Study design and data source
This retrospective cohort study was conducted using data from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV) V.3.1 Database, 2008–2022 which is a comprehensive, publicly available critical care dataset that includes data of 364,627 non-institutionalized patients and 546,028 hospitalized patients treated in the Emergency Department (ED) and Intensive Care Units (ICU, CCU) in a single center, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA, from 2008 to 2022 [17, 18]. The dataset comprises de-identified patient information, including demographic data, vital signs, laboratory test results, medications, and clinical outcomes, making it an invaluable resource for analyzing trends and outcomes in critical care [19].
Study population
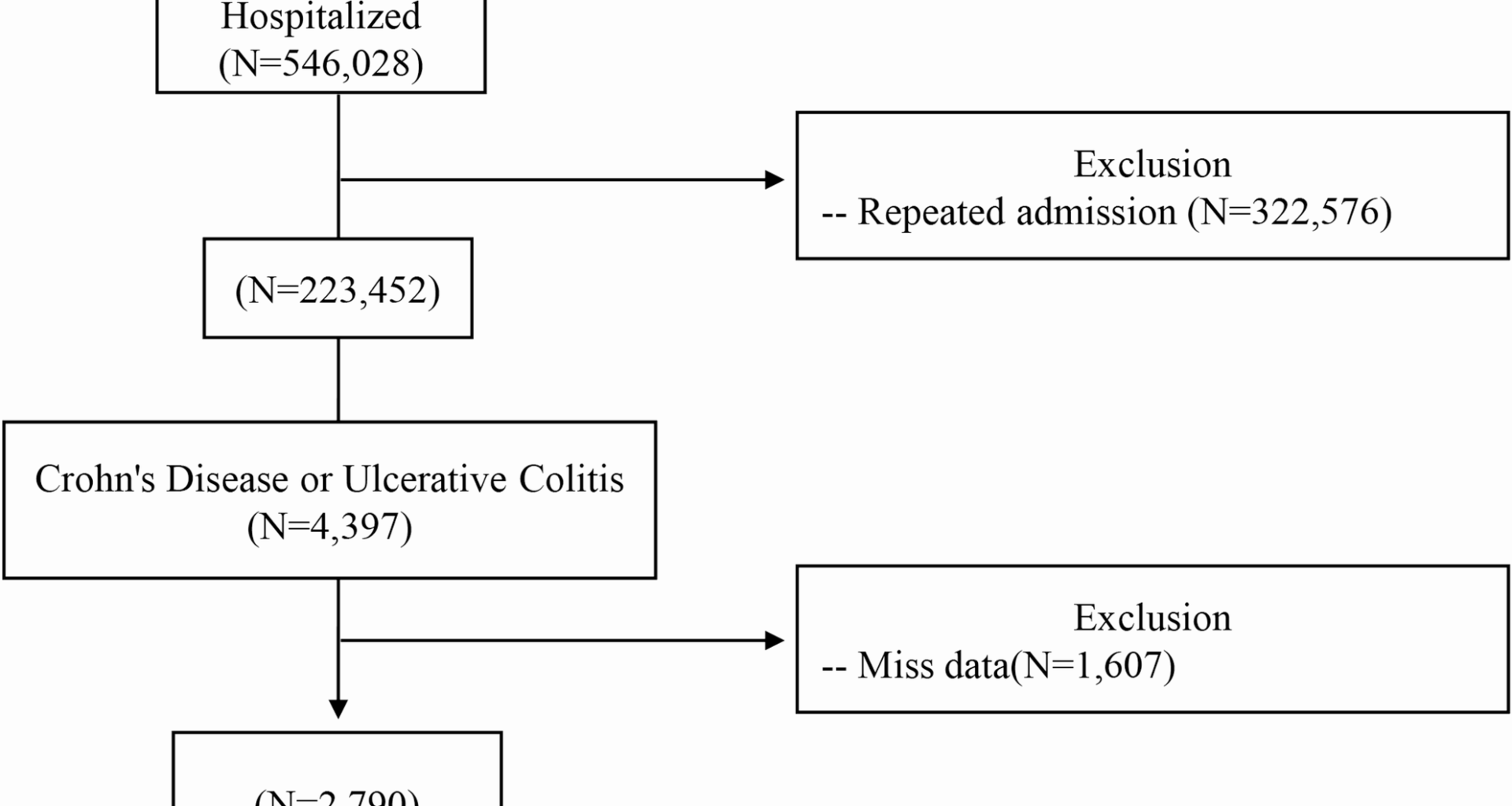
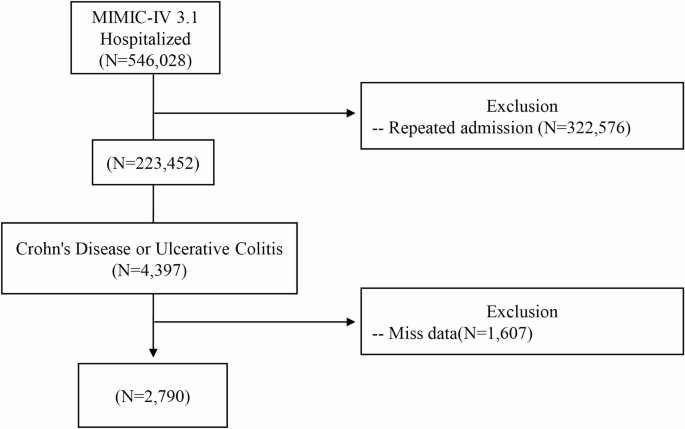
Hospitalized adult patients with IBD were included. Diagnosis of IBD was determined using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), 9th and 10th Revisions. Patients with ulcerative colitis were identified using the ICD-10 codes K51, K510x, K512x, K513x, K518x, K519x, and the corresponding ICD-9 codes 556.0, 556.1, 556.2, 556.3, 556.4, 556.5, 556.6, 556.8, and 556.9. ICD-10 codes K50, K500x, K501x, K508x, and K509x were used to identify patients diagnosed with CD, along with ICD-9 codes 555.0, 555.1, 555.2, and 555.9. Data from patients younger than 18 years, those lacking complete hospitalization records, those with missing data or repeated data (e.g., second and third hospitalizations) of those with multiple admissions were excluded in the present study. After exclusions, 2790 patients formed the analytic sample. Figure 1 depicts the patient selection process.
