In this study, the demographic characteristics, clinical histories, and surgical outcomes of 87 women who underwent hysterectomy were analyzed. The key demographic and clinical parameters of all patients are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of the study population (n = 87).
The mean age was 48.7 ± 7.5 years. A history of two pregnancies was most common (42.5%), and 58.6% had delivered vaginally. At the time of evaluation, 77.0% were premenopausal.Patients’ chief complaints and prior treatments are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Chief complaints and prior medical treatments of the study population (n = 87).
Combined Oral Contraceptive (COC), Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (HMB), Hypertension (HT), Intermenstrual Bleeding (IMB), Levonorgestrel-Releasing Intrauterine Device (LNG-IUD), Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Postmenopausal Bleeding (PMB).
The most common complaints were irregular menstruation (31.0%) and heavy menstrual bleeding (27.6%), followed by postmenopausal bleeding (20.7%), intermenstrual bleeding (10.3%), and combined IMB and HMB (9.2%). Nearly half (47.1%) had received prior medical therapy, most often hormonal therapy (25.3%), COCs (20.7%), or LNG-IUD insertion (13.8%).
Table 3 summarizes physical examination and Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS) findings.
Table 3 Physical examination and pelvic ultrasonography findings of the study population (n = 87).
TVUS revealed no endometrial hyperplasia in 43.7% of patients, while 31.1% had hyperplasia, 20.7% showed irregular endometrium, and 4.6% had a suspicious mass. Uterine myomas were present in 70.1%, most often type 3–5 (40.1%). Lesions ≥ 10 cm were most frequent (18.4%), followed by 3–5 cm (18.4%) and 5–10 cm (17.2%). Adenomyosis was detected in 5.7%, multiple intramural myomas in 13.8%, and small myomas (< 3 cm) in 2.3%. Endometrial polyps were suspected in 16.1%, and anemia was present in 34.5%.
Table 4 summarizes endometrial biopsy findings and AI-generated treatment recommendations.
Table 4 Endometrial biopsy findings and AI-generated treatment recommendations for the study population (n = 87).
Pathological evaluation after endometrial biopsy showed normal histology in 58 patients (66.7%), hyperplasia without atypia in 11 (12.6%), polyps in 11 (12.6%), endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN) in 4 (4.6%), and malignancy in 3 (3.4%).
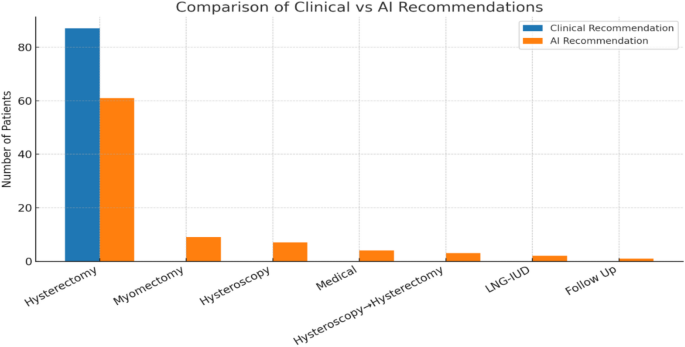
From 87 standardized clinical scenarios assessed by AI, hysterectomy was recommended for 61 patients (70.1%). Less common suggestions included myomectomy (9, 10.3%), hysteroscopy (7, 8.0%), medical therapy (4, 4.6%), hysterectomy after hysteroscopy (3, 3.4%), LNG-IUD (2, 2.3%), and follow-up (1, 1.1%).
Comparison of clinical recommendations and AI-generated treatment suggestions for 87 patients initially scheduled for hysterectomy.
As shown in Fig. 1, each case scenario incorporating clinical presentation, ultrasonographic findings, and relevant history was entered into the ChatGPT-4 model using a standardized prompt. The bar chart illustrates concordance and divergence between AI-generated and clinical decisions, along with the distribution of alternative strategies such as myomectomy, hysteroscopy, medical therapy, LNG-IUD insertion, and follow-up.