Farajollahi A, Fonseca DM, Kramer LD, Kilpatrick AM. “Bird biting” mosquitoes and human disease: a review of the role of Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes in epidemiology. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11:1577–85.
Haba Y, McBride L. Origin and status of Culex pipiens mosquito ecotypes. Curr Biol. 2022;32:237–46.
Yurchenko AA, Masri RA, Khrabrova NV, Sibataev AK, Fritz ML, Sharakhova MV. Genomic differentiation and intercontinental population structure of mosquito vectors Culex pipiens pipiens and Culex pipiens molestus. Sci Rep. 2020;10:7504.
Hinze A, Hill SR, Ignell R. Odour-mediated host selection and discrimination in mosquitoes. In: Sensory ecology of disease vectors. Wageningen Academic. Wageningen. 2022. p. 253–276
Takken W, Verhulst NO. Host preferences of blood-feeding mosquitoes. Annu Rev Entomol. 2013;58:433–53.
Lyimo IN, Ferguson HM. Ecological and evolutionary determinants of host species choice in mosquito vectors. Trends Parasitol. 2009;25:189–96.
McBride CS, Baier F, Omondi AB, Spitzer SA, Lutomiah J, Sang R, Ignell R, Vosshall LB. Evolution of mosquito preference for humans linked to an odorant receptor. Nat. 2014;515:222–7.
Rinker DC, Zhou X, Pitts RJ, Consortium AGC, Rokas A, Zwiebel LJ. Antennal transcriptome profiles of anopheline mosquitoes reveal human host olfactory specialization in Anopheles gambiae. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:1–5.
Zhao Z, Zung JL, Hinze A, Kriete AL, Iqbal A, Younger MA, Matthews BJ, Merhof D, Thiberge S, Ignell R, Strauch M, McBride CS. Mosquito brains encode unique features of human odour to drive host seeking. Nat. 2022;605:706–12.
Faraji A, Gaugler R. Experimental host preference of diapause and non-diapause induced Culex pipiens pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:1–7.
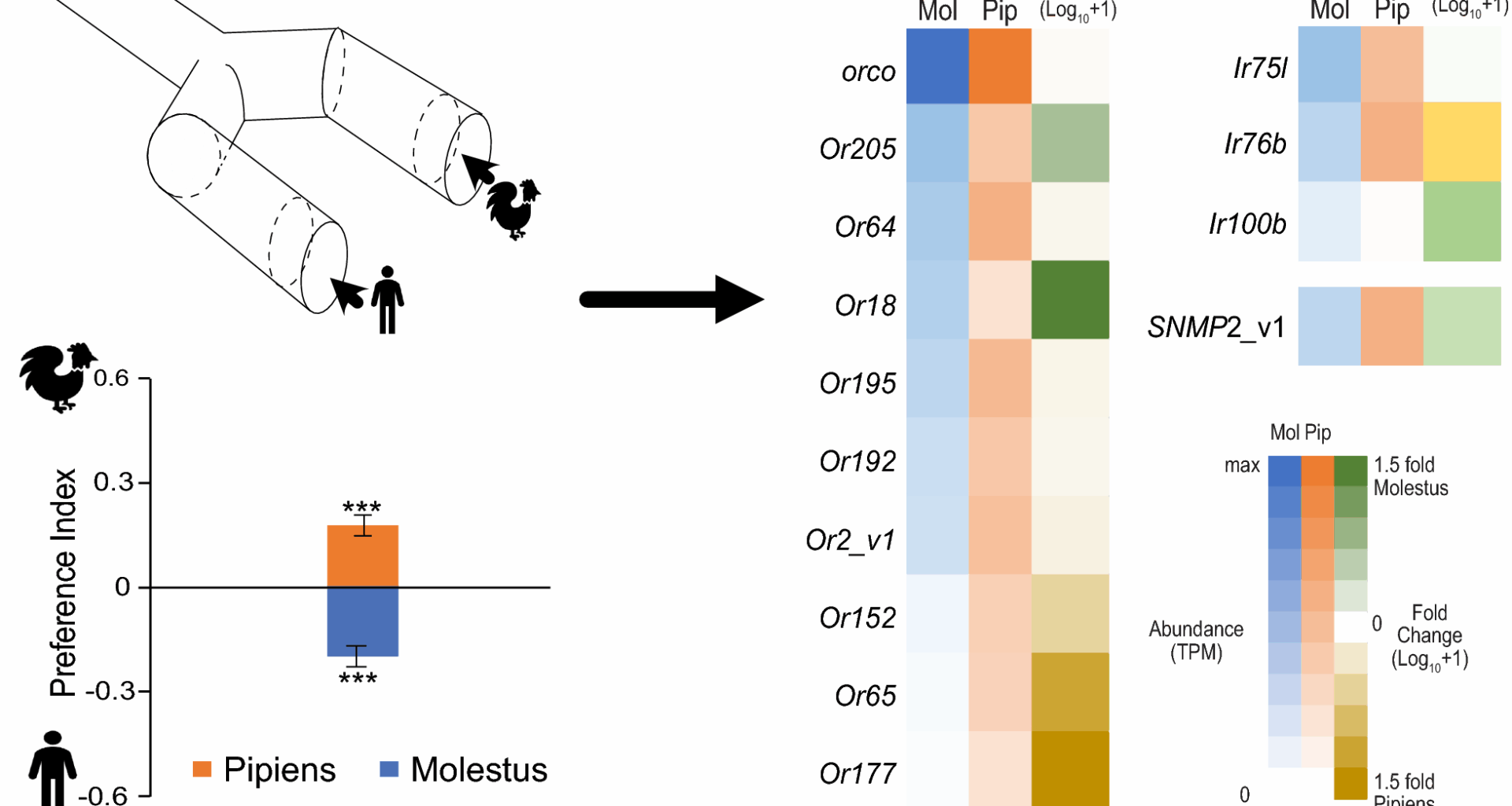
Noreuil A, Fritz ML. Differential gene expression in the heads of behaviorally divergent Culex pipiens mosquitoes. Insects. 2021;12:271.
Bell KL, Noreuil A, Molloy EK, Fritz ML. Genetic and behavioral differences between above and below ground Culex pipiens bioforms. Heredity. 2024;132:221–31.
Köchling K, Schaub GA, Schäfer M, Werner D, Kampen H. Host preference of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) collected in Germany. J Vector Ecol. 2024;49:114–25.
