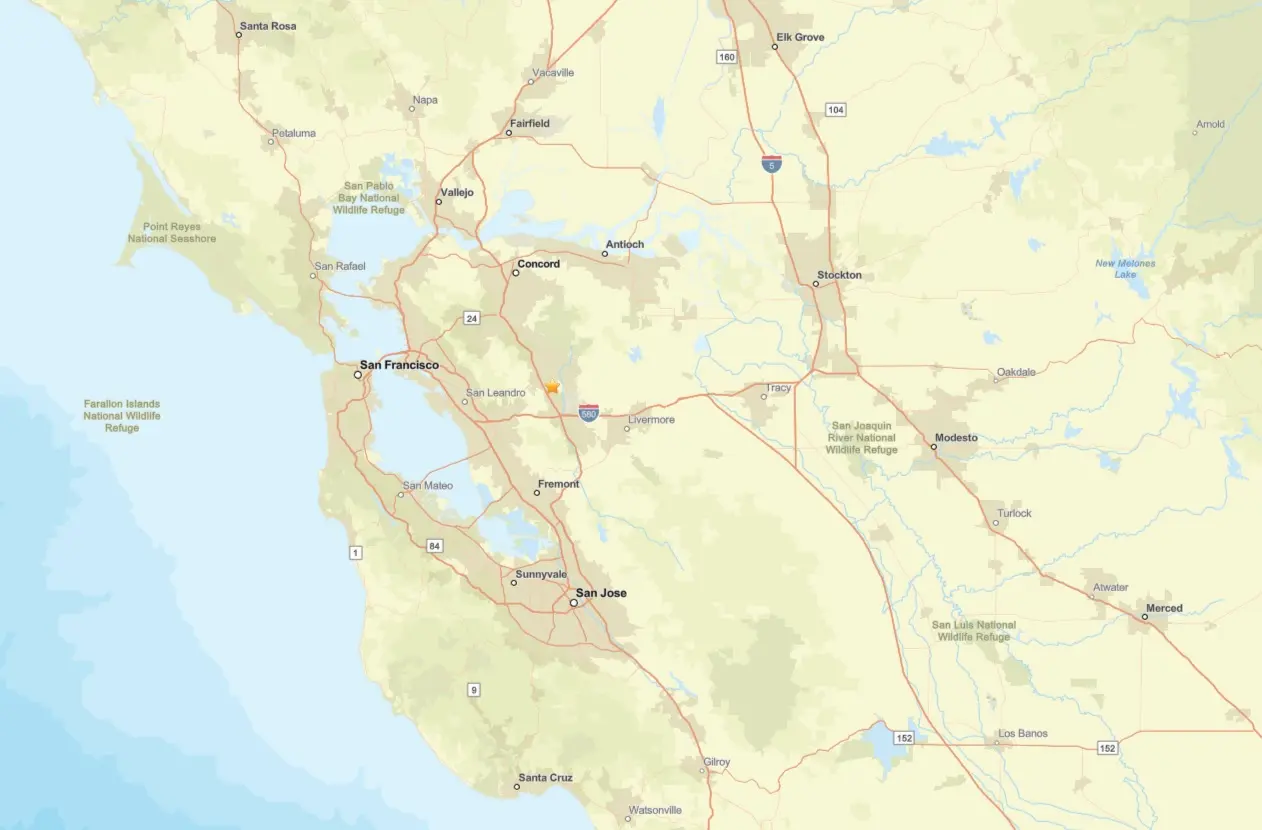
A small 3.3 magnitude earthquake struck near San Ramon, California, late Monday night local time, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) said.
The epicenter, about 2.5 miles from San Ramon, and the quake’s depth was a relatively shallow of 5.6 miles. The tremor, which struck along the Calaveras Fault at around 10:47 p.m. PST, was felt in nearby Dublin and the Bay Area.
There were no reports of damage or casualties.
More than 800 residents of San Ramon, Pleasanton, Walnut Creek and Danville reported feeling weak shaking, according to the “Did You Feel It” page on the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website.
The late Monday quake hit near where a swarm of eight earthquakes struck over about three hours on the morning of November 9.
California famously sits along the San Andreas Fault System, a major fault line that has caused some of the biggest earthquakes in U.S. history. The Calveras Fault is a branch of the San Andreas.
The San Andreas Fault runs about 750 miles from the Salton Sea in Southern California to Cape Mendocino in Northern California. It passes near major urban areas, including Los Angeles and San Francisco.
The two most recent earthquakes that struck the Bay Area were a 2001 quake along the West Napa fault, which measured magnitude 5.1, and a 2005 temblor along the Calaveras Fault, which measured magnitude 5.6.
More than 7 million people live in the region.
Famous quake
The strongest earthquake to hit California struck in 1857 and measured magnitude 7.9, with the second strongest—but perhaps most famous—earthquake hitting San Francisco in 1906 with a magnitude of 7.8, according to the California Department of Conservation.
The San Francisco event in 1906 caused a major fire and killed as many as 3,000 people, earning the name “The Great 1906 San Francisco Earthquake,” which lasted for around one minute and was felt from southern Oregon to just south of Los Angeles and as far inland as central Nevada, according to the USGS.
Out of the 14 earthquakes recorded and measured near San Francisco, only three others in recent geological history struck at or over magnitude 7: A magnitude 7 in 1838, a magnitude 7 in 1868 and a magnitude 7.1 that struck in 1989, according to Earthquake Safety.