In 2023, only 1% of EU market producer enterprises (hereinafter enterprises) were under foreign control. More than half, 60%, were controlled by institutional units from other EU countries, while 40% resided outside the EU.
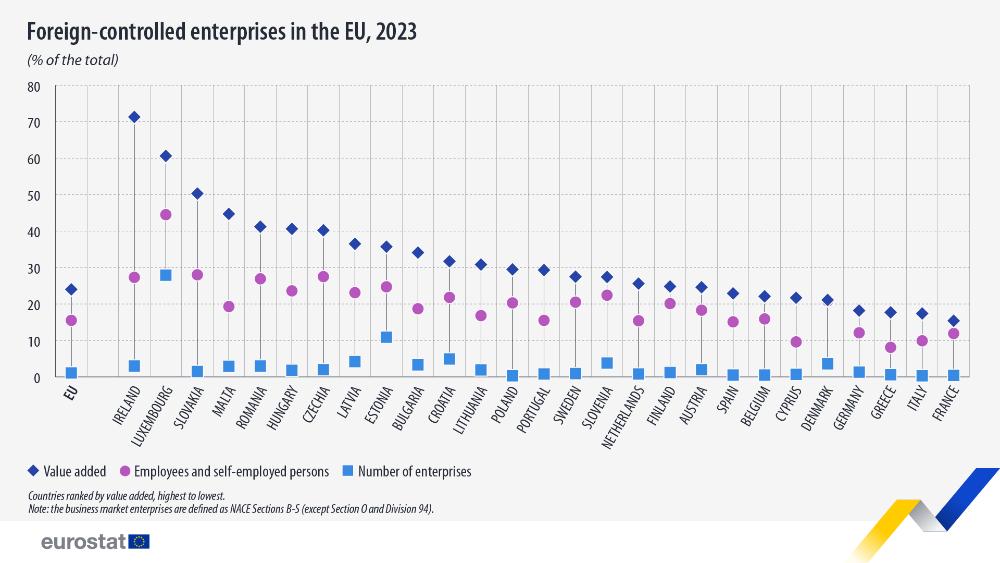
In Luxembourg, foreign-controlled enterprises represented 28% of all enterprises, the highest among EU countries, followed by Estonia (11%). In all other EU countries, foreign-controlled enterprises represented 5% or less of all enterprises, with shares ranging from 0.3% in Poland and Italy to 5% in Croatia.
Although their number is small, contribution of foreign-controlled enterprises to the EU economy in terms of employment and, especially, value added, is significant. These enterprises employed 16% of people working in the EU, and their share of total value added represented 24% of the EU total.
Source dataset: fats_activ
Among EU countries, value added by foreign-controlled enterprises was the highest in Ireland (71%), Luxembourg (61%) and Slovakia (50%). By contrast, the lowest shares of value added were observed in France (15%), Italy (17%) and Greece and Germany (each 18%).
In terms of employees and self-employed persons, foreign-controlled enterprises represented 45% of jobs in Luxembourg, and 28% in Slovakia and Czechia. Conversely, they accounted for 10% of jobs or less in Greece (8%), Cyprus and Italy (each 10%).