, all running concurrently. Some are using tools, some are doing research, and there’s a lot more. And all of this is multimodal. Look at the videos already generated by AI. It’s really incredible stuff.

2. OpenAI is expected to become the next trillion – dollar hyperscale company
Host: This really brings us to the groundbreaking moment that everyone has been talking about this week. A few days ago, you announced that huge deal with OpenAI’s Stargate project. You’ll become the preferred partner and invest $100 billion in the company. For a period of time, they’ll build at least a 10 – gigawatt AI data center, and if they use NVIDIA for the data center construction, it could mean up to $400 billion in revenue for NVIDIA. So please help us understand. Tell us something about that partnership. What does it mean to you, and why is this investment so meaningful for NVIDIA?
Jensen Huang: Let me answer the last question first. I think OpenAI is very likely to become the next trillion – dollar hyperscale company. Hyperscale companies are like Meta. Meta is a hyperscale company, and Google is also a hyperscale company. They will have both consumer – facing and enterprise – facing services. OpenAI is very likely to become the next company with a market value of trillions of dollars. If so, this is an opportunity to invest before they achieve this prediction, and these could be one of the smartest investments we can imagine. You have to invest in what you understand. It turns out that we happen to be familiar with this field. So having the opportunity to invest, the return on that money will be very substantial. So we’re very happy to have the investment opportunity. We don’t necessarily have to invest; we’re not obligated to invest, but they’re offering us the opportunity to invest.
Jensen Huang: Now let me start from the beginning. So we’re collaborating with OpenAI on multiple projects. First, the first project is to accelerate the construction of Microsoft Azure, and we’ll continue to do so. And this collaboration is going very well, and we still have several years of construction to do. There’s still trillions of dollars’ worth of work to be done just there. Second is the construction of OCI (Oracle Cloud Infrastructure). I think there are still about five, six, or seven gigawatts to be built. We’ll collaborate with OCI, OpenAI, and SoftBank. Those projects are under contract, and we’re working on them. There’s a lot of work to do. Then the third one is CoreWeave. So the question is, what is this new partnership? This new partnership is about helping OpenAI, collaborating with OpenAI, to build their own self – built AI infrastructure. So this is us directly helping them at the chip level, at the software level, at the system level, and at the AI factory level to become a fully operational hyperscale company. This will still take some time. You know, they’re experiencing two exponential growths. The first exponential growth refers to the exponential growth in the number of customers. The reason is that AI is constantly becoming more powerful, and these use cases are getting better. Almost every application is now connected to OpenAI, so they’re experiencing exponential growth in usage. The second exponential growth is in the computation per use. It’s no longer just one – shot inference; it’s thinking before giving an answer. So these two exponential growths are superimposed on their computing demand. So we can build these different projects. So the last one is a superposition on top of everything they’ve announced and all the work we’ve already been doing with them.
Host: One thing that really interests me is that you think there’s a high probability that it will become a company worth trillions of dollars, and you think it’s a good investment. Meanwhile, you know, they’re building their own. You’re helping them build their own data center. So far, they’ve been outsourcing the data center construction to Microsoft. Now they want to build a full – stack factory on their own.
Jensen Huang: They basically want to establish a relationship with us like the one between Elon and X.
Host: Yes. When you think about the advantages of the Colossus data center, they’re building a full – stack, and it’s a hyperscale cloud service provider. Because if they don’t use all that capacity themselves, they can sell it to others. Just like the Stargate project, they’re building huge capacity. They think they’ll need to use most of it, but it also allows them to sell it to others. It sounds a lot like AWS, GCP, or Azure. Do you mean it like that?
Jensen Huang: Yeah. I think they’ll probably use it themselves, but they want to maintain a direct relationship with us, a direct working relationship and a direct purchasing relationship. Just like what Zuck and Meta do with us, it’s completely direct. Our relationship with Sundar and Google is direct, and our collaboration with Satya and Azure is also direct. Right? So they’ve reached a large enough scale that they think it’s time to start establishing these direct relationships. I’m very happy to support them in this, and everyone agrees with this very much.

3. The AI industrial revolution and market potential
Host: So there’s one thing I’m really curious about. You just mentioned Oracle, $300 billion, Colossus, and what they’re building. We know what the Sovereigns are building, and we know what the hyperscale cloud service providers are building. Sam is talking about a scale of trillions of dollars, but among the 25 sell – side analysts on Wall Street covering your stock, if I look at the consensus forecast, it basically shows that your growth will stagnate starting in 2027. 8% growth from 2027 to 2030. Those 25 people, their only job is to be paid to predict NVIDIA’s growth rate.
Jensen Huang: We’re quite comfortable with this situation. We’re used to it, and we’re fully capable of exceeding these numbers.
Host: I understand that, but there’s an interesting disconnect. I hear this sentence every day on CNBC and Bloomberg. I think it refers to the situation where the shortage will eventually turn into an oversupply. They say, “Well, maybe there will still be a shortage in 2026, but maybe you won’t need those in 2027.” But it’s interesting to me. I think it’s important to point out that these consensus forecasts won’t happen, right? We also aggregate forecasts to make predictions for the company, considering all these numbers. And what this shows me is that even though we’ve been in the AI era for two and a half years, there’s still a huge difference in beliefs. There’s still a difference between what Sam Altman says, what you say, what