Vogels CB, Möhlmann TW, Melsen D, Favia G, Wennergren U, Koenraadt CJ. Latitudinal diversity of Culex pipiens biotypes and hybrids in farm, peri-urban, and wetland habitats in Europe. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0166959.
Spanoudis CG, Wondwosen B, Isberg E, Andreadis SS, Kline DL, Birgersson G, Ignell R. The chemical code for attracting Culex mosquitoes. Front Ecol Evol. 2022;10:930665.
Gu ZY, Gao HT, Yang QJ, Ni M, Li MJ, Xing D, Zhao TY, Zhao T, Li CX. Screening of olfactory genes related to blood-feeding behaviors in Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus and Culex pipiens molestus by transcriptome analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022;16:e0010204.
Majeed S, Hill SR, Birgersson G, Ignell R. Detection and perception of generic host volatiles by mosquitoes modulate host preference: context dependence of (R)-1-octen-3-ol. R Soc Open Sci. 2016;3:160467.
Suh E, Bohbot JD, Zwiebel LJ. Peripheral olfactory signaling in insects. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2014;6:86–92.
Andersson MN, Löfstedt C, Newcomb RD. Insect olfaction and the evolution of receptor tuning. Front Ecol Evol. 2015;3:53.
Hansson BS, Stensmyr MC. Evolution of insect olfaction. Neuron. 2011;72:698–711.
Zhao Z, McBride CS. Evolution of olfactory circuits in insects. J Comp Physiol A. 2020;206:353–67.
De Obaldia ME, Morita T, Dedmon LC, Boehmler DJ, Jiang CS, Zeledon EV, Cross JR, Vosshall LB. Differential mosquito attraction to humans is associated with skin-derived carboxylic acid levels. Cell. 2022;185:4099–116.
DeGennaro M, McBride CS, Seeholzer L, Nakagawa T, Dennis EJ, Goldman C, Jasinskiene N, James AA, Vosshall LB. Orco mutant mosquitoes lose strong preference for humans and are not repelled by volatile DEET. Nat. 2013;498:487–91.
Omondi AB, Ghaninia M, Dawit M, Svensson T, Ignell R. Age-dependent regulation of host seeking in Anopheles coluzzii. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9699.
Jones W. Olfactory carbon dioxide detection by insects and other animals. Mol Cells. 2013;35:87–92.
Liu F, Ye Z, Baker A, Sun H, Zwiebel LJ. Gene editing reveals obligate and modulatory components of the CO2 receptor complex in the malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles coluzzii. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;127:103470.
McMeniman CJ, Corfas RA, Matthews BJ, Ritchie SA, Vosshall LB. Multimodal integration of carbon dioxide and other sensory cues drives mosquito attraction to humans. Cell. 2014;156:1060–71.
