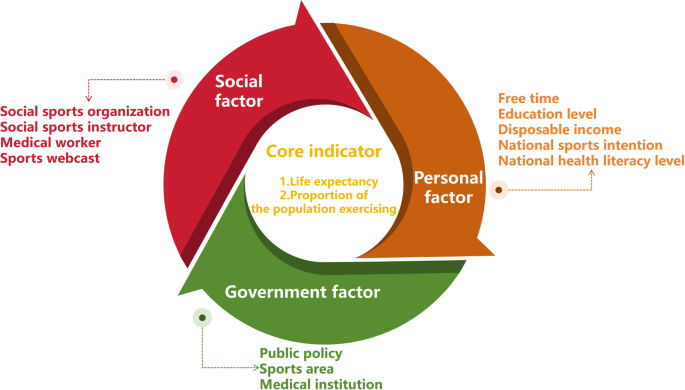
Simulation mode parameter setting
Based on the social support theory, this study sets up five modes (Table 3) for the exercise-based health promotion, namely Current development mode, Social support priority mode, Government support priority mode, Personal support priority mode, Coordinated development mode. The Current development mode represents the exercise-based health promotion mode currently implemented in China, by collecting and calculating empirical data from China, the fundamental parameters of all variables are input into the system dynamics model. The Government support priority mode, the Social support priority mode, and the Personal support priority mode correspond to development paradigms predominantly driven by governmental support, social support, and personal support, respectively. For each respective category (governmental support, social support, individual support), the parameters of the corresponding variables are proportionally increased and subsequently input into the system dynamics model. Coordinated development mode is the synergistic development mode of government support, social support and personal support, meanwhile, the corresponding variable parameters are adjusted upward and input into the system dynamics model.
Table 3 Simulation mode parameter setting.Analysis of the simulation result
The base time of the system dynamics model of the exercise-based health promotion is 2010, the running time is set to 2010–2030, and the simulation time step is set to 1 year, which can not only show the historical situation of the exercise-based health promotion in China, but also make a certain degree of prediction for the future development. According to the parameter settings of Table 3, the model was run sequentially, and the simulation results of Mode 1-Mode 5 were visualized and expressed by Origin software (Figs. 4 and 5).
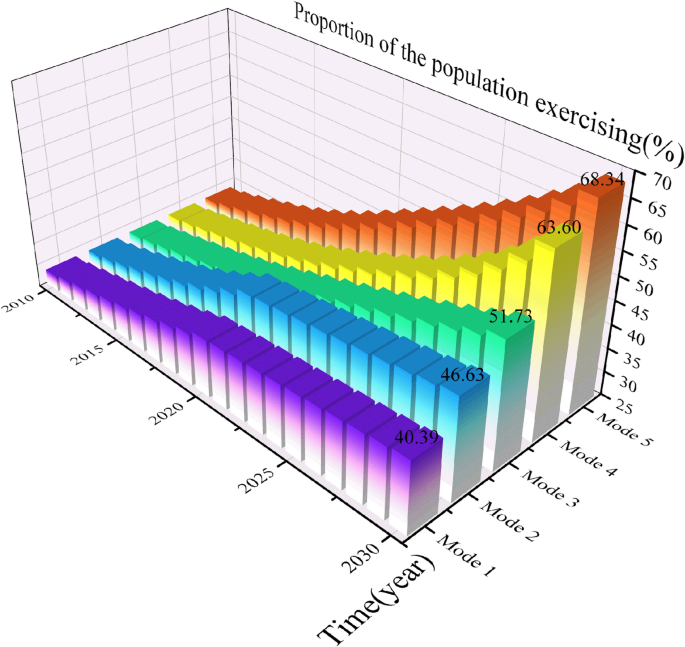
Figure 4 represents the historical development and future projections of the proportion of the population exercising in the core indicators for the exercise-based health promotion systems in the case of Mode 1-Mode 5.
Simulation results of proportion of the population exercising.
Under Current development mode (Mode 1), the proportion of the population exercising always keeps growing, but the growth rate changes. From the simulation results, it can be seen that the proportion of the population exercising has a clear growth trend before 2020 (average growth rate of 0.897%), but the growth rate tends to slow down after that (average growth rate of 0.309%), which indicates that there is a certain development bottleneck in this indicator. According to the current development mode of the exercise-based health promotion, in 2020, the proportion of people who regularly participate in exercise in China will be 37.31%, in 2025 the proportion of people who regularly participate in exercise will be 38.67%, and in 2030 the proportion of the population exercising will reach 40.39%. It is worth mentioning that the Chinese government issued a relevant document “National Fitness Program (2021–2025)”, which states it will “gradually improve the public service system of national fitness, improve the enthusiasm of the masses for sports and fitness, and the proportion of the population exercising will reach 38.5% in 2025”. Evidently, the simulation demonstrates that, under the current development trajectory, China will largely achieve its phased policy targets by 2025, even if the growth rate of the proportion of the proportion of the population exercising experiences a decline.