Flowchart of patient selection
Additionally, the database includes out-of-hospital mortality data, enriching the scope of long-term follow-up. Long‑term mortality was ascertained via the Social Security Death Index linkage available in MIMIC‑IV, which captures more than 95% of out‑of‑hospital deaths in the United States, ensuring robust follow‑up. Following the completion of web-based training and the successful completion of the Protecting Human Research Participants examination, author Min-I Su (Record ID: 42219644) obtained the necessary approval to access and extract data from the MIMIC-IV database (https://github.com/MIT-LCP/mimic-iv) [18].
Ethics statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Mackay Memorial Hospital (Number 24MMHIS460e). The IRB waived informed consent of the included patients because the research involved analysis of anonymized, retrospective data.
Covariates
Patients with VTE were identified using the ICD-10 codes I822, I8221x, I8222x, I8229x, I823, I824, I8240x, I8241x, I8242x, I8243x, I8244x, I8245x, I8246x, I8249x, I824Yx, I824Zx, I825, I8250x, I8251x, I8252x, I8253x, I8254x, I8255x, I8256x I8259x, I825Yx, I825Zx, I826, I8260x, I8261x, I8262x, I827, I8270x, I8271x, I8272x, I82A, I82A1x, I82A2x, I82B, I82B1x, I82B2x, I82C, I82C1x, I82C2x, I828, I8281x, I8289x, and I829x, and the corresponding ICD-9 codes 556.0, 4532, 4533, 4534, 45,340, 45,341, 45,342, 4535, 45,350, 45,351, 45,352, 4536, 4537, 45,371, 45,372, 45,373, 45,374, 45,375, 45,376, 45,377, 45,379, 4538, 45,381, 45,382, 45,383, 45,384, 45,385, 45,386, 45,387, and 45,389. In addition, patients’ demographic data were collected, including age, sex, laboratory tests, and comorbidities. Laboratory tests performed included measurements of white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin, platelets, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, sodium, potassium, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP). Comorbidities included VTE, Clostridium difficile infection, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, coronary arterial disease (CAD), stroke, chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes mellitus (DM), myocardial infarct (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, rheumatic disease, renal disease, cancer and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) scores. Medications, including corticosteroids (Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone, Prednisone or Budesonide ER [UCERIS]), biologics (Infliximab, Adalimumab [Humira], Cimzia, Golimumab [Simponi], Vedolizumab [Entyvio], Natalizumab [Tysabri], Ustekinumab [Stelara], Risankizumab [Skyrizi] or Upadacitinib[Rinvoq]), immunomodulators (Sulfasalazine, Pentasa, Azathioprine, Mercaptopurine or Cyclosporine) and anticoagulants (Warfarin, Coumadin, Dabigatran, Pradaxa, Rivaroxaban, Xarelto, Apixaban, Edoxaban or Savaysa), were also assessed.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as means and standard deviation (SD). Categorical variables are presented as numbers and percentages (%). The χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test was used to test comparisons between groups for categorical variables, whereas the students’ test was used for comparisons of continuous variables. In-hospital mortality and long-term mortality were evaluated using Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Cox proportional hazards regression models were used for univariate and multivariable analyses. Models were constructed to explore associations between VTE and mortality. Model 1 was adjusted for sex and age. Model 2 was adjusted for demographic factors, including sex, age, laboratory results (ALT, ALP, AST, hemoglobin, WBC, RBC, sodium, potassium, creatinine, platelets) and CCI scores. Model 3 was adjusted for Clostridium difficile infection, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, CAD, stroke, CKD, DM, myocardial infarct (MI), CHF, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, rheumatic disease, renal disease, and malignant cancer. The proportional hazards assumption for the Cox regression models was tested using Schoenfeld residuals. A p-value greater than 0.05 indicated that the assumption was met. All statistical analyses were performed using R (V.4.2.3) and SPSS (V.20). A threshold of p < 0.05 (two sided) was established as statistical significance.