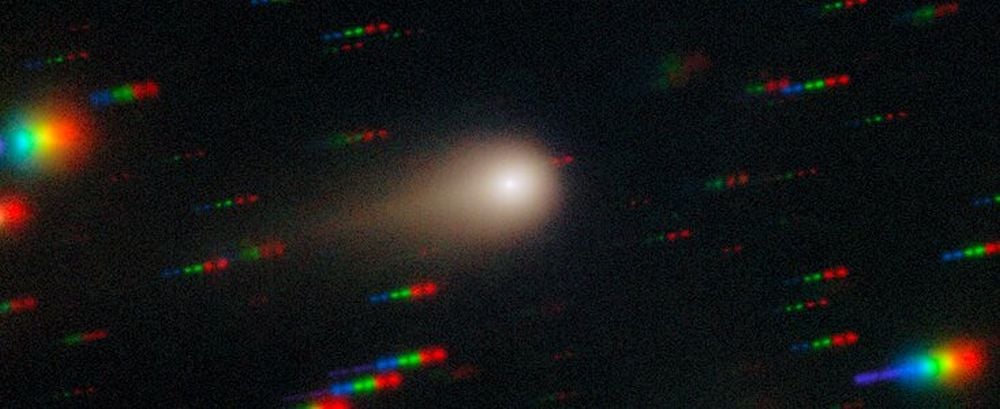
Interstellar visitors like Comet 3I/ATLAS grant astronomers a rare opportunity to study something from another solar system. It was first discovered on July 1st when it was entering the inner Solar System and was about 4.5 au from the Sun. It’s an active comet with an icy nucleus, meaning it’s warming up as it approaches the Sun and releasing gas and dust that form a coma and tail.
It’s the third confirmed interstellar object (ISO) after Oumuamua and Comet 2L/Borisov. These objects provoke extreme curiosity among astronomers, driven by the fact that they won’t be visible again. As ISOs, their trajectory will take them out of the Solar System completely, never to be seen again.
These new images of Comet 3I/ATLAS are from the Gemini South Telescope in Chile. It’s an 8.1 meter optical/infrared telescope that has a twin, the Gemini North Telescope, in Hawaii. The telescopes are operated by the National Science Foundation’s NOIRLab.
In a twist, these images aren’t part of a dedicated strictly scientific observing program. Instead, they’re from a public outreach initiative involving NOIRLab and Shadow the Scientists. Shadow the Scientists is an effort to connect astronomers working with powerful telescopes with interested members of the public.
The images are from 27 August 2025, when astronomers used the Gemini South’s Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS) to obtain deep images of Comet 3I/ATLAS, its coma, and its tail. The images show that the coma and tail are growing, when compared to earlier images of the comet.
During the outreach initiative, members of the public and students from Hawaii and Chile joined a Zoom call with astronomers at Gemini South. They were able to ask questions, interact with the scientists, and follow observations in real time. People from around the world, including from Europe, New Zealand, and South America, also joined in.
During the session, time-critical communication among the science team and observatory/telescope staff are given the highest priority. This is necessary for obvious reasons, and it gave public participants an opportunity to be immersed in real-time astronomical observations.
Gemini South’s Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS) captured the comet’s spectrum, which yields information about the comet’s chemical makeup. This lets astronomers understand the changes the comet goes through as it traverses the inner Solar System and the Sun’s energy drives changes in the comet.
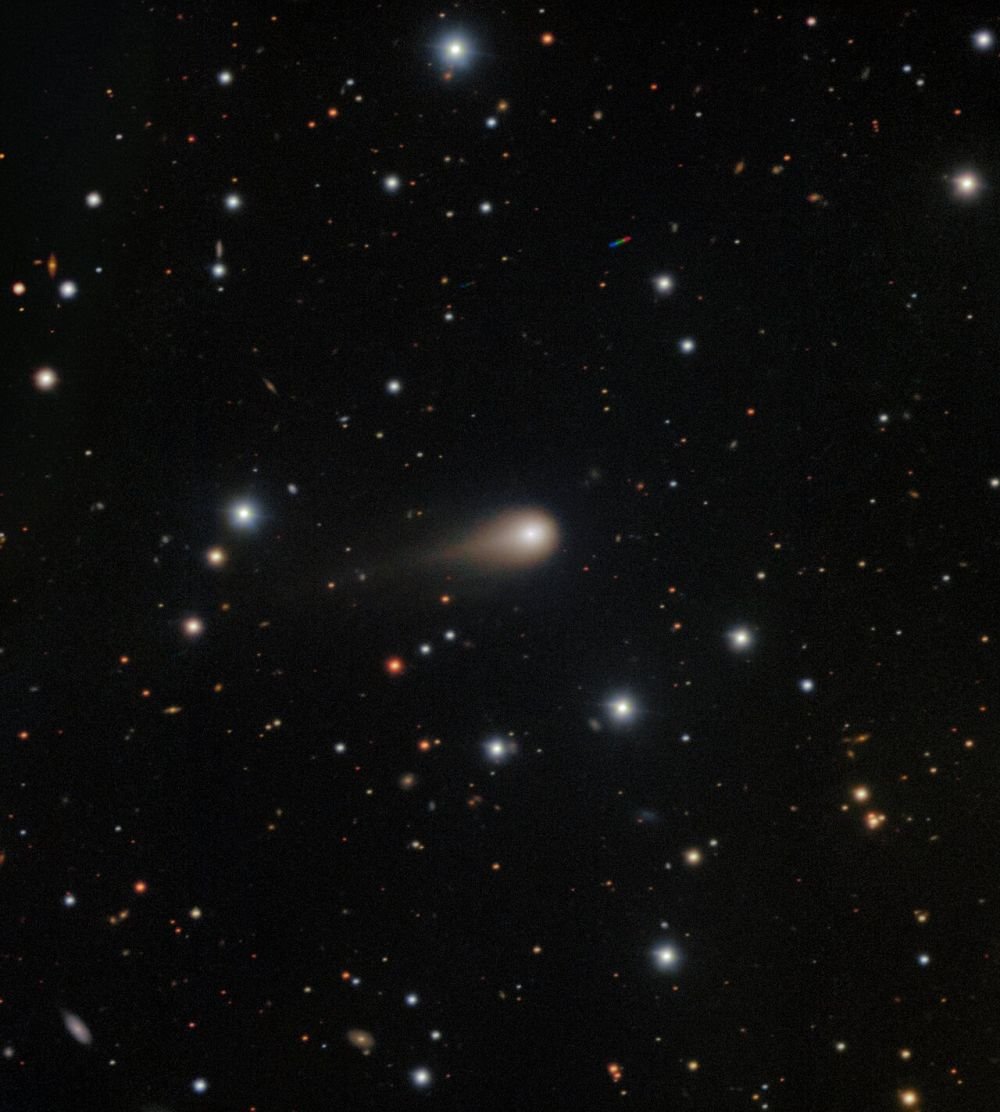 Comet 3I/ATLAS is only the third confirmed ISO to visit our Solar System, though there must have been many more of them throughout the Solar System’s history. The comet provides a rare opportunity to study something from a distant star up close. Image Credit: International Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/Shadow the Scientist Image Processing: J. Miller & M. Rodriguez (International Gemini Observatory/NSF NOIRLab), T.A. Rector (University of Alaska Anchorage/NSF NOIRLab), M. Zamani (NSF NOIRLab)
