Hawley, J. A., Hargreaves, M., Joyner, M. J. & Zierath, J. R. Integrative biology of exercise. Cell 159, 738–749 (2014).
Chow, L. S. et al. Exerkines in health, resilience and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 18, 273–289 (2022).
Williams, R. S. & Neufer, P. D. in The Handbook of Physiology, Section 12, Exercise: Regulation and Integration of Multiple Systems (eds Rowell, L. B. & Shepherd, J. T.) 1124–1150 (Oxford Univ. Press, 1996).
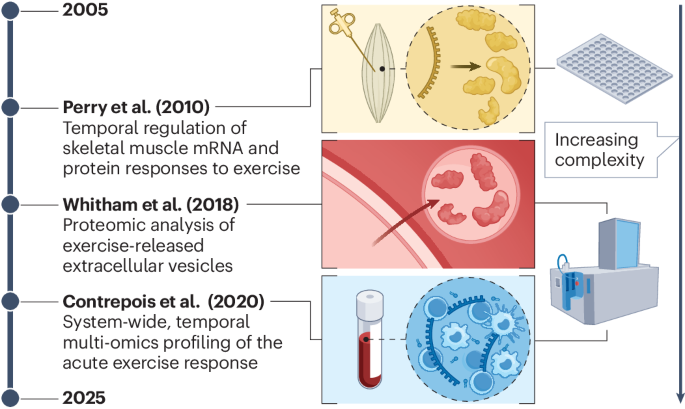
Perry, C. G. R. et al. Repeated transient mRNA bursts precede increases in transcriptional and mitochondrial proteins during training in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 588, 4795–4810 (2010).
Goldstein, M. S. Humoral nature of the hypoglycemic factor of muscular work. Diabetes 10, 232–234 (1961).
Pedersen, B. K. & Febbraio, M. A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 8, 457–465 (2012).
Whitham, M. et al. Extracellular vesicles provide a means for tissue crosstalk during exercise. Cell Metab. 27, 237–251 (2018).
Contrepois, K. et al. Molecular choreography of acute exercise. Cell 181, 1112–1130 (2020).
Hoffman, N. J. et al. Phosphoproteomics uncovers exercise intensity-specific skeletal muscle signaling networks underlying high-intensity interval training in healthy male participants. Sports Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-025-02217-2 (2025).
Bishop, D. J. et al. Discordant skeletal muscle gene and protein responses to exercise. Trends Biochem. Sci. 48, 927–936 (2023).