Main BJ, Lee Y, Ferguson HM, Kreppel KS, Kihonda A, Govella NJ, Collier TC, Cornel AJ, Eskin E, Kang EY, Nieman CC. The genetic basis of host preference and resting behavior in the major African malaria vector, Anopheles arabiensis. PLoS Genet. 2016;12:e1006303.
Vogels CB, Fros JJ, Göertz GP, Pijlman GP, Koenraadt CJ. Vector competence of northern European Culex pipiens biotypes and hybrids for West Nile virus is differentially affected by temperature. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:1–7.
European Center for Disease Prevention and Control, 2024. The European Union One Health 2023 Zoonoses report. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/european-union-one-health-2023-zoonoses-report. Accessed 10 Dec 2024.
Arensburger P, Megy K, Waterhouse RM, Abrudan J, Amedeo P, Antelo B, Bartholomay L, Bidwell S, Caler E, Camara F, Campbell
CL, Campbell KS, Casola C, Castro MT, Chandramouliswaran I, Chapman SB, Christley S, Costas J, Eisenstadt E, Feschotte C,
Fraser-Liggett C, Guigo R, Haas B, Hammond M, Hansson BS, Hemingway J, Hill SR, Howarth C, Ignell R, Kennedy RC, Kodira CD,
Lobo NF, Mao C, Mayhew G, Michel K, Mori A, Liu N, Naveira H, Nene V, Nguyen N, Pearson MD, Pritham EJ, Puiu D, Qi Y, Ranson
H, Ribeiro JM, Roberston HM, Severson DW, Shumway M, Stanke M, Strausberg RL, Sun C, Sutton G, Tu ZJ, Tubio JM, Unger MF,
Vanlandingham DL, Vilella AJ, White O, White JR, Wondji CS, Wortman J, Zdobnov EM, Birren B, Christensen BM, Collins FH,
Cornel A, Dimopoulos G, Hannick LI, Higgs S, Lanzaro GC, Lawson D, Lee NH, Muskavitch MA, Raikhel AS, Atkinson PW. Sequencing of Culex quinquefasciatus establishes a platform for mosquito comparative genomics. Sci. 2010;330:86–8.
Taparia T, Ignell R, Hill SR. Blood meal induced regulation of the chemosensory gene repertoire in the southern house mosquito. BMC Genom. 2017;18:1–9.
Tallon AK, Hill SR, Ignell R. Sex and age modulate antennal chemosensory-related genes linked to the onset of host seeking in the yellow-fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Sci Rep. 2019;9:43.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 1995;57:289–300.
Parra G, Bradnam K, Korf I. CEGMA: a pipeline to accurately annotate core genes in eukaryotic genomes. Bioinform. 2007;23:1061–7.
Harbach RE, Harrison BA, Gad AM. Culex (Culex) molestus Forskal (Diptera: Culicidae): neotype designation, description, variation, and taxonomic status. Proc Entomol Soc Wash. 1984;86:521–42.
Dekker T, Takken W, Marieta AB. Innate preference for host-odor blends modulates degree of anthropophagy of Anopheles gambiae sensu lato (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol. 2001;38:868–71.
Wolff GH, Lahondère C, Vinauger C, Rylance E, Riffell JA. Neuromodulation and differential learning across mosquito species. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2023;290:20222118.
Bruce TJ, Pickett JA. Perception of plant volatile blends by herbivorous insects—finding the right mix. Phytochem. 2011;72:1605–11.
Koutroumpa FA, Kárpáti Z, Monsempes C, Hill SR, Hansson BS, Jacquin-Joly E, Krieger J, Dekker T. Shifts in sensory neuron identity parallel differences in pheromone preference in the European corn borer. Front Ecol Evol. 2014;2:65.
Khan Z, Ignell R, Hill SR. Odour-mediated oviposition-site selection by mosquitoes. In: Sensory ecology of disease vectors. Wageningen Academic. Wageningen. 2022
Ruel DM, Yakir E, Bohbot JD. Supersensitive odorant receptor underscores pleiotropic roles of indoles in mosquito ecology. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;12:533.
Bernier UR, Allan SA, Quinn BP, Kline DL, Barnard DR, Clark GG. Volatile compounds from the integument of white leghorn chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus L.): candidate attractants of ornithophilic mosquito species. J Sep Sci. 2008;31:1092–9.
Cork A, Park KC. Identification of electrophysiologically-active compounds for the malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, in human sweat extracts. Med Vet Entomol. 1996;10:269–76.
Rankin-Turner S, McMeniman CJ. A headspace collection chamber for whole body volatilomics. Analyst. 2022;14:5210–22.
Yee WL, Foster WA. Diel sugar-feeding and host-seeking rhythms in mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) under laboratory conditions. J Med Entomol. 1992;29:784–91.