Newswise — Researchers from Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, et al. have conducted a study entitled “Machine learning modeling identifies hypertrophic cardiomyopathy subtypes with genetic signature”. This study was published in Frontiers of Medicine, Volume 17, Issue 4.
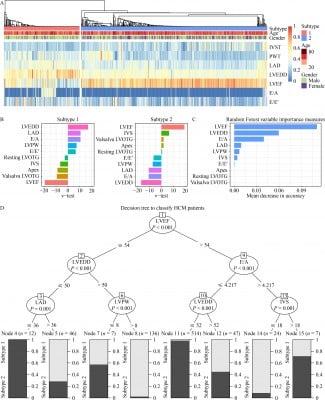
Previous studies have revealed that patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) exhibit differences in symptom severity and prognosis, indicating potential HCM subtypes among these patients. Here, 793 patients with HCM were recruited at an average follow-up of 32.78 ± 27.58 months to identify potential HCM subtypes by performing consensus clustering on the basis of their echocardiography features. Furthermore, the study proposed a systematic method for illustrating the relationship between the phenotype and genotype of each HCM subtype by using machine learning modeling and interactome network detection techniques based on whole-exome sequencing data. Another independent cohort that consisted of 414 patients with HCM was recruited to replicate the findings. Consequently, two subtypes characterized by different clinical outcomes were identified in HCM. Patients with subtype 2 presented asymmetric septal hypertrophy associated with a stable course, while those with subtype 1 displayed left ventricular systolic dysfunction and aggressive progression. Machine learning modeling based on personal whole-exome data identified 46 genes with mutation burden that could accurately predict subtype propensities. Furthermore, the patients in another cohort predicted as subtype 1 by the 46-gene model presented increased left ventricular end-diastolic diameter and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. By employing echocardiography and genetic screening for the 46 genes, the study classified HCM into two subtypes with distinct clinical outcomes.
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST. For more detailed information, the full paper is available at: https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-023-0982-1.