Comet 3I/ATLAS is only the third confirmed ISO to visit our Solar System, though there must have been many more of them throughout the Solar System’s history. The comet provides a rare opportunity to study something from a distant star up close. Image Credit: International Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/Shadow the Scientist Image Processing: J. Miller & M. Rodriguez (International Gemini Observatory/NSF NOIRLab), T.A. Rector (University of Alaska Anchorage/NSF NOIRLab), M. Zamani (NSF NOIRLab)
“The primary objectives of the observations were to look at the colors of the comet, which provide clues to the composition and sizes of the dust particles in the coma, and to take spectra for a direct measure of the chemistry,” said Karen Meech, astronomer at the University of Hawai‘i Institute for Astronomy, and leader of the scientific program. “We were excited to see the growth of the tail, suggesting a change in the particles from the previous Gemini images, and we got our first glimpse of the chemistry from the spectrum.”
The new observation and spectrum indicate broad similarity with comets from our own Solar System. This suggests that planetary system formation and evolution is similar in other Solar Systems, or at least in Comet 3I/ATLAS’s home system.
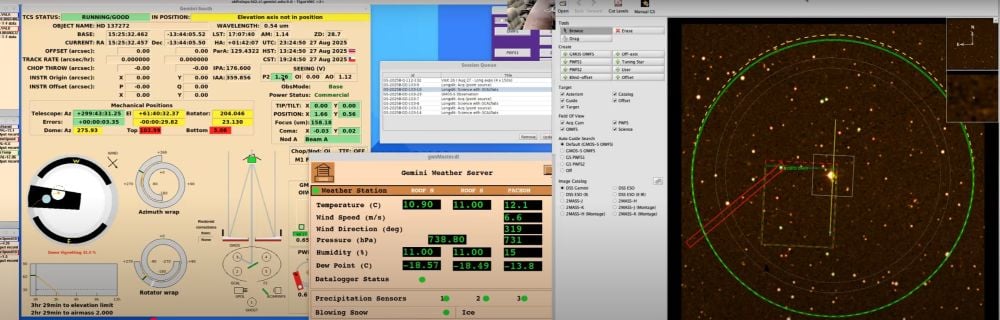 These two panels show some of what participants saw during the Gemini South’s Comet 3I/ATLAS observing session with Shadow the Scientists. The panel on the left shows a screen displaying different aspects of the telescope’s status, and also the weather. The panel on the right is the main software, called the observing tool, that astronomers use in a lot of their interactions with the Gemini South Telescope. Image Credits: NSF/NOIRLab/Gemini South
These two panels show some of what participants saw during the Gemini South’s Comet 3I/ATLAS observing session with Shadow the Scientists. The panel on the left shows a screen displaying different aspects of the telescope’s status, and also the weather. The panel on the right is the main software, called the observing tool, that astronomers use in a lot of their interactions with the Gemini South Telescope. Image Credits: NSF/NOIRLab/Gemini South
“As 3I/ATLAS speeds back into the depths of interstellar space, this image is both a scientific milestone and a source of wonder,” said Meech. “It reminds us that our Solar System is just one part of a vast and dynamic galaxy — and that even the most fleeting visitors can leave a lasting impact.”
“These observations provide both a breathtaking view and critical scientific data,” said Bryce Brolin, a research scientist who was also present. “Every interstellar comet is a messenger from another star system, and by studying their light and color, we can begin to understand the diversity of worlds beyond our own.”
Brolin will lead a follow-up Shadow the Scientists session when Comet 3L/ATLAS reappears from behind the Sun. That session will be held from the Gemini North Telescope on Mauna Kea, Hawaii.
Below is a video of the entire Shadow the Scientists observing session.

