 In the deserts of southern Australia, scientists have been captivated by tiny, shimmering glass fragments scattered across the arid terrain. Formed under extreme conditions, these delicate shards have puzzled researchers for decades, as they are neither volcanic in origin nor human-made. Recent studies reveal that these fragments are evidence of a massive asteroid impact that struck Earth millions of years ago. The mystery deepens because the crater such a catastrophic collision would have created remains undiscovered. These glassy remnants, now identified as a new type of tektite called ananguites, act as time capsules, preserving clues about Earth’s violent past. Their discovery not only sheds light on hidden asteroid impacts but also offers insights into our planet’s cosmic history.
In the deserts of southern Australia, scientists have been captivated by tiny, shimmering glass fragments scattered across the arid terrain. Formed under extreme conditions, these delicate shards have puzzled researchers for decades, as they are neither volcanic in origin nor human-made. Recent studies reveal that these fragments are evidence of a massive asteroid impact that struck Earth millions of years ago. The mystery deepens because the crater such a catastrophic collision would have created remains undiscovered. These glassy remnants, now identified as a new type of tektite called ananguites, act as time capsules, preserving clues about Earth’s violent past. Their discovery not only sheds light on hidden asteroid impacts but also offers insights into our planet’s cosmic history.
Rare Australian glass reveals unknown ancient asteroid impact
Tektites are pieces of natural glass formed when a high-energy asteroid impact melts Earth’s surface rock and ejects molten debris across vast distances. Traditionally, tektites have been identified in specific regions and linked to known impact events. However, the newly discovered glass fragments from southern Australia stand apart.Researchers, working with thousands of samples stored at the South Australian Museum, identified 417 pieces that did not match the chemical profile of previously known tektites. Detailed analysis conducted in France confirmed that at least six of these fragments had a chemical composition identical to rare samples first discovered decades ago.“These glasses are unique to Australia and have recorded an ancient impact event we did not even know about,” explained Fred Jourdan, a geochemist at Curtin University.In recognition of the local Indigenous communities, the Pitjantjatjara and Yankunytjatjara, who call themselves Anangu (meaning “human being”), the research team named these fragments ananguites. This naming highlights both the cultural and scientific significance of the discovery.
Mystery of the missing crater: Ananguites reveal a hidden ancient asteroid impact
Typically, asteroid impacts large enough to form tektites also leave behind a visible crater. Such craters can stretch tens or even hundreds of kilometers across. However, despite extensive searches, scientists have been unable to locate the crater associated with the Australian ananguites.Potential locations for the elusive crater include parts of Papua New Guinea, Indonesia, or the Philippines. In these regions, volcanic activity, erosion, and tectonic processes could have obscured or completely erased the impact site over millions of years.Jourdan describes these glass fragments as “tiny time capsules from deep in our planet’s history,” emphasizing how they preserve evidence of ancient events even when the crater itself is missing. This makes ananguites not only scientifically valuable but also a unique window into Earth’s cosmic past.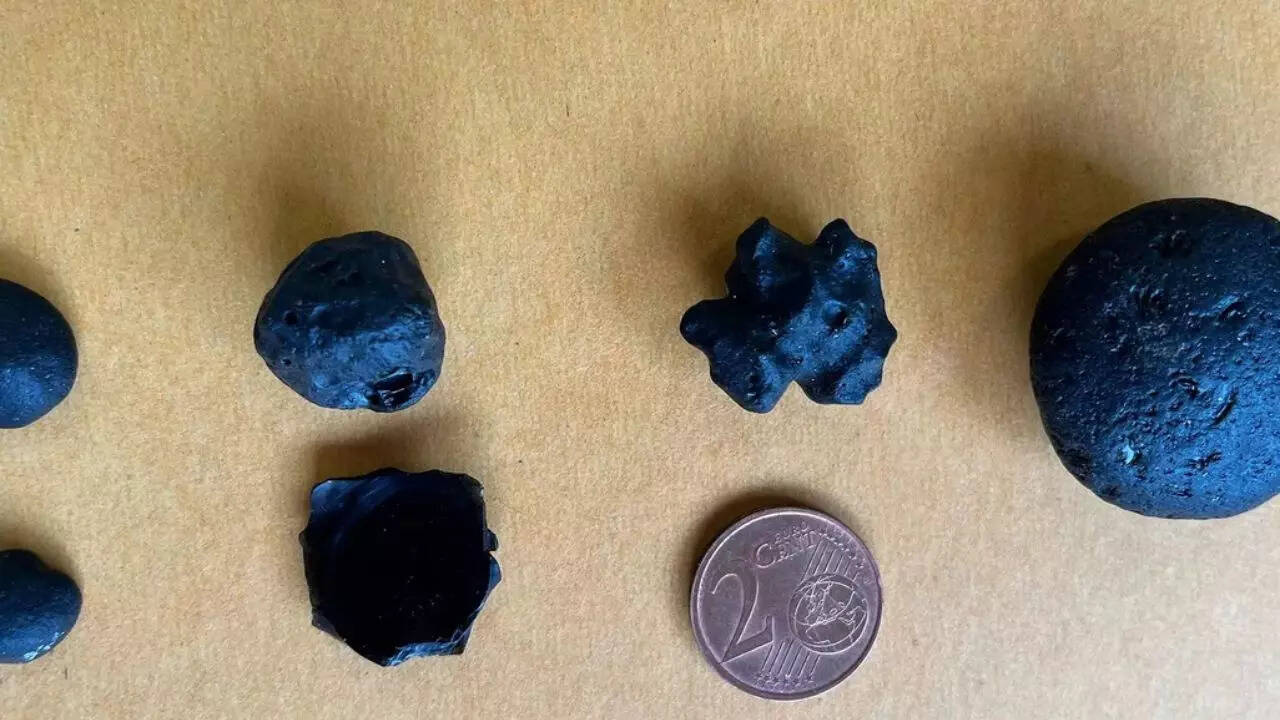
Source: Smithsonian Magazine
Significance for Earth’s asteroid impact history
The discovery of ananguites suggests that Earth may have experienced more large asteroid impacts than scientists previously thought. If an impact can create widespread tektite fields without leaving a clearly identifiable crater, our understanding of the planet’s collision history could be far from complete.Recognizing the frequency and magnitude of past asteroid impacts is critical for understanding both Earth’s geological history and assessing future risks. “Understanding when and how often large asteroids have struck Earth also helps us assess the risk of future impacts, which is important for planetary defense,” Jourdan noted.These findings may prompt a reassessment of regions previously considered free of significant asteroid impacts, suggesting that many more “hidden” craters might exist beneath layers of erosion or volcanic deposits.
Cosmic breadcrumbs Unveiling Earth’s ancient asteroid collisions
While the crater remains hidden, the ananguites themselves serve as silent witnesses to a cataclysmic event that reshaped parts of the Earth millions of years ago. They are more than just geological curiosities—they are fragments of a cosmic story, offering rare insights into how Earth interacts with celestial bodies.Through these tiny glass shards, scientists can piece together the scale and frequency of ancient asteroid impacts, adding depth to our understanding of planetary history and the threats our planet may face in the future. In essence, ananguites are cosmic breadcrumbs, bridging the gap between ancient events in space and their lasting effects on Earth.Also Read | Was that a UFO? SpaceX Falcon 9 rockets 28 Starlink satellites, lighting up Arizona sky like a comet

