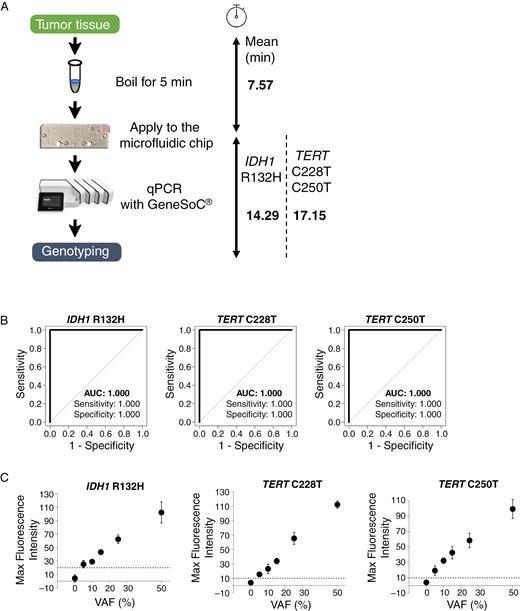
Conventional genetic analysis methods for genotyping of brain tumors usually require one or two days to obtain results but a new method can determine optimal resection margins during surgery in just a few minutes.
The ability to accurately detect genetic mutations in a brain tumor was demonstrated with isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoters, which are markers for diagnosis of diffuse glioma—the most common type of brain tumor. Their system uses a
Polymerase Chain Reaction device in combination with their own protocol and it enables DNA extraction using only heat incubation.
It was tested using 120 cases of brain tumors collected from patients and also assessed the presence of IDH1 and TERT promoter mutations, intraoperatively. They showed that they have high diagnostic accuracy, with 98.5% sensitivity and 98.2% specificity for detection of IDH1 mutations, as well as 100% sensitivity and specificity for detection of TERT promoter mutations; in under 22 minutes for IDH1 mutations and under 25 minutes for TERT promoter mutations.
Source: https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaf188
Validation was confirmed by comparing results with those obtained from conventional Sanger sequencing, widely used in clinical examinations and research, but at one to two days to provide results, impractical for intraoperative genotyping.
Citation: Sachi Maeda, Yotaro Kitano, Fumiharu Ohka, Kazuya Motomura, Kosuke Aoki, Shoichi Deguchi, Yoshiki Shiba, Masafumi Seki, Yuma Ikeda, Hiroki Shimizu, Kenichiro Iwami, Kazuhito Takeuchi, Yuichi Nagata, Junya Yamaguchi, Keisuke Kimura, Yuhei Takido, Ryo Yamamoto, Akihiro Nakamura, Shohei Ito, Keiko Shinjo, Yutaka Kondo, Shohei Miyagi, Kennosuke Karube, Ryuta Saito, Rapid intraoperative genetic analysis of adult-type diffuse gliomas using a microfluidic real-time polymerase chain reaction device, Neuro-Oncology, 2025;, noaf188, https://academic.oup.com/neuro-oncology/advance-article/doi/10.1093/neuo…