Under the Government support priority mode (Mode 2), the proportion of the population exercising is less effective and also bottlenecks in 2020. Comparing Mode 2 to Mode 1, the proportion of the population exercising on a regular basis in 2030 increases from 40.39 to 46.63%. The promulgation of exercise promotes health policy has accelerated the construction of sports venues, which provides protection for national daily sports activities, sports skills learning and competition watching, and strengthens the material foundation of national participation in sports and exercise. However, it is undeniable that the individual willingness of the masses to participate in physical exercise is also affected by social and personal support elements such as social sports instructors, cultural level, personal leisure time, etc. The simulation results of Mode 2 show that the proportion of the population exercising will increase from 28.35 to 41.54% from 2010 to 2020, an increase of 13.19%, and will increase from 41.54 to 41.54% from 2020 to 2030, an increase of 13.19%, and an increase of 13.19% from 2020 to 2030. In 2030, it increases from 41.54 to 46.63%, with an increase of only 5.09%, and the growth rate decreases significantly. The simulations indicate that it is difficult to break through the bottleneck of the development of exercise promotes health if only the government support is increased, ignoring the important role of the other elements in promoting it.
Social support priority mode (Mode 3) shows that compared with Mode 1, the growth trend of the proportion of the population exercising remains more or less the same from 2010 to 2020, but the effect of the increase is obvious after 2020: the proportion of the population exercising grows from 37.32 to 37.47% in 2020, which is an increase of 0.15%, and from 40.39 to 51.73% in 2030, which is an increase of 11.34%, meaning Mode 3 is able to break the bottleneck in the development of the exercise-based health promotion. The influence of social support on the proportion of the population exercising shows a weak and then strong trend, which is due to the fact that it takes a period of time for social sports instructors and social sports organizations and other main bodies to build a positive social atmosphere for sports and change the habits of national life. As time passes, the national view of sports gradually changes from a passive exerciser to an active participant in the pursuit of health, and this positive view of sports gradually penetrates into all levels of social culture, forming a comprehensive health concept, which helps to raise the level of the national awareness of sports, thus increasing the national enthusiasm of participating in sports.
Under the personal support priority mode (Mode 4), the proportion of the population exercising also breaks through the bottleneck and improves with better effect. Compared with Mode 1, the proportion of the population exercising in 2030 rises from 40.39 to 63.60% in Mode 4, an increase of 23.21%. The improvement of cultural level, consumption level and national health literacy level makes it easier for the nationals to become exposed and better understand knowledge surrounding physical exercise, and through extensive health education and publicity activities, it stimulates the nationals’ willingness to exercise, and makes the nationals more willing to invest their time and energy to participate in various forms of physical activities. The simulation indicates that individual support exerts a positive influence on increasing the proportion of the population exercising. Not only does individual support alter individuals’ perceptions and attitudes towards exercise, but it also fosters a social culture of lifelong physical activity and enhances public motivation for exercise, thereby contributing to an increase in the proportion of the population exercising.
Under the Coordinated development mode (Mode 5), the enhancement effect on the proportion of the population exercising is more pronounced compared to other modes. In Mode 5, the proportion of the population exercising in 2030 is 68.34%, an increase of 27.95% compared with Mode 1, which is much better than Mode 2 (6.24%), Mode 3 (11.34%), and Mode 4 (23.21%), the model suggests that the simultaneous improvement of government support, social support, and individual support can better promote the development of public sports (while economizing on resources as much as possible). With the continuous strengthening of government support elements such as exercise promotes health policies and sports venues and facilities, the improvement of social support elements such as social sports organizations and social sports instructors, and the improvement of individual support elements such as literacy, national health literacy and national fitness willingness, not only guarantees the basic conditions of physical exercise for those who have a strong willingness to work out, but also attracts those who have a weak willingness to work out to participate in physical exercise. This not only ensures the basic conditions for nationals with a strong desire to exercise, but also attracts nationals with a weaker desire to exercise to participate in physical activity, providing comprehensive, convenient and high-quality public sports services to nationals from the supply side, and stimulating nationals to take the initiative to participate in physical activity from the demand side, thus effectively increasing the proportion of the population exercising.
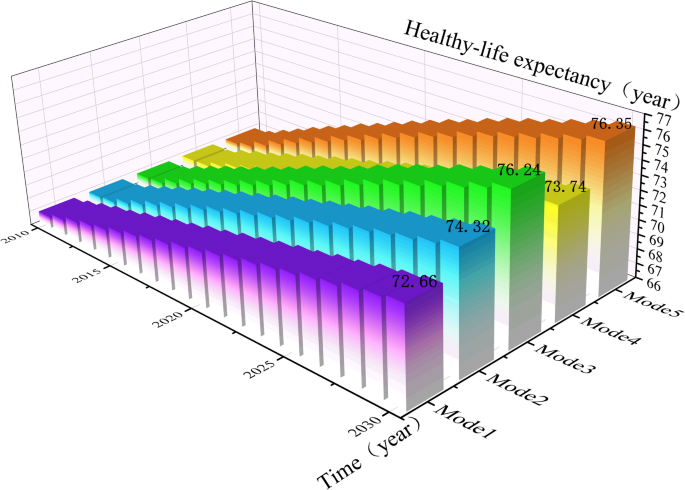
Simulation results of healthy-life expectancy.
Figure 5 represents the historical development and future projections of healthy-life expectancy in the core indicators of exercise-based health promotion systems in the case of Mode 1-Mode 5.
Under the Current development mode (Mode 1), healthy-life expectancy has steadily increased. Healthy-life expectancy in 2020 will increase from 66.83 years in 2010 to 69.85 years, which is basically in line with the relevant data in the Statistical Bulletin of China’s Health Care Development published by the National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China over the years, which is partly attributable to the successful completion of China’s 12th Five-Year Plan and 13th Five-Year Plan. With the country’s economic development and scientific and technological progress, the living standards and happiness index of the residents have continued to improve, and the healthy-life expectancy of the residents has been raised. According to the model prediction, the average healthy-life expectancy of China’s residents will reach 71.30 years in 2025 and 72.66 years in 2030. The Chinese government attaches great importance to the health of its residents, and the continuous development of health programs is the key to the steady growth of healthy-life expectancy in China.
Under the Government support priority mode (Mode 2), the simulations indicate that an increase in healthy-life expectancy. In Mode 2, compared with Mode 1, healthy-life expectancy increases from 71.30 years to 72.64 years in 2025 and from 72.66 years to 74.32 years in 2030. With the continuous implementation of public health policies, strengthening the construction of medical and healthcare institutions can bring more advanced and popularized medical technology, effectively reduce the risk of national illness, improve the level of medical care and quality of service, and through government health promotion, improve the national awareness of health, promote disease prevention and early treatment, thus promoting the improvement of healthy-life expectancy.
Under the Social support priority mode (Mode 3), the effect of healthy-life expectancy improvement is better. Compared with Mode 1, Mode 3 increases healthy-life expectancy from 72.66 years to 76.24 years in 2030, which is better than Mode 2 and Mode 4. Improving the medical personnel and widely carrying out social health education will not only help to motivate the people to actively participate in physical exercise and regular medical checkups, cultivate healthy living habits, reduce the prevalence of chronic diseases, and reduce the burden of medical care, but will also help to allocate resources to narrow the health gap between different groups, thereby raising the healthy-life expectancy of the whole society.
Under the Personal support priority mode (Mode 4), the healthy-life expectancy boost is less effective. In Mode 4, compared with Mode 1, healthy-life expectancy increases from 71.30 to 72.14 years in 2025, which is only 0.84 years, and from 72.66 to 73.74 years in 2030, which is only 1.08 years. On the one hand, personal support has a certain positive impact on healthy-life expectancy, and improving national literacy, health literacy and fitness willingness can help to improve their health-related cognitive level, which makes it easier for individuals to accept and actively participate in health promotion activities such as physical exercise, and good living habits can help to maintain their health and prolong their healthy-life expectancy, while on the other hand, the positive impact of personal support on healthy-life expectancy is weaker. Enhancing healthy-life expectancy also needs to take into account the physical foundation of society, such as the healthcare system, basic living conditions, socio-economic conditions, etc. The simulations indicate that Mode 4 mainly works at the individual level and cannot directly influence the physical elements related to healthy-life expectancy.
Under the Coordinated development mode (Mode 5), the simulations indicate that the improvement in healthy-life expectancy is significantly superior compared to other development model. Mode 5 compared with Mode 1, healthy-life expectancy in 2030 from 72.66 years to 76.35 years, an improvement of 3.69 years, the improvement effect is better than Mode 2 (improvement of 4.66 years), Mode 3 (improvement of 3.58 years), Mode 4 (improvement of 1.08 years). The implementation of exercise-based health promotion policy strongly promotes the construction of medical institutions, government support provides the material conditions for the pursuit of health, and social support such as medical personnel and personal support such as health literacy and fitness willingness create the spiritual conditions for the pursuit of health. Through the joint efforts of government support, social support and personal support, the advantages complement each other, which not only can effectively improve the level of medical services, but also can create a social atmosphere of proactive health, positively affect the national lifestyle, improve the physical quality of the nation, and reduce the prevalence of chronic diseases, thus having a significant and positive impact on healthy-life expectancy.